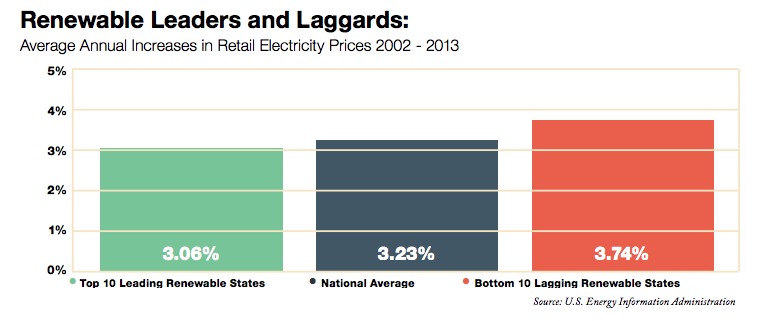Energy Trend Tracker
Energy Trend Tracker has moved! Click here to visit the new site.
Recent developments and data that help track the trends on coal and renewable energy.
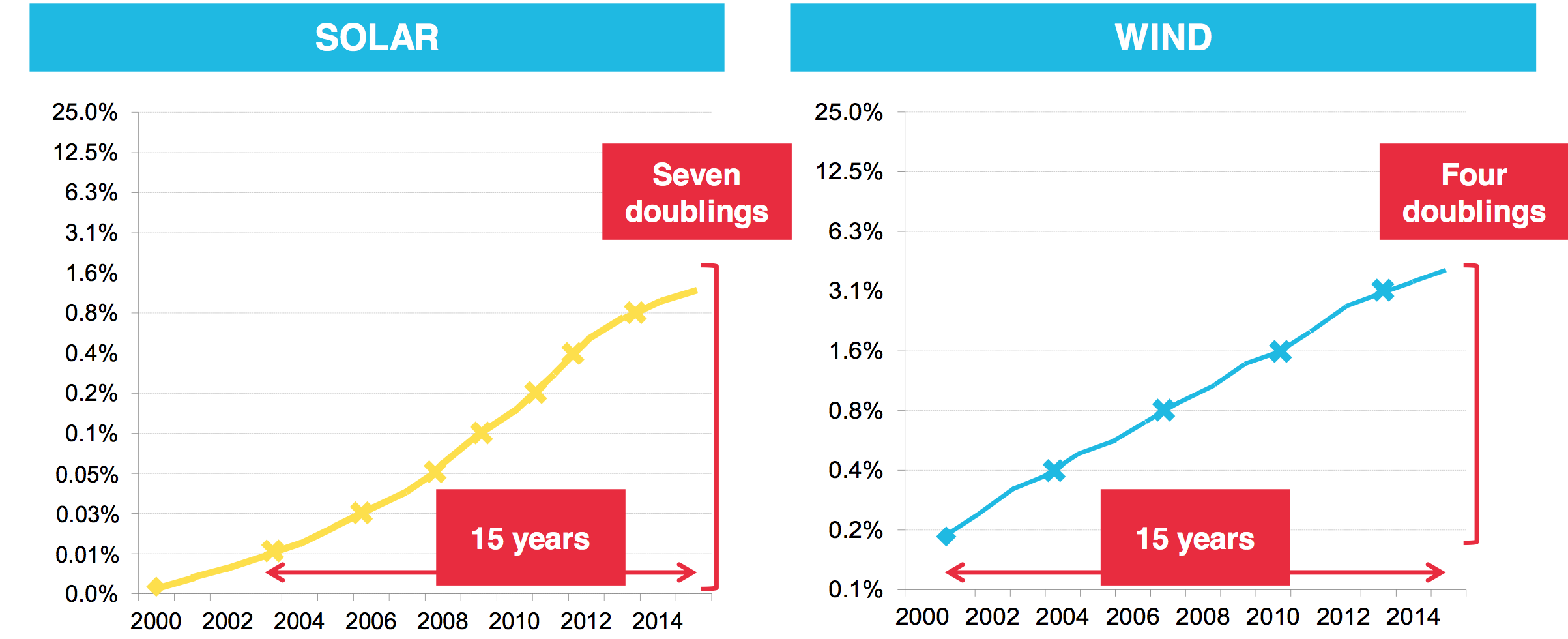
“Every time global wind power doubles, there’s a 19% drop in cost, and every time solar power doubles, costs fall 24%.”– From an analysis by Bloomberg New Energy Finance |
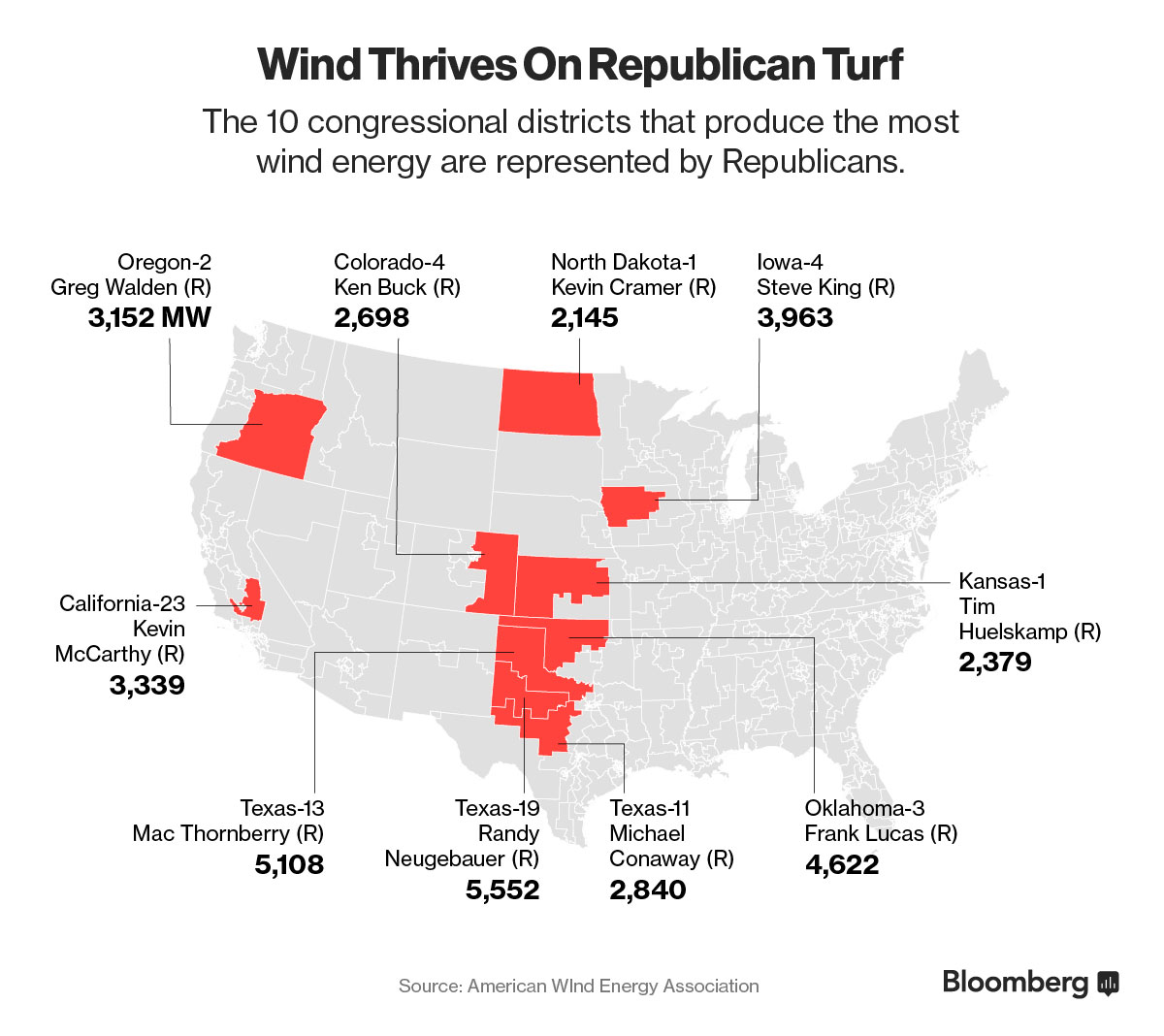
A growing faction of the GOP is bullish on clean energy
April 2016: A small but growing number of once-skeptical Republicans is embracing wind and solar energy as renewables add plentiful jobs in states like North Carolina, Georgia and Texas. Several factors are behind the conservative surge toward renewables. The first is economic; as prices drop and clean energy becomes less reliant on subsidies, supporting it is less problematic for Republicans. It is a powerful job creator, with wind and solar jobs now numbering four times as many as the coal sector. And wind and solar farms are often built on farmland, providing rental income for farmers and others in typically conservative parts of the country. In fact, all of the top 10 wind-energy producing congressional districts are represented by Republicans, according to The American Wind Energy Association.
India far surpasses target growth for renewable energy in 2015-16
April 2016: For the second year in a row, India’s renewable energy sector has surpassed target growth, by a substantial margin. In fiscal 2015-16, India beat its target of 4,460 MW of new renewables by more than 50%, adding 6,937 megawatts of new capacity. Solar was the big winner, with installations more than doubling the initial expectations. India also hit two major milestones: total installed wind capacity reached 25 gigawatts and for the first time, new solar additions were on par with new wind.
Port facilities could help Virginia create 14,000 offshore wind jobs
April 2016: Virginia could become a hub for the offshore wind industry and see as many as 14,000 jobs created over the next 15 years as the sector grows, according to a report issued by a group called the American Jobs Projec in collaboration with researchers at Virginia Tech. The report said the state is particularly well-positioned for the placement of offshore turbines because of port infrastructure such as at Hampton Roads, which could become an East Coast hub for shipping turbines and their components.
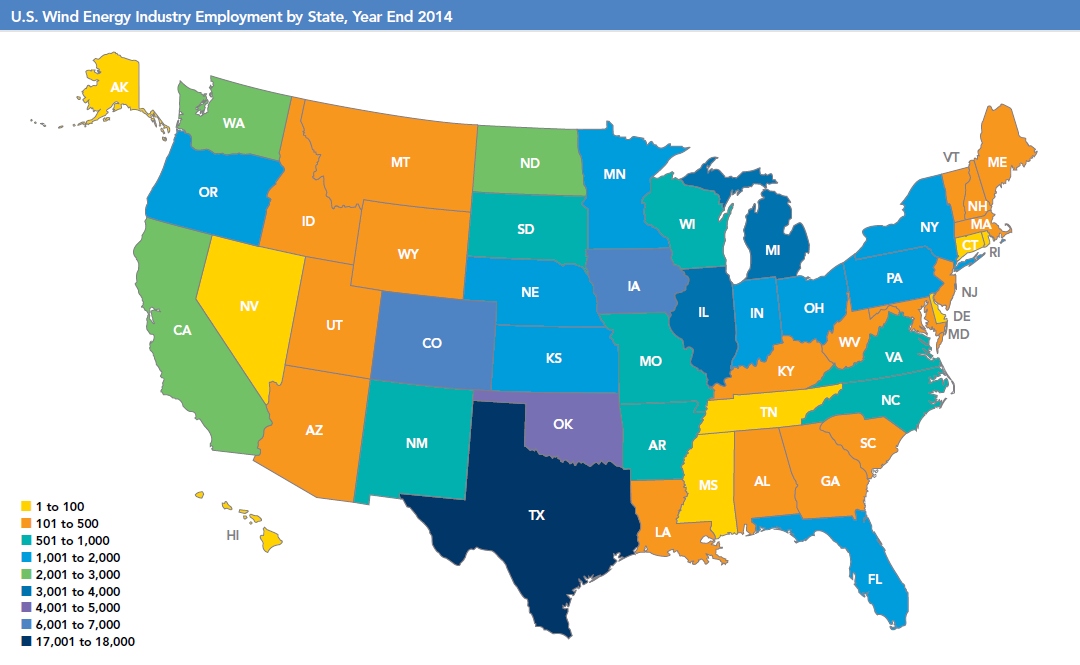
Wind industry jobs hit record in 2015
April 2016: The latest date from the wind industry show that wind power supported a record 88,000 jobs in the United States at the start of 2016, an increase of 20% for the year. According to the American Wind Energy Association’s Annual Market Report, the windpower workforce is on pace to grow to 380,000 jobs by 2030. “Wind power benefits more American families than ever before,” said Tom Kiernan, AWEA’s. “We’re helping young people in rural America find a job close to home. Others are getting a fresh chance to rebuild their careers by landing a job in the booming clean energy sector.”
IKEA selling solar panels in the UK
April 2016: How mainstream is solar becoming? IKEA has begun selling solar panels online and at three stores in the United Kingdom, and will make them available for purchase at all its stores by the end of the summer. The Swedish furniture giant decided to enter the market despite huge government cuts to solar subsidies for homeowners in Britain, saying it was confident there is still demand for the panels. “Our research showed a third of homeowners would really like to invest in solar, and the majority of those are driven by the opportunity to save money,” said IKEA’s head of sustainability at in the UK and Ireland.
As solar booms in India, costs are on the verge of beating coal
April 2016: Solar energy prices in India hit a new record low in January, and the country’s energy minister said solar would likely beat coal on cost. Speaking at the release of a new action plan for India’s renewable sector, Piyush Goyal said he thinks “a new coal plant would give you costlier power than a solar plant.” The winning bid in the January solar auction was for 4.34 rupees a kilowatt-hour, on par with coal prices that range between 3-5 rupees/kWh. As a result of solar’s increasing competitiveness, Goyal said India would quintuple its current target of 20 gigawatts of solar power generation by 2022 to 100 gigawatts.
Solar on the rise in Britain, surpassing coal for first time ever
April 2016: In a symbolic milestone, solar has provided British homes and businesses with more power than coal-fired power stations for the first time ever over an entire day. Data gathered by climate analysts Carbon Brief showed that solar provided the UK with 29 gigawatt-hours on April 9, compared with 21 GWh from coal. “This first for solar reflects the major shifts going on in the electricity system,” said Carbon Brief in an analysis. England now has 12 gigawatts of solar capacity, out of the UK’s total capacity of 80-90 GW. Meanwhile, while there was around 18GW of coal capacity going into last winter, this year there will be less than 10GW.
Obama statements wind costs beating out coal and gas hold water
April 2016: President Barack Obama has been on a streak of talking up the cost benefits of wind energy in 2016, and recent fact-checks of his statements have detailed the veracity of his statements. In his 2016 State of the Union address, the president said that “in fields from Iowa to Texas, wind power is now cheaper than dirtier, conventional power,” a fact backed up by data from the U.S. Energy Information Administration. And at a March rally in Dallas, the president said “Right now, here in Texas, wind power is already cheaper than dirty fossil fuels,” a statement that PolitiFact concluded was “true.”
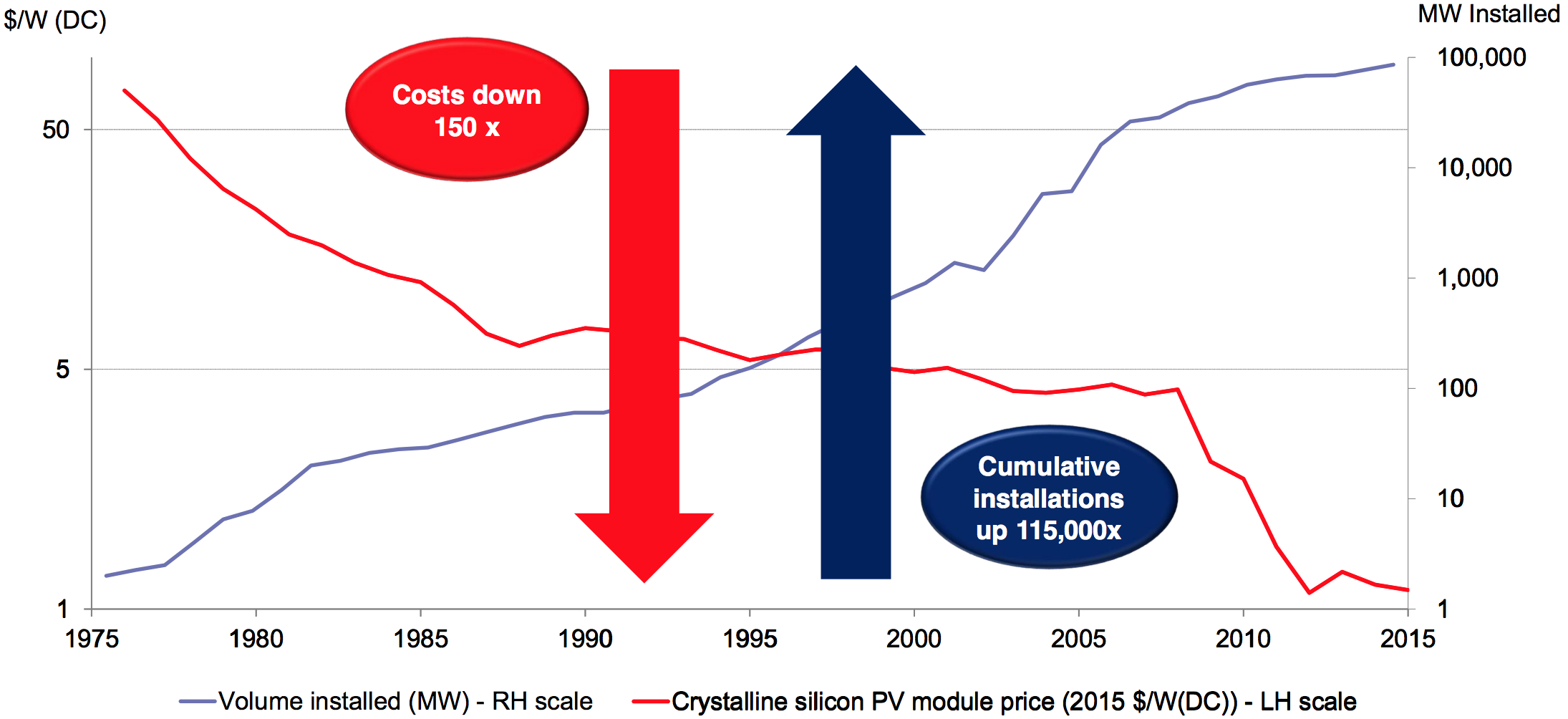
With coal, oil and gas crashing, clean energy is crushing fossil fuels
April 2016: With economies of scale finally ramped up, wind and solar are crushing fossil fuels on cost. According to Bloomberg New Energy Finance, the cost of solar has fallen to 1/150th its level in the 1970s, and the total amount of installed solar has soared 115,000-fold. Since 2000, the amount of global electricity produced by solar power has doubled seven times over, and wind power has doubled four times over.
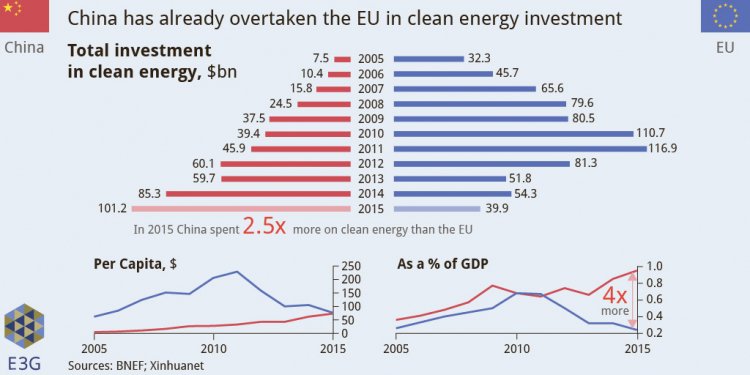
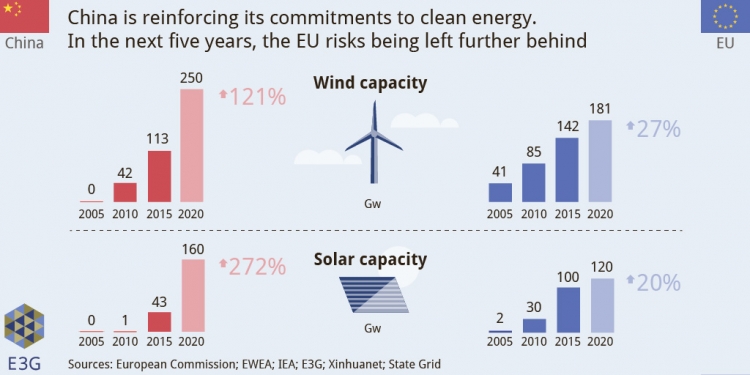
Surpassing Europe, China is on its way to global clean energy dominance
March 2016: By building infrastructure for cleaner electricity at a speedy clip, China is poised to overtake the European Union in a number of low-carbon economic measurements that will soon make it the dominant force in global clean energy development. According to a report by analyst group E3G, China’s new five-year plan lays out a plan to more than double its wind energy capacity, nearly triple its solar capacity and increase electric vehicle sales by a factor of 10. Chinese R&D spending on clean energy has risen 73% in the last five years, compared to just 17% in the EU.
NREL study: rooftop solar could provide 40% of U.S. electricity demand
March 2016: Rooftop panels could provide 40% of the electricity demand in the U.S. and as high as three-quarters in California, the most bullish state on solar, according to a new study from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory. A previous NREL study in 2008 determined that solar could supply about 21% of the country’s electricity demand, around 800 terawatt-hours a year. Improvements in the efficiency of panels and more accurate data analysis upped the estimate by 79% to 1,432 terawatt-hours annually, which would meet around 39% of U.S. electricity demand.
Utilities see explosive growth in community solar projects
March 2016: Growth in community solar programs over the six years is a further indication of the dramatic shifts taking place in energy markets. Community solar projects, or gardens, allow customers to buy shares of larger projects even if they can’t install solar panels on their own roofs. In 2010, there were only two shared solar projects in existence in the United States. Today, 77 utilities administer more than 110 projects across 26 states, accounting for a total capacity of about 106 megawatts, according to a new report by Deloitte.
Over a half million Midwesterners employed in the clean energy sector
March 2016: Clean energy jobs are proving to be an economic powerhouse in the Midwest, with more than a half million workers employed in various sectors – renewable energy generation, clean transmission, energy efficiency, clean fuels and advanced transportation – according to a recent survey. Illinois led the pack with more than a fifth of the region’s 568,979 clean energy jobs. Looking ahead, clean energy employers project a growth rate of approximately 4.4% over the coming 12 months, which will add around 25,000 jobs and outpace the average employment growth rate over the next 10 years by a factor of nine.
DOE participation in Clean Line firms up clean energy transmission project
March 2016: After five years of review, the U.S. Department of Energy has decided to participate in the Plains & Eastern Clean Line Project, which will carry 4,000 megawatts of low-cost wind energy from Oklahoma and the Texas panhandle to the Southeast. The 700-mile Clean Line will deliver wind power to more than 1.5 million homes and businesses in Tennessee, Arkansas and other Southern states. DOE will help secure the transmission route, if and only if the developer can’t reach agreement with a state (Oklahoma and Tennessee have already endorsed the project).
100% of new generating capacity in January came from wind and solar
March 2016: In the first month of 2016, 100% of new electrical generating capacity in the U.S. came from renewable energy projects. According to the latest Energy Infrastructure Update report by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, there 468 megawatts of new wind and 145 MW of new solar added in January. No new capacity for nuclear, coal, gas or oil was reported. Renewables accounted for 64% of all new electrical generating capacity installed in 2015.
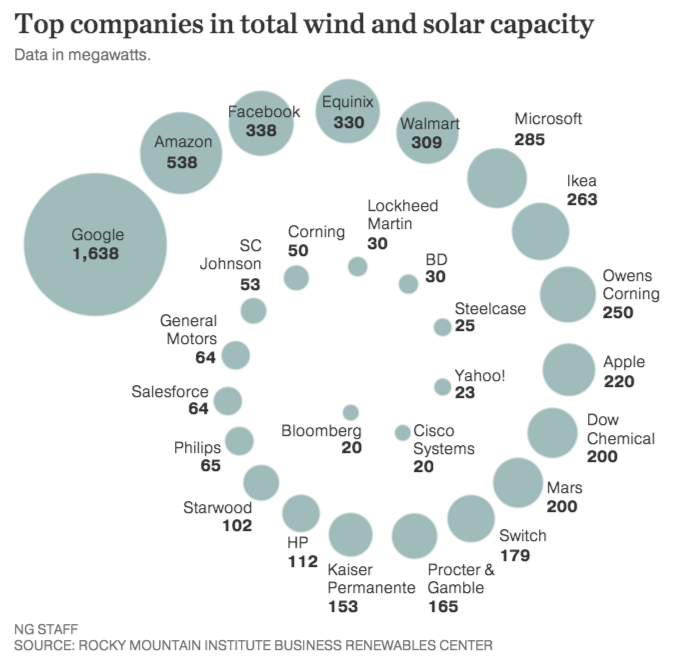
Old-school companies join high-tech ventures in ramping up renewables
March 2016: Digital-age companies like Google, Amazon, Microsoft and Apple still dominate the leaderboard for corporations turning to clean energy, but increasingly they are being joined by industrial and manufacturing stalwarts such as Lockheed Martin, Dow Chemical and Owens Corning. These companies recently signed long-term deals to buy clean energy to power their operations, taking advantage of wind and solar costs that continue to fall.
World’s largest battery storage system helps Korea cut energy costs
March 2016: Two massive energy storage battery systems installed in South Korea, which will be used to help regulate frequency variations on the grid, are expected to save the country’s largest utility millions of dollars. Korea Electric Power Corporation expects the two systems, one 24 megawatts and one 16 MW, to improve grid efficiency, allowing it switch to lower cost energy sources and cut down on wear and tear on plants and transmission equipment. The storage systems are expected to save the utility $13 million annually in fuel costs alone, three times the cost of the batteries.
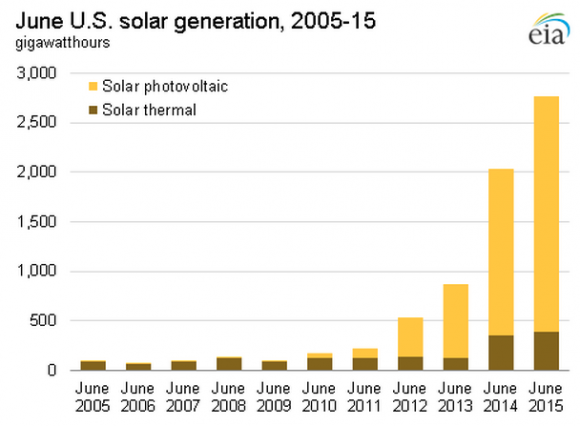
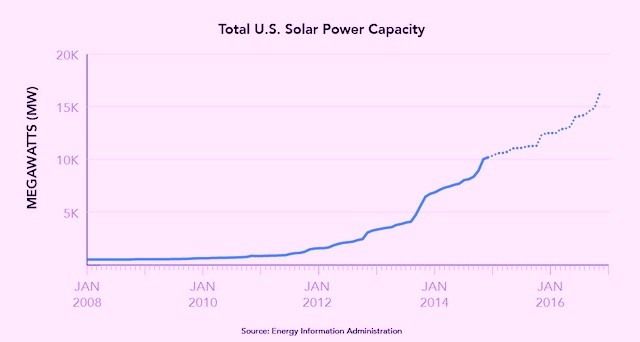
2015 a “monumental” year for solar
February 2016: Solar development surged again in the U.S. in 2015, with growth 17% higher than it was in 2014, which itself was a benchmark year. Nationwide, a record 7.3 gigawatts of capacity were installed in the U.S. last year. And for the first time, the capacity of solar installations surpassed those of natural gas. Residential rooftop PV was the fastest-growing segment, according to a report from GTM Research and the Solar Energy Industries Association. California, North Carolina and Nevada were the top three solar states in added capacity. Total U.S. solar installations now exceed 25 gigawatts, equal to about one quarter of the country’s nuclear fleet, and up from just 2 gigawatts only five years ago. Last year, said SEIO CEO Rhone Resch, “was a monumental year for us. What’s most amazing is that we’re just getting started.”
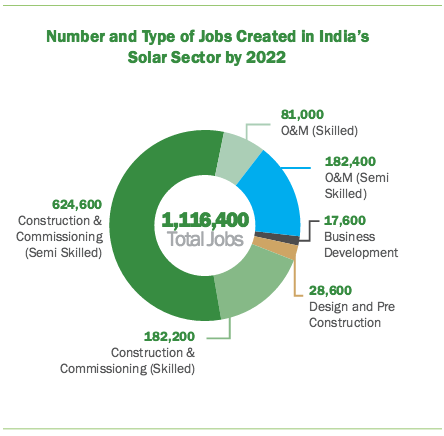
Analysis: India’s solar ambitions could create more than 1 million jobs
February 2016: India’s plans for a massive expansion of the nation’s solar sector could create more than 1 million new jobs, according to an analysis by the Natural Resources Defense Council and the Council on Energy, Environment and Water. The country has set a goal of adding 100 gigawatts of solar capacity by 2022. The analysis found that the build-out would require 210,800 skilled engineers, 624,000 construction works and 182,400 low-skilled workers for ongoing project operations and maintenance. The analysis does not take into account manufacturing jobs, which could also be significant.
Morocco striving for energy independence with solar projects
February 2016: As part of a move to become more energy independent, Morocco has officially flipped the switch on the first phase of what will be the world’s largest concentrated solar power plant. The Noor I power plant, located on the edge of the Sahara Desert, is capable of generating up to 160 megawatts of power. The next two phases will add another 300 MW of solar capacity. Combined, the three plants will provide enough energy to serve more than a million people. Using molten salt technology, they will also be capable of generating electricity after nightfall. Morocco currently relies on imported sources for 97% of its energy consumption.
Wind helps Nova Scotia meet clean energy goals, stabilize prices
January 2016: The main electricity provider for the the Canadian province of Nova Scotia set a new renewable energy record in 2015, with wind, hydropower and biomass contributing 26.6% of its electricity over the course of the year. The total exceeded the benchmark of 25% required by law. Nova Scotia Power said it is on target to meet the 40% renewable requirement by 2020. As recently as 2007, only 9% of Nova Scotia’s electricity came from renewables. Just as notable, utility officials said the transition is helping stabilize power rates. For most customers, rates did not increase in 2015 and have gone down in 2016. Wind makes up the lion’s share of the new generation being addd in Nova Scotia.
New frontier of battery storage to grow 15-fold in next 10 years
January 2016: World-wide revenue for utility-scale battery energy storage is forecasted to grow 1,500% over the next decade, expanding from $231.6 to $3.6 billion by 2025, according to an analysis by Navigant Research. Buoyed by new business models and financing investors are pouring money into new generation batteries that helps stabilize the grid and improves the economics of individual generating facilities. The increased investment is expected to lead to even bigger growth in storage capacity, which is projected to expand 30-fold to 42.7 gigawatt-hours by 2025. ability of the grid.
India dramatically expands solar capacity, drives record low prices
January 2016: With a rapid expansion of its solar capacity driving the market, India is seeing record low bids come in for new projects>. In late 2015 and the beginning of 2016, there have been a wave of bids for solar costing in the range of $.07 per kilowatt-hour. Just a year ago, solar contributed almost none of the country’s power. By 2021 the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis estimates that solar will contribute 10% of India’s electricity.
Tiny Cook Islands big on clean energy
January 2016: After an effort to transfrom its energy that began just six years ago, the tiny nation of the Cook Islands in the South Pacific is now on track to provide 100% of its electricty with renewables by 2020. The country, comprising 15 islands southwest of Tahiti set its course for a transition to renewable energy in 2010 to wean itself off of expensive imported diesel-generated power.
Municipal buildings in Santa Monica to be powered 100% by clean energy
January 2016: The city of Santa Monica, Calif. has signed a contract that will supply all of its municipal operations with 100% renewable energy, most of it solar and wind power generated in California. The contract will provide clean energy for more than 500 city-owned accounts.
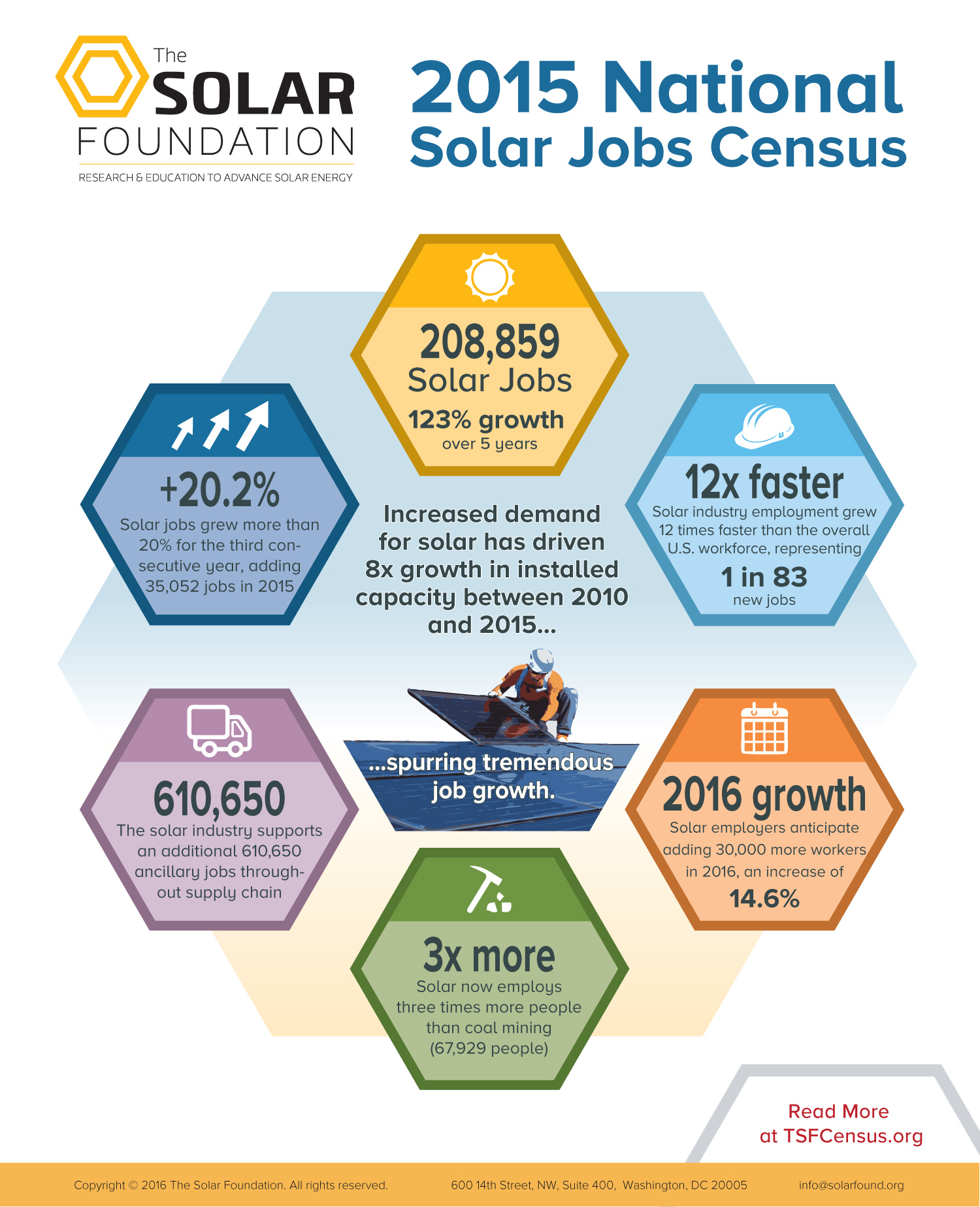
Solar jobs growing at meteoric pace
January 2016: Employment growth in the U.S. solar industry continued its rapid expansion in 2015, adding 35,052 new workers over the year, according to the latest annual jobs census by The Solar Foundation. With an employment increase of 20%, the solar sector grew nearly 12 times faster than the national employment growth rate of 1.7% last year. In fact, one out of every 83 new jobs created in the U.S. last year was in the solar industry. Since 2010, employment in solar has grown an extraordinary 123%, and projections are for that pace to continue. Companies surveyed for the census expect to see total employment in the solar industry increase by 14.7% to 239,625 solar workers in 2016. “Solar is surging. Renewable energy deployment is on track to transform our world,” said former U.S. Labor Secretary Hilda Solis.
France installing innovative, durable solar panels on 1,000 km of roadways
January 2016: In a unique new appiclation for solar, France will install flexibile, traffic-durable solar panels on 1,000 kilometers of roadway over the next five years, providing enough electricity to power public lighting for a city of 5,000 a thousand times over. The project is a private-public collaboration between French a transport infrastructure company Colas and France’s National Institute for Solar Energy. The panels, just 7 millimeters thick and made of layers of material “that ensure resistance and tire grip,” are glued on the top of existing pavement and strong enough to stand up to regular traffic, even heavy trucks.
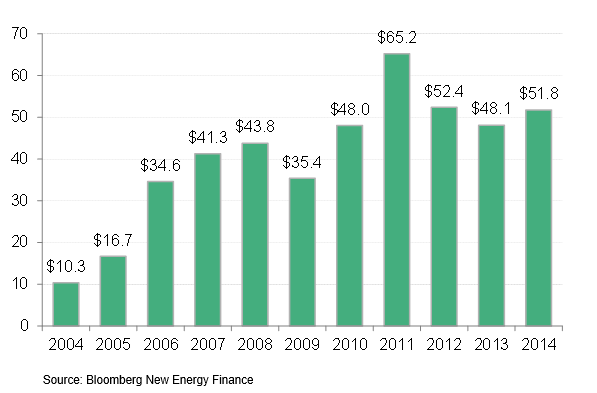
Despite Cheap Fossil Fuel, Clean Energy Set Records In 2015
January 2016: Worldwide clean energy investment and installations both surged to their highest levels ever in 2015, according to a report from Bloomberg New Energy Finance. Total investment in solar, wind and other renewables rose 4% from 2014, reaching $329 billion, while both wind and solar PV saw around 30% more capacity installed worldwide in 2015 than the previous year. Moreover, BNEF noted that the records were set despite plunging fossil fuel prices. “These figures are a stunning riposte to all those who expected clean energy investment to stall on falling oil and gas prices,” says Michael Liebreich, chairman of the advisory board at BNEF. “They highlight the improving cost-competitiveness of solar and wind power.”
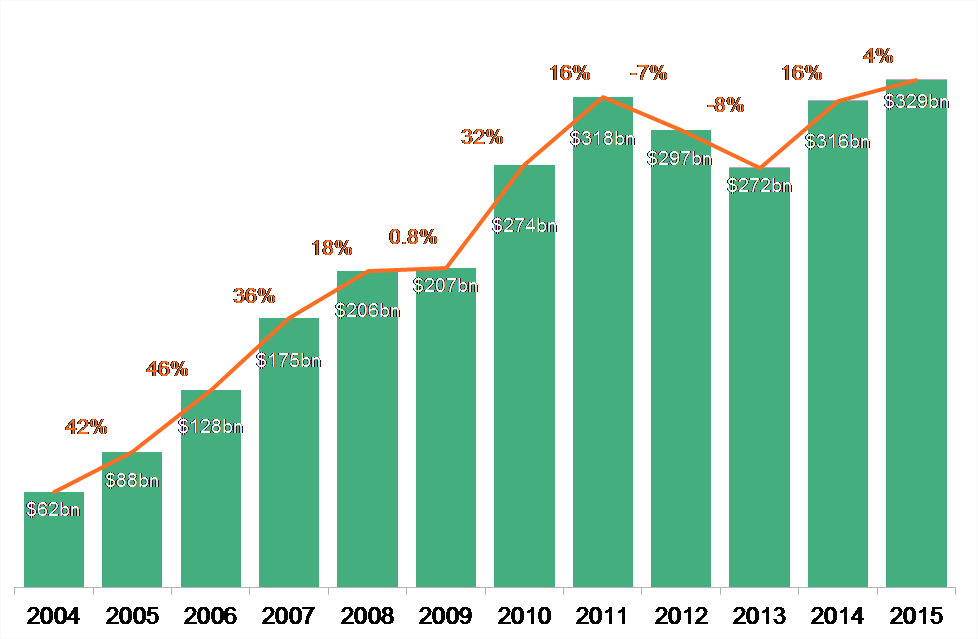
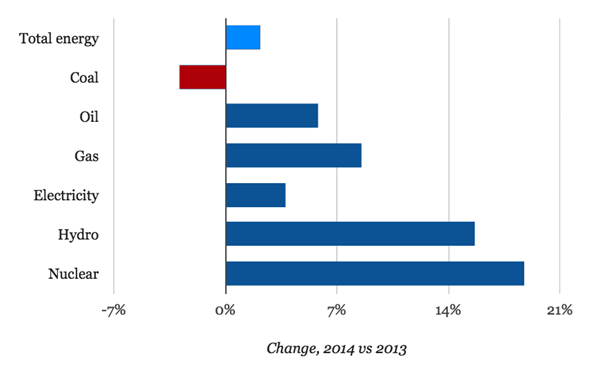
Source: Bloomberg New Energy Finance
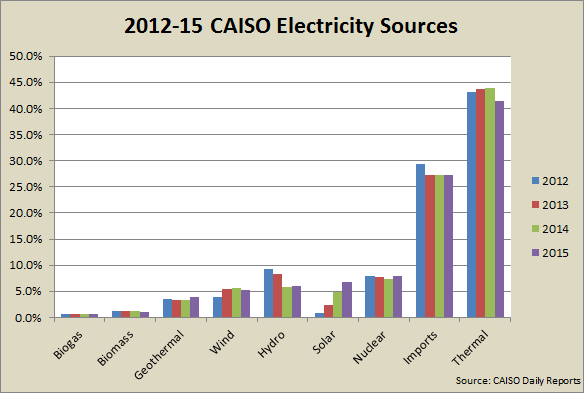
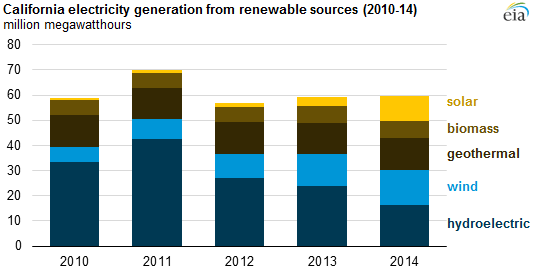
Solar is now California’s leading source of clean energy
January 2016: Rapid expansion has made solar the top renewable energy source for the grid serving about 80% of California. According to California Independent System Operator data, utility-scale solar now comprises 6.7% energy on the system, wind 5.3% and hydropower 5.9%. If rooftop solar were also counted, it would increase solar’s share to nearly 10% of the state’s electricity. Three years ago, solar contributed just was 0.9% of CAISO’s generation mix. Renewables now account for 24.3% of the state’s energy, coal less than 1%.
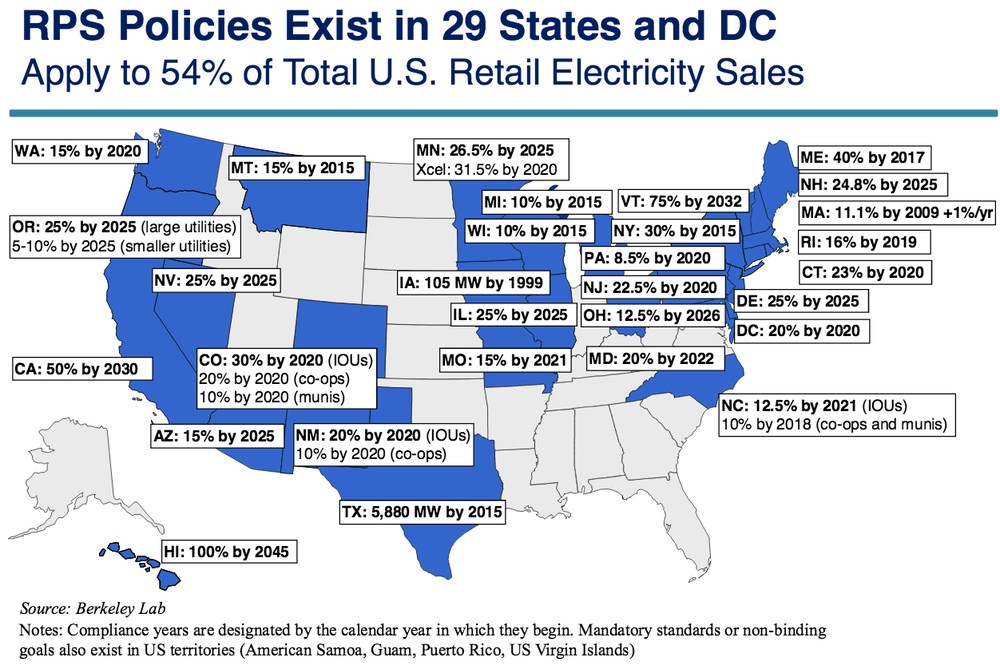
Research: State RPS’s provide $7.4 billion in pollution-cutting benefits
January 2016: A new study by federal energy researchers estimates that nationwide the net benefits of pollution cuts from state renewable portfolio standards collectively totaled $7.4 billion 2013, dwarfing the costs of the rules. The analysis, conducted jointly by Lawrence Berkeley National Lab and the National Renewable Energy Lab, calculated the net benefits of reducing greenhouse gas emissions at $2.2 billion and the benefits of cutting other air pollution – such as fewer lost work days and hospital visits – at $5.2 billion.
Better ecomonics prompt Indian coal plant builder to switch to solar
January 2016: Saying the economics of photovoltaics are more attractive, a prominent developer of coal-burning power plants in India has changed course on a 800-acre site planned for a coal plant in the state of Punjab and decided to build a solar project instead. According to the report in Bloomberg, the decision is the latest example of India’s increasing interest in solar. Prime Minister Narendra Modi has set a target of installing 100 gigawatts of new solar capacity by 2020. The Indian government has created numerous incentives and regulations to attract overseas developers, a move that has reduced the cost of solar electricity to record lows.
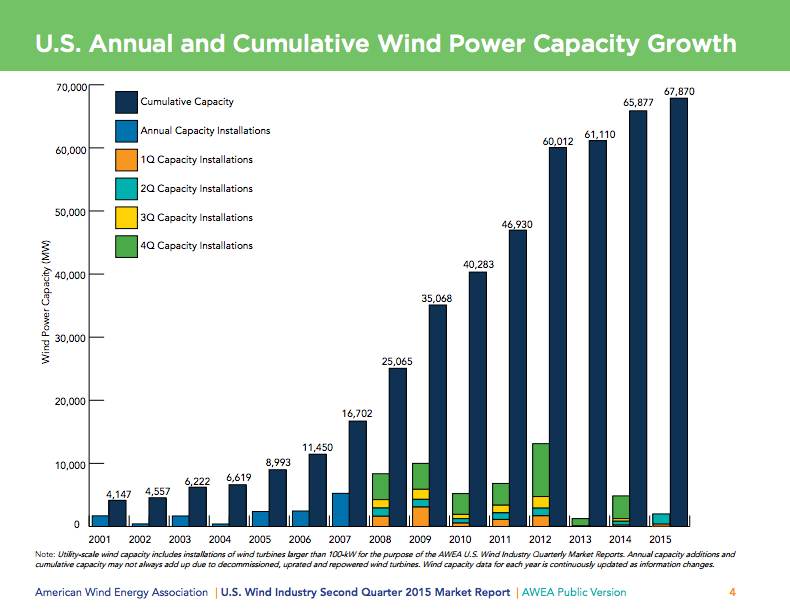
U.S. wind industry cracks 70 GW of capacity, and more is on the way
December 2015: The U.S. wind industry reached a new milestone in November, topping 70 gigawatts of installed generating capacity nationwide, enough to power about 19 million homes. According to the American Wind Energy Association, there are more than 50,000 wind turbines operating across 40 states and Puerto Rico. Wind suprassed the 50 GW and 60 GW milestones in 2012. In just eight years, wind power has gone from producing less than 1% of America’s electricity to 5% now. And with Congress enacting a 5-year extension of federal tax credits for wind and a new climate agreement in place from Paris, growth in wind is on-track to meet DOE projections for generating a fifth of the country’s electricity by 2030.
African nations use Paris to map out plan for doubling clean energy
December 2015: As part of the climate accord brokered in Paris, African nations have announced an ambitious goal to tap into the continent’s “massive potentials” for renewable energy by building at least 300 gigawatts of new clean energy capacity in the next 15 years. The plan, backed by commitments from a $100 billion annual fund pledged by wealthy countries to fight climate change, would double Africa’s total generating capacity, which currently is about half as much as Japan, a country with one-tenth Africa’s population.
Study: Pac Northwest’s cleantech growth outpaces overall economy
December 2015: The Pacific Northwest’s clean economy is growing at a rate twice as fast as the overall economy, according to a new study. The West Coast Clean Economy: 2010-2014 Jobs Update, compiled by the Delphi Group, looked at economic drivers in Oregon, Washington, California and British Columbia, which have a combined GDP of $2.8 trillion and together represent the world’s fifth largest economy. As of 2014, the region housed 577,372 clean economy jobs, an increase of 19% since 2010.
Las Vegas city buildings to be powered 100% by renewable energy
December 2015: The city of Las Vegas will be powered exclusively by renewable energy, city officials have announced. As part of an expanded partnership with utility NV Energy that will provide a mix of energy-efficiency programs and a large-scale solar project, all fire stations, streetlights, city parks and other municipal facilities in Las Vegas will be powered completely by clean energy within two years. The move would make Las Vegas the largest city in the U.S. with municipal operations completely powered by renewable energy. City officials said the deal was possible due to dramatically falling costs; solar, for example, is roughly half the price it was just five years ago. “It’s cheaper than what we could build a new natural gas plant for,” NV Energy’s president told the Las Vegas Sun.
Pennsylvania boosts clean energy commitment as part of climate plan
December 2015: The newest update to Pennsylvania’s climate change action plan includes a significant expansion of renewable energy and added energy efficiency programs, as well as fixing methane leaks from natural gas pipelines and coal mines. The actions are some of the dozens of steps laid out by the state’s Department of Environmental Protection to help limit the damage caused by rising global temperatures, which the report calls “one of the most serious issues facing the world.” Pennsylvania is the third largest emitter of energy-related carbon dioxide in the country, but the plan has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 338 million metric tons CO2 equivalents through 2030.
Everything is big in Texas, especially projected growth in renewables
December 2015: The vast majority of new electricity generation in Texas will come from renewable enegy, especially wind power, in 2016. The Electric Reliability Council of Texas, which manages nearly 90% of the state’s grid load, also projects that solar power growth will exceed natural gas capacity next year. In 2016, ERCOT anticipates adding more than 4,200 megawatts of new power capacity, including nearly 2,800 MW of wind power, more than 1,000 MW of solar and the remaing 10% from a new natural gas plant. By 2018, ERCOT expects the amount of solar on the grid in Texas to grow tenfold to about 2,000 MW.
Bill Gates sets sights on renewables
November 2015: Microsoft co-founder Bill Gates has made renewable energy his next big project, pulling together a multinational band of investors to pump billions in clean energy. The goal of the group, called the Breakthrough Energy Coalition, is to continue lowering the cost of clean energy to make it competitive with fossil fuels in order to get poor countries to make the switch without sacrificing economic growth. The coalition comprises more than two dozen public and private entities, including national governments, billionaire philanthropists, investment fund managers and tech CEOs.
Alberta officials set bold clean energy goals in home of tarsands
November 2015: Under new leadership elected earlier this year, Alberta’s provincial government has set a goal of getting a third of its electricity from renewable energy and completely phasing out coal by 2030. ”This is the day we start to mobilize capital and resources to create green jobs, green energy, green infrastructure, and a strong, environmentally-responsible, sustainable and visionary Alberta energy industry with a great future,” Alberta Premier Rachel Notley said in a speech during the plan’s roll-out.
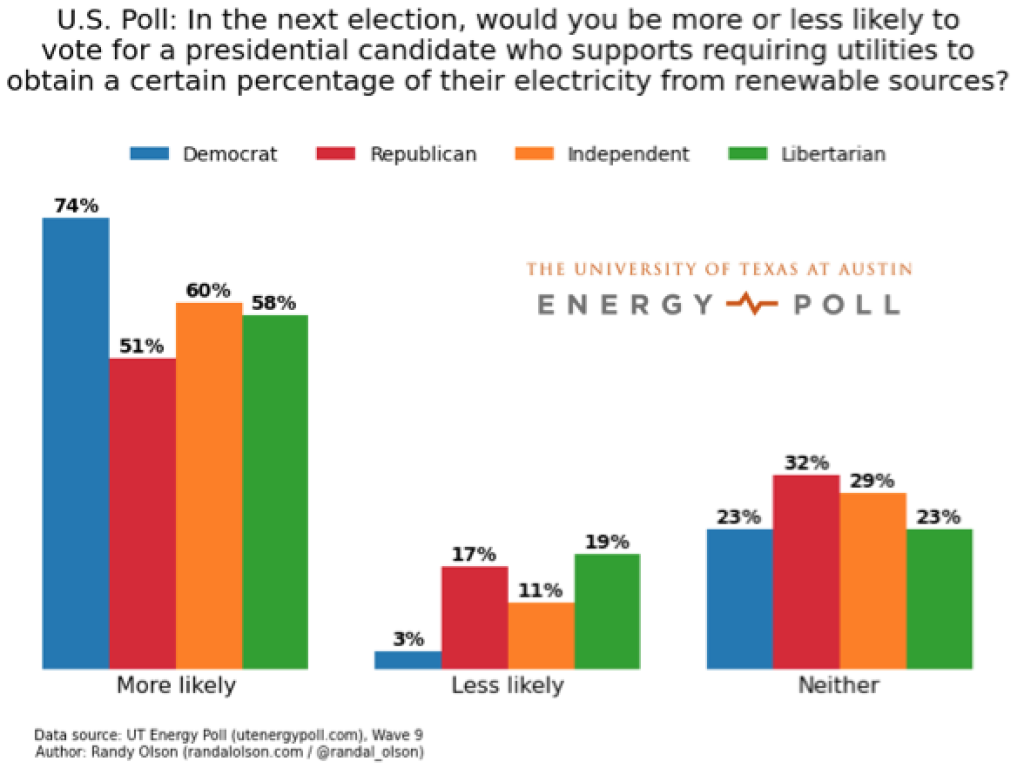
Voters in 6 swing states favor clean energy, support Clean Power Plan
November 2015: Voters in six key swing states overwhelmingly want power generated by wind and solar over coal and natural gas, according to polling commissioned by the Sierra Club. The poll surveyed between 550 and 770 registered voters each in Ohio, Illinois, Missouri, Iowa, Virginia and Maine. It also found that clear majorities in all six states support the Clean Power Plan, and that voters in four states would be more likely to vote for a U.S. Senate candidate who supports the plan
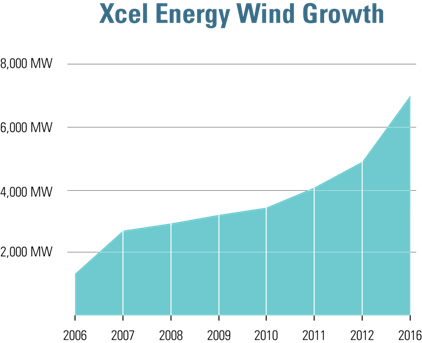
Winds blow big in October, setting numerous output records
November 2015: October saw wind energy output records fall across the country as a result of a “wind rush” of projects and long-needed grid upgrades coming online. Both the Texas and Midwest grid operators passed the milestone of 12,000 megawatts of wind output in the third week of the month, trading spots for all time peaks for a regional grid operator. On Oct. 2, Xcel set a new record of 2,352 MW of wind output in Colorado. The grid operator for Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska, and parts of neighboring states, hit 8,458 MW of wind on Oct. 18, and the American Wind Energy Association is working to validate record outputs for grid operators in the Mid-Atlantic and Great Lakes regions, as well.
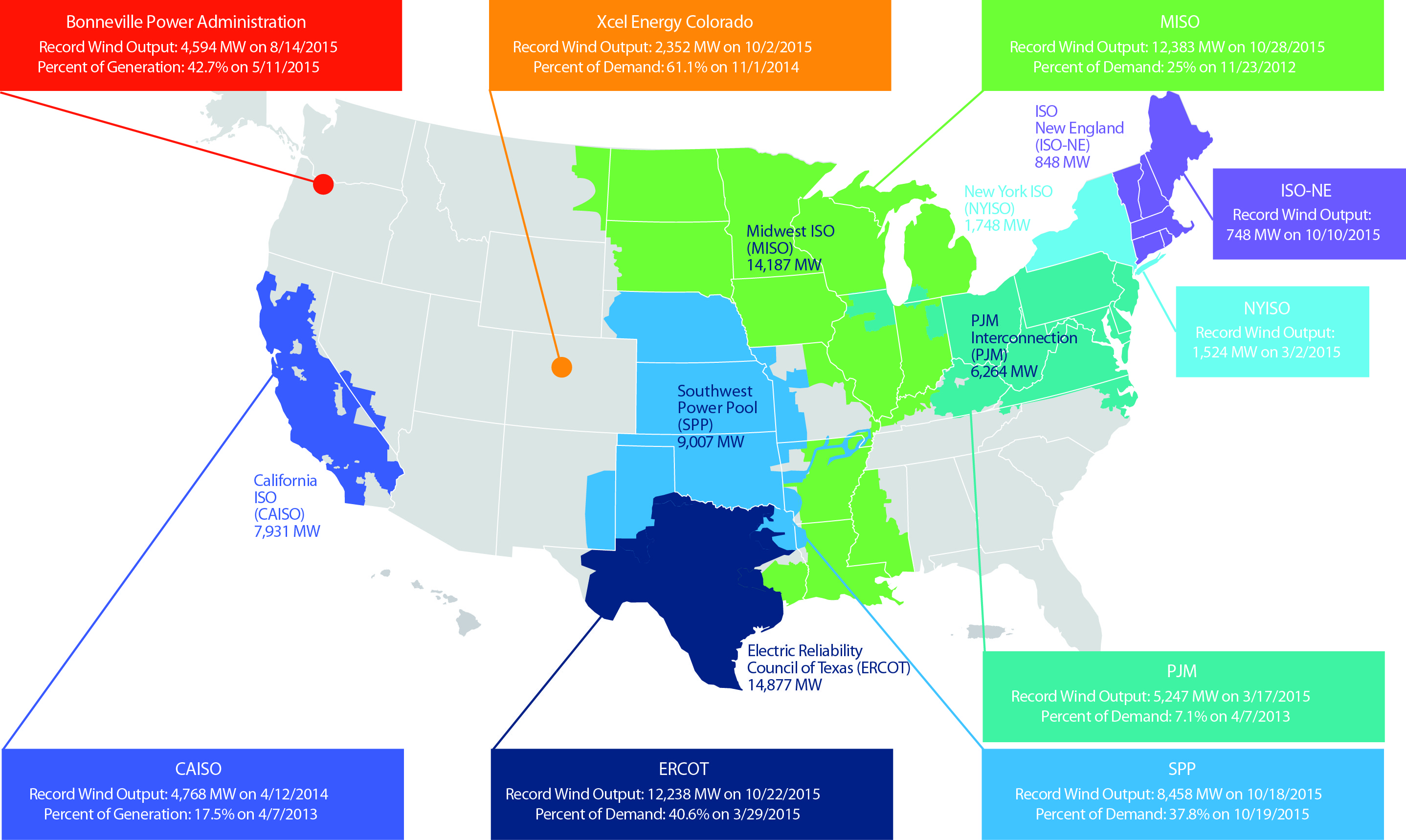
Source: AWEA
China’s solar capacity projected to jump fourfold by 2020
October 2015: China’s solar capacity, already the biggest in the world, will balloon more than fourfold by 2020, according to a senior official. The Chinese government’s goal is to increase solar PV capacity by 20 gigawatts annually from 2016 to 2020. Total solar capacity will reach 150 GW over that timeframe, up from 35.8 GW this summer.
New Mexico utilities expand solar at bargain basement prices
October 2015: Utilities in New Mexico have announced three large-scale deals that will add 165 megawatts of solar to the state. Southwest Public Service Co., a subsidiary of Xcel Energy, has signed a long-term agreement to buy power from two 70 MW solar facilities being built near Roswell. Southwest will pay about 3.5 cents per kilowatt-hour starting in 2017, one of the cheapest power agreements in the nation for utility-scale solar and less expensive than some of Excel’s older natural gas plants. “The way the economics are changing, we’re often looking to add renewables now because of the economic value and the diversified mix of energy it provides for our system,” an Xcel splkesman said. Colorado-based Tri-State Generation and Transmission, also announced a deal to build a 25-MW solar facility in Luna County.
Calif. ups the ante on renewable energy, efficiency with new law
October 2015: In signing a sweeping new law for a for a “decarbonized future,” Gov. Jerry Brown has put California’s clean energy policies even further ahead of the pack. The measure expands the state’s renewable energy standard, requiring it to generate half of its electricity from solar, wind and other renewables by 2030, and it doubles energy efficiency requirements for homes, offices and factories. Brown said the legislation was necessary both to combat climate change and to continue cleaning up air in cities where pollution is still problematic. The bill also lays the groundwork for a regional electricity grid, which could make renewable energy more available throughout the West.
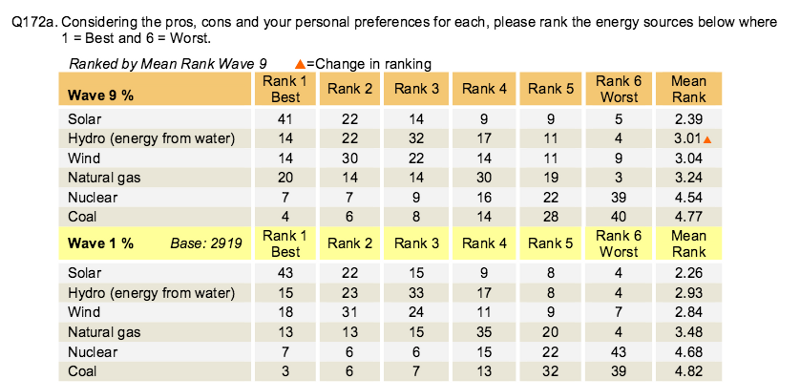
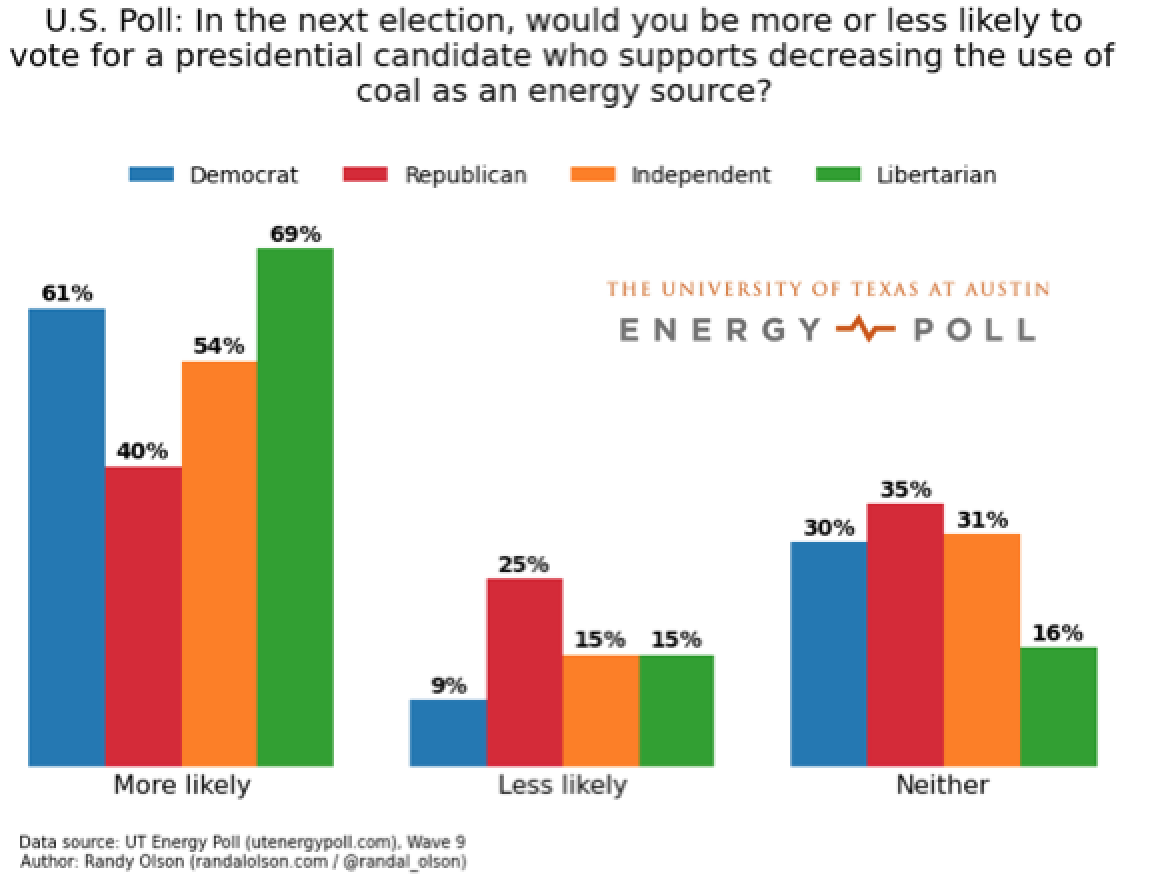
Poll: Americans support clean energy, don’t like coal much
October 2015: A new nationwide poll shows that large majorities of Americans support renewable energy like solar, while coal is considered “the worst” energy source than any other form of energy. In the poll, conducted by the University of Texas at Austin, 41% of Americans said ranked solar energy as the best energy source for the country, while coal was ranked the worst by 40% of Americans, slightly ahead of the next least favorite, nuclear power. The poll also found that opposition to coal translates to support for candidates working to move us away from it as an energy source.
Global clean energy, fossil fuel costs headed in opposite directions
October 2015: An analysis of the levelized cost of electricity worldwide showa average onshore wind and solar costs continuing to decline while those for coal and natural gas were on the rise for the second half of 2015. The Bloomberg New Energy Finance analysis, based on thousands of cost data points from projects around the world, found that the global average levelized cost of electricity for onshore wind fell from $85 per megawatt-hour in the first half of the year to $83 in the second half, while that for solar PV solar fell from $129 to $122. In the same period, the cost for coal-fired generation both increased. Onshore wind, the data showed, are now fully competitive against gas and coal in Europe.
Official says China will quadruple solar capacity in next five years
October 2015: China, which is already the world’s largest solar market, is set to more than quadruple its current capacity by 2020, a senior government official was quoted saying in the official state news agency. The director of new energy for China’s National Energy Administration told the Xinhua news agency that the government’s goal is to boost photovoltaic solar output by 20 gigawatts annually from 2016 to 2020, bringing the country’s total capacity to nearly 150 GW. China had 35.8 GW installed as of July.
Xcel CEO says wind power now cheaper than natural gas
October 2015: The head of the biggest utility provider of wind energy in the U.S. said his company anticipates long-term contracts for wind power to beat out natural gas in costs. Minneapolis-based Xcel, which serves customers in eight states and often has wind providing as much as 60% of its electricity, is getting bids from contractors offering 20-year power purchase agreements at about $25 a megawatt-hour for wind. Even with natural gas prices close to historic lows, CEO Ben Fowke told Bloomberg News that Xcel expects prices for electricity from gas to average closer to $32 a MWh over the same period. “When we’re buying wind at $25, it’s a hedge against natural gas,” he said, adding that with plans to continue adding significant amounts of wind to the Xcel system, the utility is “going to be able to retire coal plants earlier than we expected.”
Aspen becomes 3rd U.S. city to get all its power from renewables
September 2015: After a decade of work, the city of Aspen, Colo., is now receiving all of its power for municipal buildings and operations from renewable energy sources. Aspen’s Utilities and Environmental Initiatives Director told the Aspen Times that even though just under 7,000 residents live in the city year-round the achievement was symbolically important because it “demonstrated that it is possible. Realistically, we hope we can inspire others to achieve these higher goals.” According to Climate Progress, Aspen is the third U.S. city to get 100% of its energy from renewables, joining Burlington, Vt. and Greensburg, Kans.
Solar project + battery storage will meet evening load in Hawaii
September 2015: As part of efforts to continue combatting Hawaii’s highest-in-the-country electricity prices, the utility serving the island of Kauai is expanding its solar capacity with battery storage in order to cut costs with less expensive clean energy. The Kauai Island Utility Cooperative has signed a contract to buy power from a 17-megawatt solar PV project being built on the island. The project includes a 52-megawatt-hour battery storage system that will be used to feed up to 13 MW of electricity onto the grid to reduce the evening peak load from 5-10 p.m. KIUC will buy power at 14.5 cents per kilowatt-hour, more than 30% less expensive than the oil-based electricity typically need at night, which costs 22 cents per KWh.
FERC ruling opens door to more clean energy development by co-ops
September 2015: A recent ruling by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission may have removed one of the biggest obstacles to more clean energy development by rural electric cooperatives, which have lagged behind regulated utilities and remain one of the most coal-dependent energy providers in the utility sector. A Colorado co-op, Delta Montrose Electric Association, appealed to FERC to settle a dispute over its desire to buy clean power from a small local hydro-electricity producer. DMEA was stymied in its efforts by its “all requirements contract” with Tri-State Generation and Transmission Association, which generates a majority of the power it sells DMEA from coal. FERC ruled that the Public Utilities Regulatory Policy Act of 1978 supersedes contracts. Under federal law, power providers are obligated to buy power generated by “qualifying facilities.” The ruling doesn’t allow co-ops to develop their own clean energy resources beyond contractual limits, but it does open the door to outside clean energy developers getting around a big obstacle to sell their power to willing co-ops.
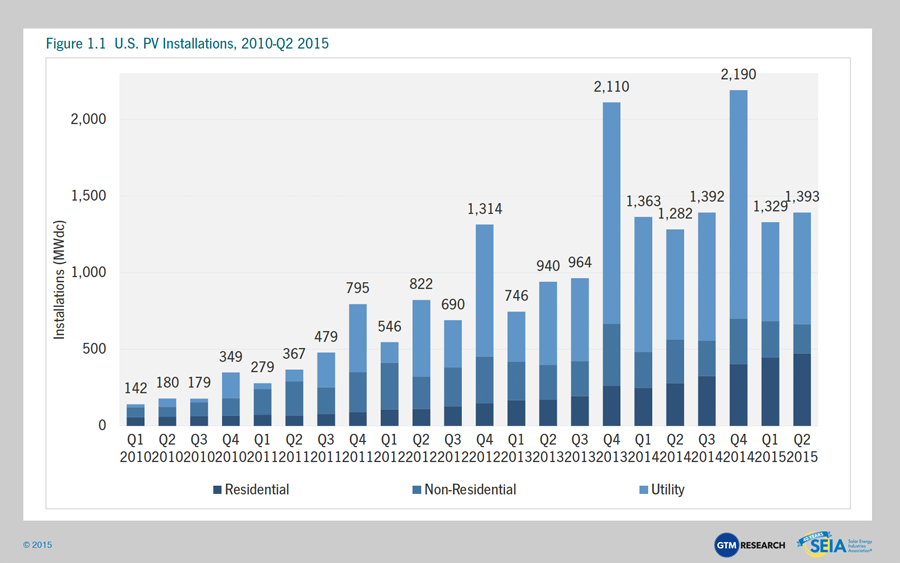
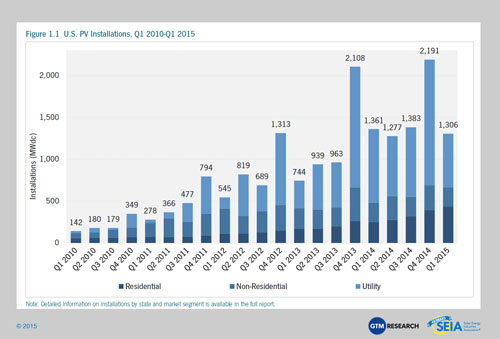
2015 shaping up as another record-breaker as PV hits 20 GW milestone
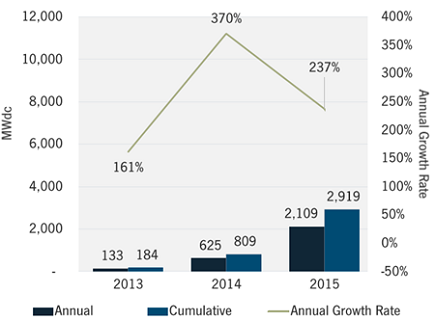
September 2015: The U.S. solar market remains on pace for yet another record-breaking year, with a strong second quarter and expectations for the last six months of 2015 to be significantly larger, according to a market analysis by GTM Research and the Solar Energy Industries Association. Overall, 1,393 megawatts of solar PV were installed in Q2 2015, the seventh consecutive quarter in which the nation added more than 1 gigawatt of PV panels. The second quarter also marked the milestone of cumulative installations eclipsing the 20 GW mark. During the first half of 2015, 40% of all new electric generating capacity brought on-line in the U.S. came from solar.
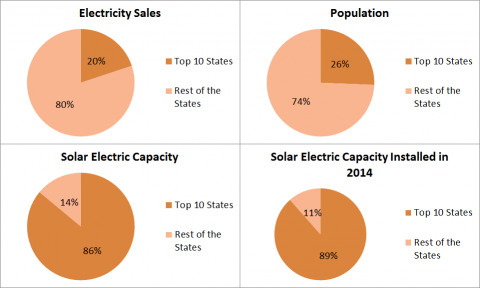
Top 10 states are driving America’s solar growth in a big way
September 2015: A new report shows that America’s Top 10 states in solar energy have driven huge gains in the past three years. The nation’s rooftop solar PV capacity has tripled in the past three years as the cost of solar energy has fallen rapidly, according to “Lighting the Way,” a report by by Environment America, and the top 10 states have led the charge, now accounting for 86% of the nation’s total installed solar electricity capacity. The top 10 states are: Arizona, California, Colorado, Hawaii, Massachusetts, Nevada, New Jersey, New Mexico, North Carolina and Vermont. California has the most rooftop solar installed, but Hawaii has surpassed Arizona as the state with the most solar capacity per capita.
“Remarkable” job growth boosts R.I. clean energy employment to 10,000
September 2015: A new report by officials in Rhode Island says there are now nearly 10,000 clean energy jobs in the state. The state’s Office of Energy Resources and the Executive Office of Commerce said the clean energy sector added 613 jobs over the last 12 months, bringing the total to 9,832. The agencies also projected that another 1,600 positions in energy efficiency, renewable energy and related fields would be created over the next year. Job growth in clean energy hit 6.6% over the past year, a “remarkable” surge for such a new sector, said a separate report, that easily outpaced Rhode Island’s overall rate of less than 1%. a separate report found. The majority of new clean energy jobs — about 52.5% — are in energy efficiency, which includes retrofitting buildings. Another 11% were in renewable energy, including installation and construction jobs.
DOE Sec. Moniz: renewables are cost-competitive, even without subsidies
September 2015: Speaking to reporters, U.S. Energy Secretary Ernest Moniz said that while the administration supports the extension of renewable energy tax credits, he sees solar continuing to grow even without subsidies because the value proposition is so favorable. Moniz cited data projecting that the cost of electricity from rooftop solar panels will soon fall as low as 6 cents per kilowatt-hour, making it “extremely competitive” with natural gas and other fossil and non-fossil power plants.
Calif. county’s switch to solar is saving taxpayers big on energy costs
September 2015: With the installation of a second solar project on county buildings in Yuba County, Calif., officials expect have all of the county’s facilities powered by renewable energy, and to be saving money. The county is spending $5.2 million to install 1.6 kilowatts of solar at the county airport but anticipates saving $16 million in energy costs over the next 30 years. A similar county solar project installed in 2011 at a cost of $10 million 2011 project helped cut the county’s annual power costs from about $1 million to $500,000 in one year.
Michigan tea party legislator pushing for clean energy incentives, growth
August 2015: Michigan State Rep. Gary Glenn, a first-term tea party Republican, says he wants to boost solar energy growth in the state through market incentives to increase competition and consumer choice. In an interview with Midwest Energy News, Glenn, the majority vice chair of the House Energy Policy Committee, said he is preparing a package of “competition-driven, free-market and incentive-based” bills to encourage distributed generation and allow ratepayers to buy renewable energy from alternative suppliers. “The fact that there’s not more solar is not because there are more cloudy days in Michigan than other states,” he said. “We have the least incentivizing policy in the country. … I don’t believe in mandating any form of energy, but we should be incentivizing solar as much as possible.”
Former Duke Energy CEO: Light the world with clean energy, not coal
August 2015: Former Duke Energy Jim Rogers, whose career made him responsible for tens of billions of dollars in centralized coal- and gas-fired generating capacity, is now pushing clean energy as a solution for energy poverty worldwide. In a new book, Rogers lays out his vision for bringing electricity to 1.2 billion people in the world who live without it. Lighting the World calls for governments, financial institutions and entrepreneurs to support small-scale, local clean energy projects such as rooftop solar in remote areas in Africa and other regions. “We can’t bring electricity to the rural areas of the world using an old-fashioned industrial grid based on building more coal plants and running copper lines from timber pole to timber pole across Sub-Saharan Africa, or running cables underwater to connect the archipelago of Indonesia,” Rogers wrote in the book. “The environment and financial impediments make that impossible.”
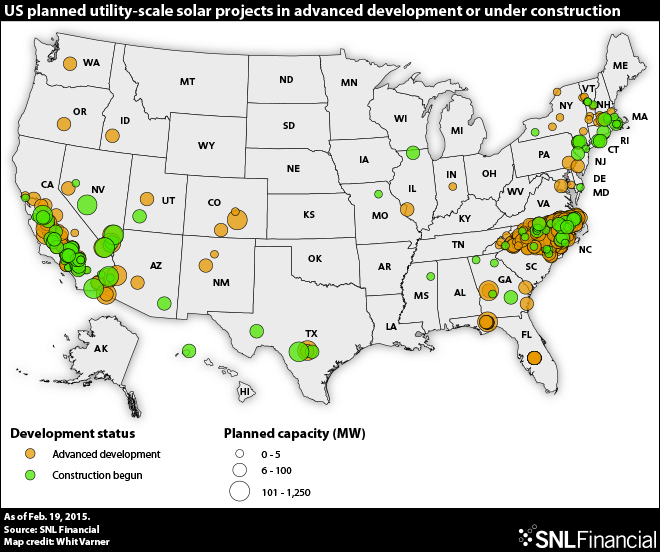
After a brief roadbump, utility-scale solar is again setting records
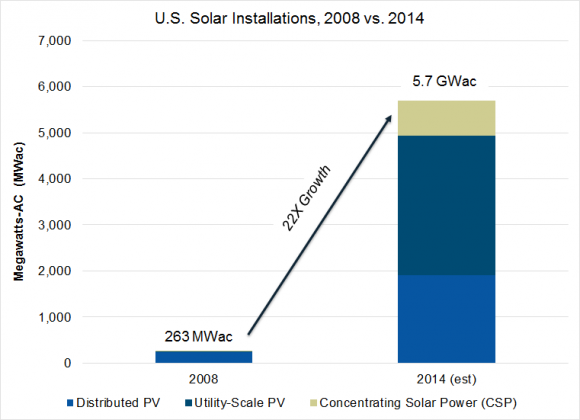
August 2015: After a slowdown in the growth of utility-scale solar in 2013 and early 2014, the sector has bounced back impressively, reports GreenTech Media’s Stephen Lacey. In the latter half of 2014, utilities around the country signed an unprecedented number of contracts for utility-scale PV projects, in large part because the technology had gotten so cheap. That momentum continues, with utility-scale solar hitting both cost and generation records. In June, for example, Austin Energy revealed that the average bid from developers in the second round of a 600-megawatt procurement averaged below 4 cents per kilowatt-hour. And in March, California became the first state to generate 5% of its electricity from utility-scale solar. Nationwide, the amount of electricity generated by utility-scale solar is 31 times higher than it was just a decade ago.
Utility exec: clean energy is the only way to electrify the third world
August 2015: The former CEO of America’s largest electric utility says the only feasible way to bring electricity to places like Africa where millions still live without it is by developing local, small-scale connections to distributed clean energy sources such as solar and wind. In a new book, Duke Energy’s Jim Rogers said constructing large centralized facilities like coal, gas and nuclear plants won’t work. “We can’t bring electricity to the rural areas of the world using an old-fashioned industrial grid based on building more coal plants and running copper lines from timber pole to timber pole across Sub-Saharan Africa, or running cables underwater to connect the archipelago of Indonesia,” Rogers writes. “The environment and financial impediments make that impossible. Instead, we’ll do it with modern technology: solar and other clean energy sources, new kinds of batteries, LED lights, efficient cook stoves and TVs, and plenty of innovations that now are surfacing.”
Global solar capacity to grow at compound rate through 2020
August 2015: The amount of solar PV capacity installed worldwide will grow at a compound rate of nearly 20%, more than doubling to at least 480 GW by 2020, according to projections in a report by consulting firm Hexa Research. At the end of 2014, global solar capacity totaled about 178 GW. Until now, growth in solar has been driven by developed countries but in the future, a majority of demand will come from rapidly developing Asia Pacific markets like China, India and Taiwan, the report said.
Federal court rejects challenge to Colo. renewable energy standard
July 2015: The 10th Circuit Court of Appeals in Denver has ruled that Colorado’s renewable portfolio standard does not harm interstate commerce and is therefore legal. The RPS, which requires Colorado’s biggest utilities to get 30% of their power from clean energy, was challenged in federal court in 2011 by legal institute connected to the coal industry. The 10th Circuit’s three-judge panel disagreed, saying in their opinion that Colorado’s renewable energy requirement “isn’t a price-control statute, it doesn’t link prices paid in Colorado with those paid out of state, and it does not discriminate against out-of-staters.”
HP to commits to powering Texas data centers with wind energy
July 2015: Hewlett-Packard has signed a 12-year contract to buy 112 megawatts of power from a wind farm in Texas, the latest in a growing trend of nontraditional companies turning to clean energy. In February, Kaiser Permanente announced a 20-year contract to buy 153 MW of wind and solar power in California. A month later, Dow Chemical said it would buy 200 MW of wind power in Texas. And earlier this month, Amazon Web Services said it would build and operate a 208-MW wind farm in North Carolina. The HP deal will provide electricity equivalent to that used by 42,600 homes and will be sufficient to fully power the company?s data centers in Texas.
Once a laggard, Alabama now looking for 500 MW of new clean energy
July 2015: Alabama’s largest utility has asked regulators for permission to install up to 500 megawatts of solar and other renewable energy projects, a substantial change in direction in a state dominated by coal and lagging behind others in clean energy development. Alabama Power, which still needs approval from the Alabama Public Service Commission, will focus on projects up to 80 MW to serve large companies, not residential customers. A company spokesman said no additional costs would be passed on to customers as part of the project. Once built out, the 500 MW will account for 4-5% of Alabama Power’s total capacity.
Wind power growth in first half of year doubles that of 2014
July 2015: With 1,661 megawatts of new wind turbine capacity coming online during the second quarter of 2015 and more than 13,600 MW under construction, wind power growth in the U.S. is at near-record levels. The American Wind Energy Association’s Second Quarter Market Report shows that 1,994 MW were installed during the first half of 2015, more than doubling installations from same period in 2014 but still below the record growth of 2012, when more than 2,900 MW was installed in the first half of the year. One of the most notable trends so far this year, AWEA noted, is the growing interest by Southeastern states in building and purchasing wind power, including announcement for new projects in Florida and North Carolina, the latter’s first venture into utility-scale wind. Looking forward, more than 100 wind projects are under construction in 24 states, representing more than 13,600 MW of total wind capacity and over $20 billion worth of private investment.
U.S. backs wind and solar projects in Jamaica to boost energy security
July 2015: As part of an effort to beef up energy security, U.S. interests are funding the construction of a 20 MW solar plant in Jamaica, The $60 million project, which will create 400 construction jobs and another 20 long-term operations jobs, is expected to cut Jamaica’s use of imported fuel oil by 3 million gallons a year. It is being funded by the federal Overseas Private Investment Corp., which also is bankrolling construction of a new wind farm in Jamaica. “We do not intend to forever remain hostage to imported fossil fuel and all the challenges that it brings,” Jamaican Prime Minister Portia Simpson Miller said.
Study says power bills in VA could fall thanks to new federal rules
July 2015: Implementing the Clean Power Plan in Virginia could result in lower electricity bills that save customers in the state up to $145 a year, according to a new analysis. In contrast to alarmist projections for cost increases made by Dominion Power, the report by the group Public Citizen group indicates that power bills could drop about 8% if state lawmakers focus on energy efficiency for Virginia’s implementation of the Clean Power Plan. The state has efficiency goals, the group said, and broadening them would result in lower bills for most households even if electricity rates rise slightly.
Japanese telecom giant commits $20 billion to solar projects in India
June 2015: Japanese telecom giant Softbank has committed to investing around $20 billion in solar projects in India through a partnership with Indian and Taiwanese enterprises. Coal currently dominates India’s energy mix, but the Indian government has set a goal of expanding the country’s solar output 33-fold to 100 gigawatts by 2022.
National clean energy job growth doubles rate from first quarter 2014
June 2015: Nationwide, more than 9,800 clean energy and clean transportation jobs were created during the first three months of 2015, according to data compiled by the nonpartisan business group Environmental Entrepreneurs. The growth is almost double the number of jobs E2 tracked in the same quarter of 2014. The top three states for job growth in the clean energy sector were: Georgia (2,870 jobs), California (1,885) and Texas (1,612). Nationally, solar was the top sector in Q1, with more than 6,600 new jobs announced.
The sky is the limit for wind energy jobs and economic impact in Iowa
June 2015: Iowans could save $3.6 billion on their electricity bills over the next 35 years if the state expands its already healthy wind capacity, according to a new report by the American Wind Energy Association and the Wind Energy Foundation. Iowa already gets more than 28% of its electricity from wind, U.S. Department of Energy data show, which supports around 7,000 well-paying jobs. By 2020, wind could supply more than 40% percent of Iowa’s electricity, generating $49 million in annual property tax revenue and more than $19 million a year in lease payments to farmers and rural Iowa landowners. “In Iowa, we understand that an investment in wind power is an investment in jobs,” U.S. Rep. David Young (R) commented regard the report.
Residential solar installations in Q1 2015 shatter previous record
June 2015: Over the first quarter of 2015, the U.S. residential solar market grew 76% over the same period a year earlier, shattering installation records. Nationwide, companies installed 437 MW of rooftop solar PV in the first three months of 2015 – a total of 66,440 new home rooftop systems – according to a market report from the Solar Energy Industries Association. Little slowed the growth, including one of the worst winters in the Northeast’s history, yet the residential solar market had its biggest quarter of all time. During the quarter, solar accounted for 51% of all new electric generating capacity. The average cost for a residential solar system also fell to $3.48/watt, a 10% decrease from 2014.
Solar shines bright on Golden State
June 2015: With solar continuing to sprout up all across the state, California would rank sixth in the world in installed solar capacity if it were a nation, says Rhone Resch, president and CEO of the Solar Energy Industries Association. In a column in RenewableEnergyWorld.com, Resch pointed to SEIA’s Q1 solar market report showing that California has more solar assets than the United Kingdom, France, Spain, Australia and Belgium, and is the first state in the U.S. to top 10,000 megawatts of installed solar capacity — enough to power nearly 2.6 million homes. To that in perspective, the state has 10 times more installed solar capacity today than the ENTIRE U.S. had in 2007.
Investors commit $4 billion to Obama clean energy investment initiative
June 2015: Far surpassing expectations, philanthropic groups, pension funds and other institutional investors have committed $4 billion toward a White House initiative to shift the world to a low-carbon economy. The investments, announced at a White House clean energy investment summit, double the goal of $2 billion that the Obama Administration set out earlier this year and will be invested in projects such as technological fixes to cut carbon. As part of the summit, the White House also announced a series of related executive actions to drive additional private-sector investment in solar, wind and other clean energy technologies.
Savings are so great, Iowa school district goes completely solar
May 2015: Wind is usually what grabs the clean energy headlines in Iowa, but a school district in the southern part of the state is about to be completely powered by solar. In January, the WACO district installed an array of PV panels at an elementary school in Crawfordsville, which the district’s superintendent has saved about $20,000 in power costs this year alone. This summer, workers will add another set of panels to the junior-senior high building in Wayland, which will provide enough electricity to power more than 90% percent of the district’s needs.
Clean energy a huge job creator in IL
May 2015: According to a new comprehensive report, Illinois has added more than 7,500 clean energy jobs in the past 15 months. The Clean Jobs Illinois Report documented 104,449 clean energy jobs in the state – those connected with electric or alternative transportation fuels, greenhouse gas management, energy efficiency, wind power, geothermal, or solar power – up from just under 97,000 in late 2013.
Buffett antes up again on Iowa wind with new $900 million investment
May 2015: Warren Buffett’s MidAmerican Energy has committed to spending $900 million on 552 MW of new wind energy projects in Iowa over the next two years, bringing the utility’s total wind assets in the state to $6.7 billion. Once built by the end of 2016, wind will supply a projected 57% of Mid-American’s retail energy demand. Republican Gov. Terry Branstad said because of Iowa’s “low electricity prices and commitment to renewable energy, major tech companies and other energy-intensive businesses are interested in locating and expanding facilities here.” Google, Facebook and Microsoft have sited large data centers in Iowa as a result of its affordable clean energy. A company spokesman said wind energy also reduces MidAmerican’s reliance on coal, which protects customers from rising costs tied to stricter environmental standards, including carbon limits.
Hawaii is on track to get 100% of its electricity from renewables
May 2015: Under a bill passed last week by the Hawaii legislature, Hawaii could become the first state to get all of its electricity from renewable energy sources. If Gov. David Ige signs the measure into law – he has until the end of June – Hawaii would have the most ambitious energy goals of any state, aiming to convert to 100% renewable energy by 2045. Hawaii has no fossil fuel reserves and must import coal and oil for power generation, leaving residents paying some of the highest rates in the country.
AWEA: 2014 brought records for wind capacity and jobs
April 2015: Buoyed by the 2014 extension of the production tax credit on wind turbines, the U.S. enjoyed a revived “wind rush” in 2014, with records for output and jobs and according to the Annual Market Report from the American Wind Energy Association. The U.S. wind industry added 23,000 jobs in 2014, boosting the sector’s total to 73,000 jobs. Of those, 20,000 are manufacturing jobs at more than 500 facilities across 43 states. Four times more new wind generating capacity came online in 2014 than the previous year, and 2015 began with 12,700 MW of wind projects under construction, a record for the start of any year. Wind generation in the U.S. has more than tripled since 2008, providing 4.4% of the nation’s electricity in 2014.
Renewables buildout: “an order of magnitude larger” than coal & gas
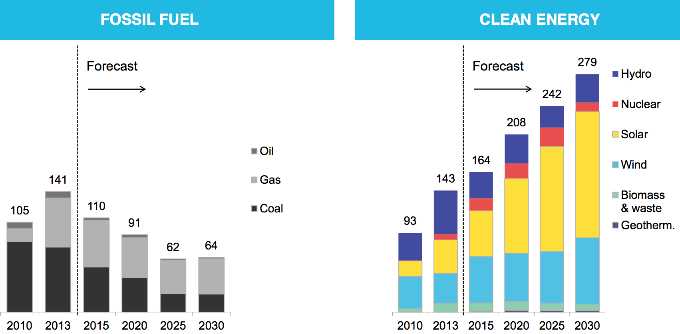
April 2015: The world has passed a turning point in the development of clean energy and is now adding more renewable capacity each year than coal, natural gas and oil combined. And, says Bloomberg New Energy Finance’s founder, there’s no going back; “The question is no longer if the world will transition to cleaner energy, but how long it will take” writes Tom Randall. In 2013, renewables added 143 gigawatts of new capacity globally, compared with 141 gigawatts in new plants that burn fossil fuels, according to a BNEF analysis. “The electricity system is shifting to clean,” BNEF’s Michael Liebreich said in a keynote address at a BNEF summit. “Despite the change in oil and gas prices there is going to be a substantial buildout of renewable energy that is likely to be an order of magnitude larger than the buildout of coal and gas.”
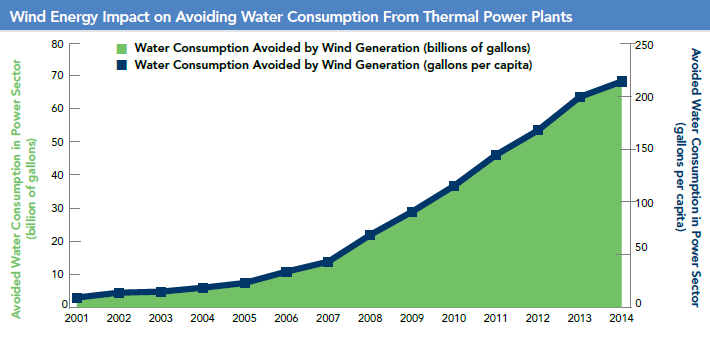
Wind saves the equivalent of 215 gallons of water for every American
April 2015: Wind energy avoided the consumption of more than 68 billion gallons of water in the United States in 2014, according to data from the American Wind Energy Association. The savings were equivalent to conserving roughly 215 gallons per person in the U.S. or 517 billion bottles of water. In drought-ravaged California, wind energy saved 2.5 billion gallons of freshwater in 2014, while Texas led the nation with savings of 13 billion gallons of water.
White House initiative aims to train 75,000 new solar workers by 2020
April 2015: President Obama has announced an initiative aimed at helping cut carbon emissions by boosting support for the solar industry. The goal of the initiative, which will be run through the Department of Energy, is to train 75,000 solar workers by 2020. It also includes as a component a Solar Ready Vets program that will utilize the GI Bill to train military veterans for the solar workforce at 10 U.S. military bases.
Americans unified in overwhelming support for clean energy
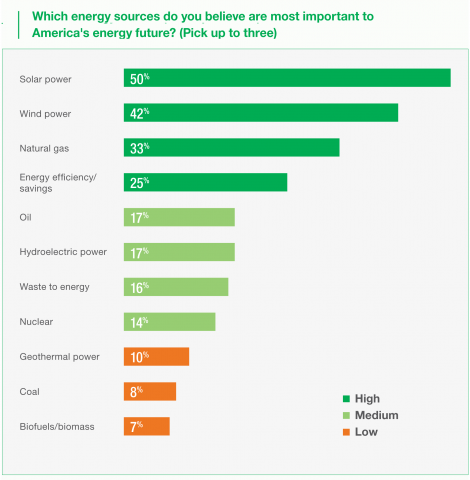
April 2015: In a national survey, American homeowners are overwhelmingly unified in their support of clean energy. The poll, conducted for Clean Edge and SolarCity, found that 87% of Americans believe renewable energy is important to the country’s future. Solar was the top choice when respondents were asked which energy sources are most important to the nation’s future, followed by wind, natural gas and energy efficiency. Coal and biomass received the least support. The support for clean energy crosses geographic, political and social boundaries. Solar power, for example, was the top choice among most of the demographic groups in our survey, including Republicans, Democrats, Independents, conservatives, liberals, city and rural dwellers, youth, and the elderly, as noted in a column by Clean Edge’s Ron Pernick in Renewable Energy World.
Record growth projected this year for offshore wind installations
April 2015: Analysts expect developers to install a record 4.2 gigawatts of offshore turbines in 2015, according to Bloomberg New Energy Finance, doubling the 2.1 gigawatts added in 2013. Germany is expected to lead offshore installations, accounting for more than half the total. Some of the new capacity results from delays in projects last year that will be completed this year, but offshore technology is also maturing, BNEF told Renewable Energy World in an interview. Worldwide offshore wind power is expected to reach 48 gigawatts by 2020. “Offshore wind installation is increasing year-on-year until at least 2020. There’s increased confidence that the technology is working and the cost of the technology is coming down,” a BNEF analyst said.
Rural electric co-ops capturing the benefits of locally generated solar
April 2015: Three rural electric cooperatives are among the national leaders in providing solar power, according to rankings compiled by the Solar Electric Power Association. Co-ops in Iowa, Tennessee and Utah ranked in the top 10 for solar watts per customer, SEPA reported in its annual snapshot. Solar is attractive to rural electric co-ops for a number of reasons, but locally generated energy is one of the main ones. “Solar power is helping us keep our members’ dollars local,” said Warren McKenna, CEO and general manager of Farmers Electric Cooperative in Kalona, Iowa, which ranked second nationally and meets 20% of its demand with solar and wind.
Energy Star competition showcases $50 million in energy cost savings
April 2015: Collectively, competitors in the EPA’s fifth-annual Energy Star Battle of the Buildings saved more than $50 million in energy costs by instituting programs that cut energy use last year by the equivalent annual energy use of more than 37,000 homes. One hundred teams entered more than 5,500 individual buildings in the competition, and together they reduced energy use by an average of 6%, or nearly $20,000 per building. The winner, a team from the small town of Woodville, Ala., cut average energy use in five buildings by 25%, freeing up $2,000 for street improvements and other town services.
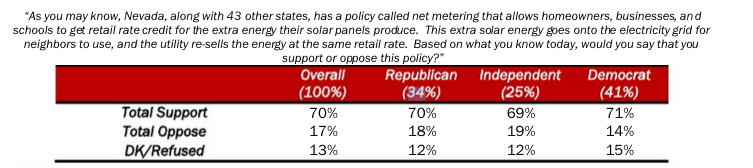
Poll finds strong support for solar, net metering policy in Nevada
April 2015: By substantial margins, Nevada voters support solar energy and a proposal to raise the limit on the amount of solar that homeowners, businesses and schools are paid for. Of the 300 likely voters surveyed in the poll, which was paid for by a consortium of solar companies, 84% said have a favorable impression of solar, and 70% said they support the net metering policy. Solar developers are pushing the Legislature to raise the cap on net metering from 3% to as much as 6%, saying the policy helps create jobs and compensate solar customers for the energy they contribute to the grid. NV Energy, the state’s biggest utility, is fighting the proposal.
Study: Top 10 renewable states saw lower energy costs than bottom 10
March 2015: A new analysis shows that in the top 10 states with the greatest share of renewable energy, average retail electricity prices are on par with or slightly cheaper than the 10 states with the smallest share. The study by clean energy fund managers DBL Investors did not draw a direct correlation between renewables and electricity prices, but rather showed that leading clean energy states leading have not experienced disproportionate price growth, as some critics imply, the authors said. In their analysis, the top 10 renewable states had an average increase in retail electricity prices of 3.06% between 2002 and 2013. The bottom 10 states had a 3.74% increase. “The cost curves are coming down for renewables. And they will continue to come down as markets grow and technologies achieve economies of scale. It is a virtuous cycle,” one of the authors told The Denver Post.
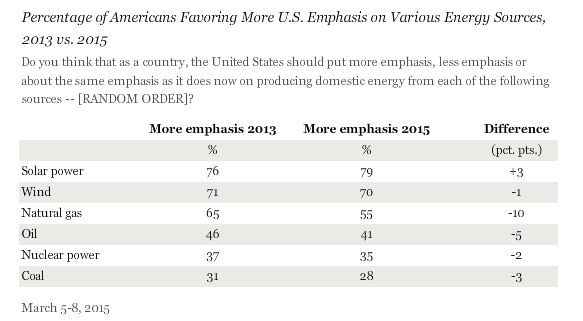
Gallup poll: Americans favor clean energy over coal by wide margin
March 2015: A new Gallup poll shows that Americans overwhelmingly support the country putting more emphasis on developing renewable energy. Gallup interviewed a sample of 1,025 random adults from all 50 states and the District of Columbia in early March, and the results show solar power as the most popular energy source, with 79% of Americans saying the want more emphasis on producing energy from the sun. Wind was the second most favorable energy source. Only 28% of the respondents said they want more emphasis on coal. In a blog post on the results, Greenpeace’s Joe Smyth noted that the numbers reflect that “the coal industry’s PR campaign to attack clean air and climate change policies as a ‘war on coal’ has mostly failed.”
Dow Chemical signs wind contract as hedge against price volatility
March 2015: Dow Chemical has signed a long-term agreement to supply one of its plants in Texas with 200 MW of wind energy from a project being built nearby, which according to the company is the first time in the U.S. that wind has been used to power a large-scale manufacturing facility. The wind power acquisition makes Dow the third largest corporate purchaser of wind energy in the U.S. “Adding large scale renewable energy to Dow’s manufacturing process is just one smart move that we can make to secure a future of sustainability, growth, and long-term competitive advantage,” Seth Roberts, Dow’s global business director of the Energy and Climate Change, was quoted saying in FierceEnergy. “This decision also serves as a systemic hedge against both energy and power price volatility, while improving our overall carbon footprint.”
Obama orders aggressive fed shift to renewables to cut CO2 emissions
March 2015: The Obama Administration has ordered all federal government agencies to reduce their CO2 emissions 40% below 2008 levels over the next 10 years by shifting to renewable energy. President Obama signed the executive order this month, building on a 2010 White House directive requiring 35 U.S. agencies to limit their energy consumption to help fight global warming, as reported in Renewable Energy World. The federal government is the largest energy consumer in the United States, and Obama said it is “important for us to lead by example … We’re proving that it is possible to grow our economy robustly while at the same time doing the right thing for our environment and tackling climate change in a serious way.”
In the heart of oil country, a Texas town opts for 100% renewable energy
March 2015: In a perspective piece in Time Magazine, the mayor of fast-growing Georgetown, Texas said his city’s decision to switch to 100% renewable energy was “a business decision based on cost and price stability.” Georgetown will fully convert to wind and solar power by 2017 as newly signed contracts kick in. Mayor Dale Ross said the switch made sense for a number of reasons. It will “provide wholesale electricity at a lower price than our previous contracts … that will enable the city to avoid the price volatility and regulatory costs we were likely to have seen had we continued to use electricity generated by burning fossil fuels.” He also said solar and wind will cut down on water use in a drought-plagued state, and that he expects the commitment to renewable energy to attract companies looking to achieve “sustainability goals at a competitive price.”
Clean energy tallies $1 billion-plus in savings for Fortune 500 companies
March 2015: Clean energy is becoming mainstream for Fortune 500 companies and those that invest in renewable energy and cutting their carbon emissions are saving more than $1 billion a year, according to a new study. Published Ceres, WWF, Calvert Investments and consultants David Gardiner & Associates, “Power Forward, How American Companies Are Setting Clean Energy Targets and Capturing Greater Business Value,” found that 43%, or 215 of the companies in the Fortune 500, have set targets to cut CO2 emissions, boost renewables or improve energy efficiency. Among the Fortune 100 companies, 53 report that their investments in on climate and energy projects are collectively saving $1.1 billion annually.
Target on target to boost solar at 180 of its locations nationwide
March 2015: Keeping step with rival retailer Wal-Mart, Target has announced that it will install large solar PV systems on the roofs of 180 stores and distribution centers in 12 states, about 10% of the company’s locations. On average, there will be 1,700 panels per site, with a combined output across all locations of 100 MW of electricity that will meet 20-30% of each facility’s demand. The panels will actually be installed and owned by Connecticut-based Greenskies Renewable Energy; Target will buy 100% of the electricity generated “at a fixed and sharply discounted rate for the length of the contract.” The projects are expected to be complete by the winter of 2016. Walmart solar PV systems on 250 of its U.S. stores.
California is 1st state to produce 5% of electricity from solar plants
March 2015: With a number of new large solar projects coming online – including including two 550 MW plants, the 377 MW Ivanpah project and a 250 MW plant – California has become the first state to get more than 5% of its electricity from utility-scale solar power. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, large-scale solar generated 9.9 million megawatt-hours of electricity in 2014, triple the amount from 2013. The data show that California’s solar production was more than all other states combined, and more than three times as much as Arizona, which came in second place for 2014.
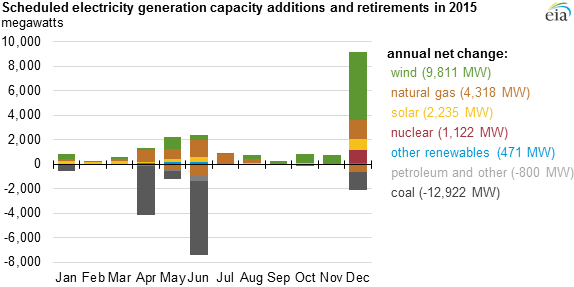
EIA: renewables, natural gas in, coal out for new capacity in 2015
March 2015: The latest projections compiled by the U.S. Energy Information Administration indicate in 2015, renewables and natural gas will make up the vast majority of new more than 20 GW of new generating capacity that utilities expect to add to the power grid. EIA data show that 9.8 GW of wind are in the pipeline to be switched on this year, 6.3 GW of natural gas, and 2.2 GW of solar. Together, they comprise 91% of total new capacity expected this year. Conversely, EIA data show nearly 16 GW of generating capacity on the drawing board to be retired this year, with 81% of the total (12.9 GW) coal-fired generation.
Analysts: grid parity will make solar the world’s leading energy source
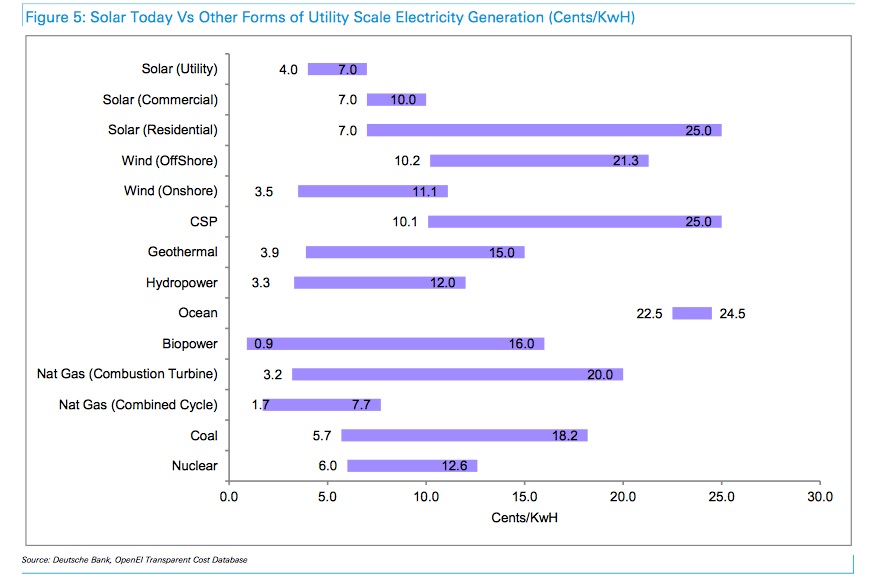
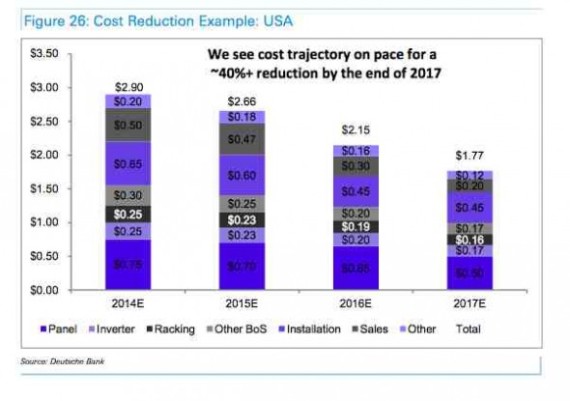
March 2015: A new report by analysts at Deutsche Bank projects that solar will become the dominant electricity source globally over the next 15 years as prices continue to drop, displacing large amounts of fossil fuel. As reported in Renew Economy, the analysis says that by 2030, the solar market will increase ten-fold, adding more than 100 million new customers. Solar energy already costs the same or less than conventional fossil fuel-generated energy (grid parity) in more than half of all countries, and within two years, it will be at parity in around 80% of the countries worldwide. “Over the next 5-10 years, we expect new (solar) business models to generate a significant amount of economic and shareholder value,” the Deutsche Bank analysts wrote.
Wisconsin Lt. Gov. says renewables give others a “competitive advantage”
March 2015: In a radio interview on March 20, Wisconsin’s lieutenant governor acknowledged that states working to cut their carbon pollution and emphasizing the development of clean energy have a “competitive advantage” over states like Wisconsin that are fighting to maintain their reliance on coal. Republican Lt. Gov. Rebecca Kleefisch was criticizing the Obama administration’s proposed Clean Power Plan, which will sharply cut carbon pollution from power plants, when she said that Wisconsin’s refusal to move away from coal, which provides about 60% of the state’s electricity, hurt her state’s competitiveness. Neighboring states like Iowa and Minnesota have invested heavily in ramping up their wind and solar capacity.
Costa Rica has been completely fossil fuel-free so far in 2015
March 2015: For the first 75 days of 2015, Costa Rica got 100% of its energy from renewable sources, according to the state-run Costa Rican Electricity Institute. Hydroelectric power makes up the majority of the country’s renewables, and heavy rains have helped the country avoid using any fossil fuels at all so far this year. Fortuitously for residents, the boost to renewable capacity also has helped lower electricity rates by 12% percent. Costa Rica has a goal of becoming carbon-neutral by 2021.
The market for energy storage projects made big gains in U.S. in 2014
March 2015: The market for energy storage technology grew more than 40% in 2014 in the United States, according to a joint research partnership between GTM Research and the Energy Storage Association. Last year, 180 projects with the capacity to store 62 came on line, up from 44 megawatts from 2013. “The U.S. energy storage market is nascent but growing fast,” a GTM executive was quoted saying in Fierce Energy . “Attractive economics already exist across a broad array of applications, and system costs are in rapid decline. We expect some fits and starts, but significant overall growth for the market in 2015.”
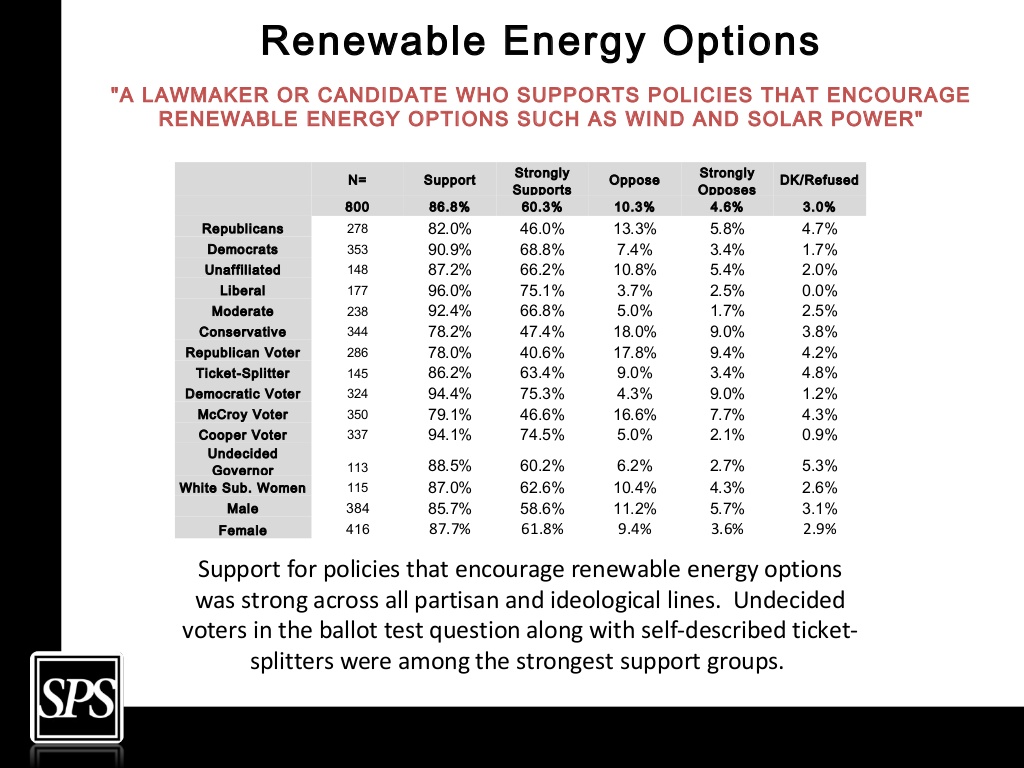
Poll shows overwhelmingly lopsided support for clean energy in NC
March 2015: A poll conducted by conservative clean energy advocates in North Carolina has found overwhelming support for solar, wind and energy efficiency in the state, regardless of party affiliation or ideology. In a survey of 800 North Carolina voters, the group Conservatives for Clean Energy found that 87% said they would support a candidate who favored policies that encourage renewable energy, including 82% of Republicans, 91% of Democrats and 87% of unaffiliated voters. Similarly lopsided support was seen for tax incentives for renewable energy and the state’s renewable energy standard.
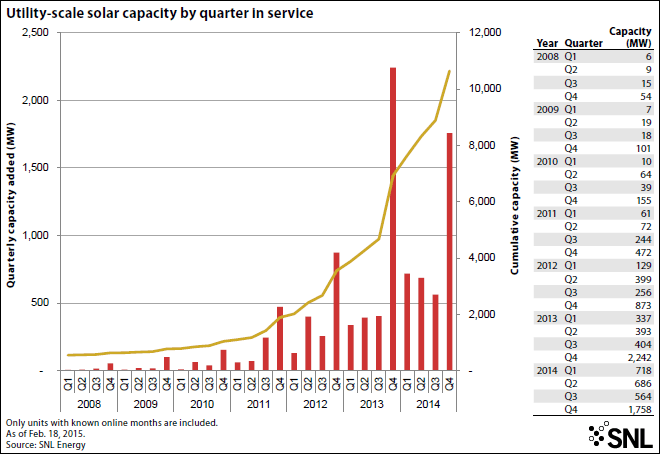
2014 was the biggest year ever for new utility-scale solar projects
February 2015: Utility-scale solar had its best year ever in 2014, with the installation of more than 3.7 GW of new capacity from 109 projects, 10% higher than the 3.4 GW installed in 2013. In total, there are now 10.6 GW of utility-scale solar capacity operating in the U.S., according to SNL Energy Notable projects included the 280-MW Abengoa Mojave Solar, the largest built last year, and the 255-MW phase four of the Topaz Solar Farm, which brings the total capacity of the PV project to 567 MW, making it the largest solar farm in the world.
Countries setting records worldwide for new wind power installations
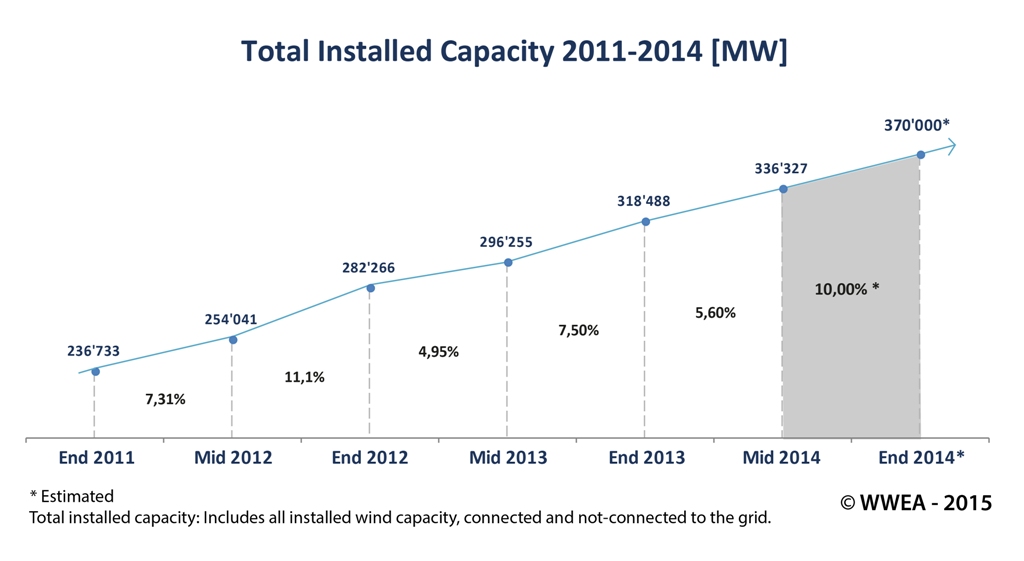
February 2015: There were a record number of wind turbine installations worldwide in 2014, according to data from the World Wind Energy Assocation. In all, more than 50 GW of capacity were added last year, bringing total global wind power capacity close to 370 GW. China led the pack, installing 23 GW on new wind in 2014, the largest amount a country has ever added in one year, followed by Germany and the U.S. Brazil joined the top five, the first time a South American country has cracked the top 10 in wind energy (a full list of leading wind countries is available here). Half of the top 12 countries set records for new capacity.
Red, blue, doesn’t matter. Solar job growth doesn’t pick political sides
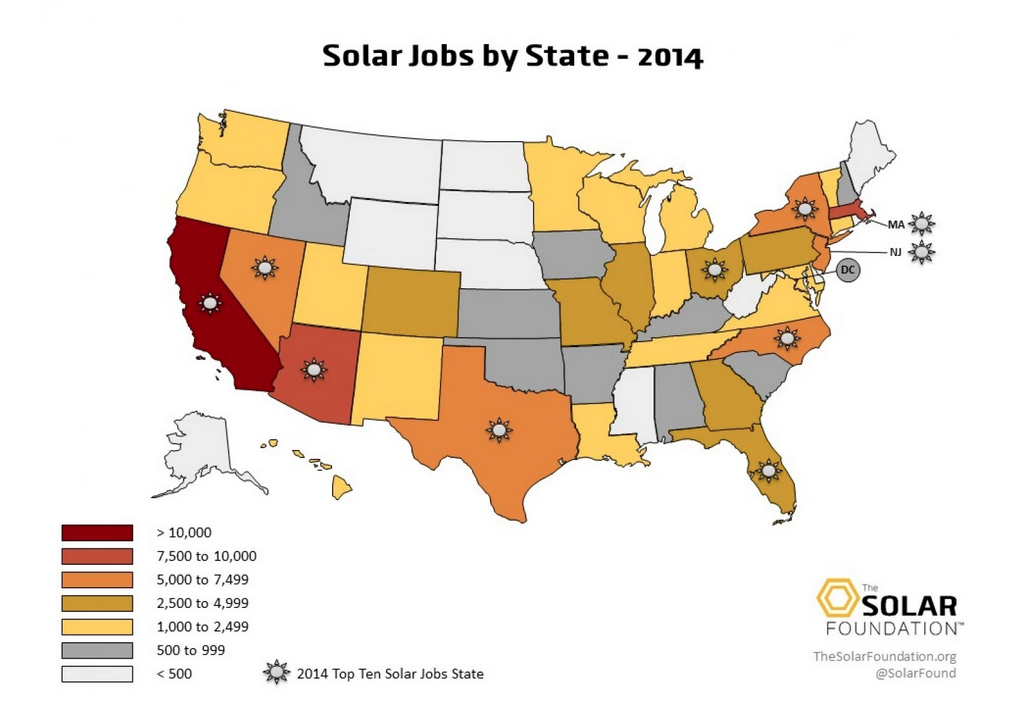
February 2015: One of the upshots of solar job growth in the U.S., says Washington Post journalist @Chris Mooney, is that it’s “catching on in a lot of states that we don’t traditionally think of as being liberal, do-gooder territory.” While California and Massachusetts are the top solar job states, other leaders include conservative Arizona, Texas and Nevada –– for obvious reasons – but also North Carolina, Ohio and highly conservative Georgia, which saw a mind-boggling 261% increase in solar employment in just two years. A key reason for solar’s geographic and political diversity, says Mooney, is that solar “appeals to a libertarian style of thinking — you generate your own power, rather than being dependent upon some utility somewhere. It increases your independence, your economic liberty.”
Solar job growth outpaces U.S. economy, leaves coal in the dust
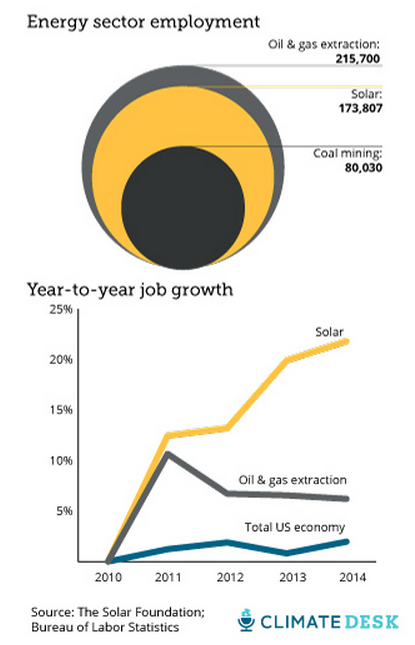
February 2015: Jobs in the solar industry in the United States grew 10 times faster than the overall economy, according to The Solar Foundation’s 2014 State Job Census. As of November 2014, the solar industry employed 173,807 workers (in installation, manufacturing, sales and distribution), a 22% jump from the previous year. Notably, solar job growth is significantly outpacing the fossil fuel industry. Solar jobs now outnumber coal mining jobs 2-to-1 and are quickly catching up to jobs in oil and gas extraction, the report noted. The coasts are well represented, with California’s 54,700 jobs ranking number one and Massachusetts number two at 9,400 jobs.
Apple continues to lead the way on merging high-tech and clean energy
February 2015: In separate deals, Apple has cemented its leadership position on clean energy in the high-tech sector. In the U.S., Apple has signed the largest clean energy agreement ever for a commercial end-user. The computer giant will pay $848 million to buy 130 megawatts of power from First Solar’s 2,900-acre California Flats solar PV project for 25 years. Construction on the project is scheduled to be complete by the end of 2016. In Europe, Apple has announced a plan to build two data centers that will be powered 100% by renewable energy. One center will be built in Viborg, Denmark and be powered mainly by wind energy. The other, in County Galway, Ireland will be powered partly from biomass. Both data centers are expected to open by 2017.
Europe on target for 20 percent renewable energy by 2020
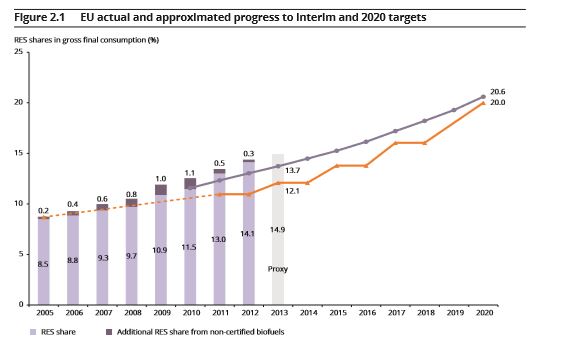
February 2015: The European Union is on target to achieve its goal of 20% renewable energy by 2020, according to a report from the European Environment Agency, which analyzed data from 2013. Some nations, such as Britain, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg, are their targets with less than 5% energy from renewables, while Austria, Finland, Sweden and Latvia are all above 30%. Hydropower (42.6%) and onshore wind (26.2%) provided the majority of electricity from renewables, with percent and 26.2 percent, respectively. Beyond 2020, EU countries have agreed to a 27% renewable target by 2030 and 55-75% percent by 2050. “We can go even further: if we support innovation in this area [renewable energy] could become a major motor of Europe’s economy, bringing down emissions while creating jobs,” said EEA Executive Director Hans Bruyninckx.
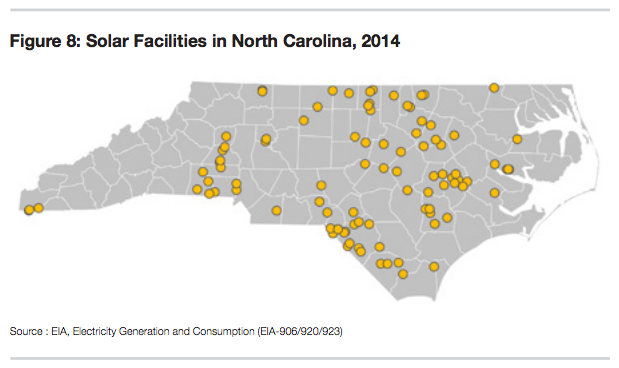
North Carolina’s solar leadership spreads profits across the state
February 2015: North Carolina’s continued investment in solar is paying handsome dividends, according to a new report by Duke University. “The Solar Economy: Widespread Benefits for North Carolina” credits business-friendly policies such as its renewable energy standard and a renewable tax credit with stimulating economic development. As a result, the state now has 150 solar facilities bigger than 1 megawatt and the industry employs 4,300 workers at 450 companies, representing more than $2 billion of investment. The benefits are being felt in all parts of the state and in both rural and urban areas. Paraphrasing one company executive they interviewed, Duke researchers said, “North Carolina is good for solar, but solar has also been very good for North Carolina.”
South Africa’s economy sees net profit from wind and solar projects
February 2015: South Africa’s renewable energy program helped save the country more than $450 million in energy costs in 2014, according to a recent study by the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research. The country’s 600 MW of wind and 1 GW of solar capacity was helped along by subsidies totaling $390 million, leaving a net ‘profit’ to the economy of around $60 million. Electricity generated from renewable projects replaced more than 2 terawatt-hours of electricity generated by diesel- and coal-fired power plants.
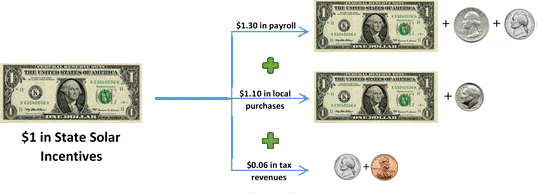
Washington state solar incentives pay for themselves ‘many times over’
February 2015: Data from a survey of solar installers and manufacturers in Washington state show that every dollar of incentives provided to owners of solar PV systems injected $2.46 back into the economy in 2013. Solar Washington collected the data to gain insight into the industry’s impact on Washington’s economy. For 2013, state incentives of $19.6 million resulted in $48.2M in economic impact, including $25.4 million in payroll and $21.5 million in equipment purchases from in-state suppliers. “Based on the data we’ve gathered, solar incentives in Washington State pay for themselves many times over and are a boon to the state economy,”said David Nicol, president of Solar Washington’s board.
Bloomberg: U.S. clearly on a path toward a clean energy future
February 2015: As total U.S. investment in clean energy climbed to $386 billion last year, the evidence that the U.S. “is clearly preparing for a future in which sustainable sources of energy play a much larger role” is laid out in sharp focus by Bloomberg New Energy Finance’s “Sustainable Energy in America Factbook.” BNEF highlights several major developments as proof:
- New government policies at both the national and state levels that promote clean energy, chief among them the Obama administration’s Clean Power Plan and its bilateral climate pact with China.
- Energy-intensive industries such as data centers gravitating to the U.S. due to favorable energy economics.
- Major new infrastructure, including natural gas pipeline expansions and widespread deployment of smart grid technologies.
- Increased capital flowing into financial vehicles such as green bonds specifically aimed at sustainable energy development, which will help raise the huge amounts needed for buildout.
India betting on solar to power nation’s expanding economy
February 2015: Construction is expected to begin soon in India on what will eventually be the world’s largest solar facility. The 750-megawatt plant in Madhya Pradesh, which is scheduled to come online in August 2016, will generate enough electricity to power roughly 2 million Indian homes. All told, India has plans to install around 100 gigawatts of solar power by 2022, which would boost the nation’s solar capacity 33-fold, second only to China. A large chunk of that will come from U.S.-based SunEdison and First Solar, which have committed to building more than 20,000 megawatts of clean energy capacity in those seven years. Reuters reports that SunEdison will build 15,200 MW of solar and wind power capacity by 2022, while First Solar made a commitment to develop 5,000 MW of solar by 2019. The government of Prime Minister Narendra Modi has made renewable energy a priority. “We have no option but to make a quantum leap in energy production and connectivity,” Modi said of the country’s solar goals.
Explosive 1,200% increase in 1MW+ solar plants in U.S. between 2008-2013
February 2015: Worldwide solar capacity has mushroomed by more than 50x in less than 10 years as the price of solar energy has fallen exponentially. In the U.S., this has led to the construction of around 630 solar plants of 1 MW or bigger in size between 2008-2013, equating to a 1,200% increase in capacity, or about 6,000 MW, in just five years (Click the map below to watch the growth year by year starting in 1983). That is enough electricity to power roughly 1.7 million homes, and according to DOE forecasts, the trend of exponential growth will continue, with solar expected to power around 4 million homes by 2017.
Burlington, Vermont is on its way to 100% clean energy … and saving money
January 2015: Although there is some quibbling about the accuracy of how Burlington, Vt. counts its renewable energy supplies and whether it truly is the nation’s first 100% renewable city, there is little doubt the state’s capital is making huge strides in clean energy and saving its residents money in the process. In an interview with NPR, an official at local utility Burlington Electric said that switching from fossil fuel energy to renewable energy will likely save Burlington about $20 million over the next two decades and that unlike other cities in the U.S., where electricity costs have increased, the city’s rates haven’t gone up since 2009. Most of Burlington’s ‘renewable energy’ comes from hydropower, about a third from a biomass facility that burns scrap wood, and the remaining 20% from wind turbines and solar panels.
Onshore U.S. wind turbine installations rose sixfold in 2014
January 2015: Installations of wind power in the United States surged sixfold in 2014, adding 4.7 GW of new onshore wind capacity last year, compared with just 764 MW a year earlier. According to an analysis by Bloomberg New Energy Finance, much of the growth can be attributed to the extension of the Production Tax Credit in January 2013. Total U.S. onshore wind installations are now 64.2 GW, second only to China, which also saw record wind growth in 2014, with turbine installations rising 38 percent, or 20.7 GW, from a year earlier.
Survey: utility execs are jumping on the clean energy bandwagon
January 2015: After staunchly fighting the integration of clean energy for years, utility executives are finally beginning to see the opportunities that come with embracing solar, wind and energy efficiency. In a survey of 400 utility executives from across the country by trade publication Utility Dive, 88% said they see distributed energy as an opportunity for their businesses over the next five years and 31% listed that as their biggest growth opportunity. Similarly, fully 84% of utilities project that their use of distributed energy resources will increase. And the top three emerging technologies that executives said their companies should invest in (in order) are: battery storage, energy efficiency and utility-scale renewables. As Grist’s David Roberts noted in a column summarizing the survey, “[U]tility execs have gotten the memo about the rise of distributed energy.”
Efficiency outdoes other energy sources to meet PJM’s demand
January 2015: At an auction last year for resources to meet future electricity demand for the the largest electric grid operator in the United States, the winning low bid went not to coal, gas or even renewable energy like wind or solar. According to a report in LiveScience, the most competitive bid for meeting new electrical capacity in the PJM Interconnection, which supplies electricity to 13 northeastern U.S. states and the District of Columbia, was energy efficiency. So-called “demand-response” measures aimed at reducing peak demand will supply 47.5% of all new electrical capacity for PJM in 2017–2018.
CEO: Riding on the back of solar, NRG plans to double earnings
January 2015: In a presentation to investors and analysts, NRG Energy President and CEO David Crane says the company has ambitious plans to double its revenue over the next two years, and that much of the growth will be built on NRG’s renewable energy business. Crane outlined plans for NRG to build the company into the second largest U.S. rooftop solar company, behind Solar City, by year-end, particularly through solar expansion in Texas, California and the Northeast. “Electricity is on the cusp of a massive transformation,” Crane was quoted saying in Bloomberg. “If you want to win today and tomorrow, you have to have a strategy that is at least bifurcated” between conventional power and alternative energy.”
Analysts: solar costs have plunged and will continue to do so
January 2015: A new report by the International Renewable Energy Agency says that biomass, hydropower, geothermal and onshore wind are all competitive with or cheaper than coal, oil and gas-fired power stations, even without financial support and despite falling oil prices. “Any remaining perceptions that renewable power generation technologies are expensive or uncompetitive are at best outdated, and at worst a dangerous fallacy,” said IRENA’s director-general Adnan Amin. “Renewable energy projects across the globe are now matching or outperforming fossil fuels, particularly when accounting for externalities like local pollution, environmental damage and ill health. … The game has changed; the plummeting price of renewables is creating a historic opportunity to build a clean, sustainable energy system and avert catastrophic climate change in an affordable way.” IRENA said that the biggest cost declines are coming from solar PV, which have fallen 75% since the end of 2009. And analysts expect that trend to continue. Due to improvements in energy efficiency and economies of scale and falling financing and manufacturing costs, Deutsche Bank analysts project that solar prices will fall 40% below current prices within two years to around 50 cents per watt, while SunEdison and other manufacturers have projected panel prices to drop to as low as 40 cents per watt by the end of 2016.
Solar irony: record low price for large-scale solar in Middle East
January 2015: As the collapse in oil prices leads to the cancellation of tens of billions of dollars in oil projects, oil rich Saudi Arabia is developing solar at record-low prices. Last week, a Saudi firm signed an agreement to provide electricity from a 200-MW project it is developing in Dubai at a cost of $58 per megawatt-hour for the next 25 years, reportedly the lowest price ever for a utility-scale PV project.
Chile leads explosive growth in solar PV in Latin America
January 2015: Solar installations in Latin America grew by 370% last year. Led by Chile, which accounted for three-quarters of the growth, the region that includes Mexico, Central America, South America and the Caribbean, added 625 NW of solar in 2014. In fact, in the fourth quarter alone, Chile installed double the amount of solar that was in Latin America in 2013. Mexico and Brazil added the second and third most solar, respectively. GTM Research projects that the region will install 2.1 gigawatts of solar this year – a 237% increase in annual growth over last year –
with Chile, Honduras and Mexico leading the field.
Citi predicts massive expansion, cost declines for battery storage market
January 2015: By 2030, the global battery storage market will have grown to $400 billion, according to projections by Citigroup analysts. A trifecta of demand for expanded battery storage – from consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and combination of renewable energy and smart grids – will promote rapid growth in the industry Citigroup said in a report on global investment trends for 2015. The analysts also foresaw a scenario for the cost of battery storage similar to that driving steep cost declines in solar: “falling costs lead to increased deployment, leading to further cost reductions.” Citi estimated that storage costs could fall ultimately fall to $150 per megawatt-hour, which would eliminate the need for subsidies.
U.S. solar installations expand by a factor of 22 in just six years
January 2015: Few industries have fared as well as solar in the six years since the 2008 Recession. Data from GTM Research shows that the United States installed 22 times more solar in 2014 than in 2008, adding 5.7 gigawatts of PV and concentrating solar, compared to only 263 megawatts six years prior. That means, according to Greentech Media’s Stephen Lacey, that a new solar installation is now being completed every two and a half minutes in the U.S., up from one every two hours a decade before. One company, SolarCity, is installing almost as much solar capacity in one quarter as the entire industry put on-line in all of 2008.
GE’s sails filled with orders for new wind turbines in 2014
January 2015: Orders for General Electric wind turbines increased 26% over 2014, with almost 40% of the company’s 3,227 total orders coming in the final quarter of the year, a 61% increase over the fourth quarter of 2013. Company executives project further sales increases for 2015.
No brainer! Six new projects will give big boost to Sunshine State’s solar
January 2015: Two recent announcements by Florida utilities will dramatically increase the Sunshine State’s solar capacity. Florida Power & Light has plans to build three projects totaling 225 MW in the coming year in south Florida, tripling the utility’s solar output and providing enough electricity for roughly 40,000 homes. More importantly, FP&L said that the economics of solar have improved to the point that customers will not see any rate increase related to the projects. “[O]ur analyses have determined that the plants can be built without resulting in net costs to our customers over the facilities’ operating lifetimes,” spokeswoman Sarah Gatewood said. Gulf Power also has made a commitment to boosting its solar capacity substantially. In joint ventures with the Navy and Air Force, the Southern Co. subsidiary plan to build solar plants, totaling 120 MW, at three military installations in the Panhandle by the end of 2016. Florida currently has only 229 MW of solar installed statewide.
2014 was record-breaking year for Canada’s wind energy sector
January 2015: Canada’s wind energy sector saw record growth in 2014, adding 1,871 MW of new capacity during the year. According to the Canadian Wind Energy Association, the country now has a total of 9,698 MW of windpower installed nationwide, enough to meet the annual electricity demand for roughly 3 million Canadian homes. Projections are for Canada to add at least 1,500 MW of new wind power capacity this year.
Growth in solar jobs in the U.S. outpaces overall economy by 20X
January 2015: Exceeding already optimistic growth expectations, the solar industry created jobs at a rate nearly 20 times faster than the economy overall last year, accounting for 1.3% of all jobs created in the U.S. in 2014. According to The Solar Foundation’s National Solar Jobs Census, as of November 2014, the solar industry employed nearly 174,000 workers, an increase in jobs of 22% since November 2013. Solar jobs now outnumber older, well-established industries in the energy sector, including coal mining (93,185 jobs). The solar sector also added nearly 50% more jobs in 2014 than the total created by both the oil and gas pipeline construction industry (10,529), and the crude petroleum and natural gas extraction industry (8,688).
Touchdown! Super Bowl XLIX to be powered by renewable energy
January 2015: Lighting and other electricity needs for Super Bowl XLIX at the University of Phoenix Stadium in Glendale, Ariz. will be powered by 100% renewable energy. Through a $1 million sponsorship agreement with the NFL, Arizona-based Salt River Project will provide in-kind services and enough renewable energy credits to cover all the energy used for the game on Feb. 1.
Global clean energy investment rose to near-record levels in 2014
January 2015: Anchored by big leaps in the cost competitiveness of solar, approval of new offshore wind projects in the U.S., and China’s expanded commitment to renewables, global investment in clean energy rose to near-record levels in 2014. According to an analysis by Bloomberg New Energy Finance, total clean-energy investment jumped 16% last year to $310 billion, more than five times the amount invested just a decade earlier. The market’s performance was just shy of the record $317.5 billion invested in 2011. “Throughout last year, we were predicting that global investment would bounce back at least 10% in 2014, but these figures have exceeded our expectations,” Bloomberg analyst Michael Liebreich said in a statement.
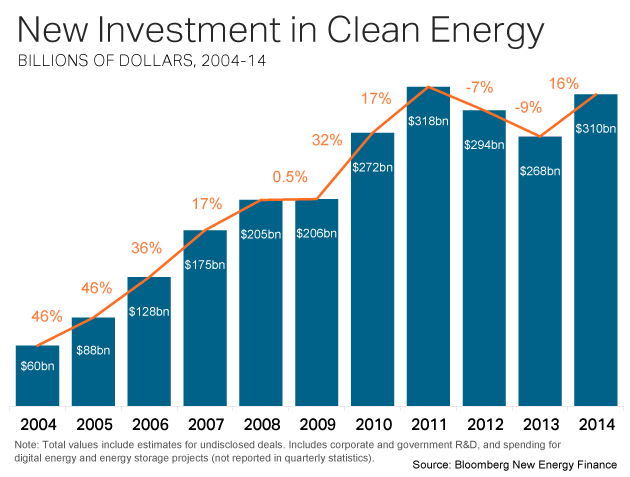
Source: Bloomberg New Energy Finance via Grist
Study: rooftop solar is a better investment than stocks
January 2015: U.S. homeowners who install a typical rooftop solar system are making a better investment than if they put their money into the stock market, according to a study by the NC Clean Energy Technology Center. The analysis (available here), funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, ranked the relative value of investing in solar in each of America’s 50 largest cities against a long-term investment indexed to the Standard and Poor’s 500 index. In 46 of those cities, a fully financed, typically-sized (5-kilowatt)
solar system is a better investment than the stock market, and in 42 of these cities, the same system already costs less than energy from a residential customer’s local utility.
Mix of EE, renewables and hydro a fix for high energy prices in Mass.
January 2015: A report commissioned by the Massachusetts Department of Energy Resources has found that by prioritizing energy efficiency, renewables and imports of Canadian hydroelectricity, the state can insulate itself from spikes in energy prices in the winter. Conducted Synapse Energy Economics, the analysis is intended to assess investments in clean energy as a means of reducing over-reliance on natural gas. The region’s natural gas infrastructure is insufficient to meet demand during peak winter use, which leads to high electricity prices.
Deutsche Bank: 80% of world will see grid parity for solar within 2 years
January 2015: Solar systems will reach grid parity in up to 80% of the global energy market within two years, according to projections by Deutsche Bank. The forecast assumes that electricity prices will continue rising across the world and that solar costs will continue their downward trend, but even if electricity prices don’t climb, the bank estimates solar will still be cheaper than current conventional energy for two-thirds of the world. Unsubsidized rooftop solar electricity costs 13-23 cents per kilowatt-hour, well below retail electricity prices in many markets globally. “We believe the trend is clear: grid parity without subsidies is already here, increasing parity will occur, and solar penetration rates are set to ramp worldwide,” Deutsche Bank analyst Vishal Shah was quoted saying in Clean Technica.
Aiming to cut reliance on oil and gas, Mexico to invest heavily in wind
January 2015: As part of efforts to diversify its heavy dependence on oil and gas, Mexico expects to see investments in wind farms reach $14 billion between 2015 and 2018, almost quadrupling the country’s installed capacity to 9,500 megawatts. According to a report in Reuters Mexico’s state-run electricity company CFE plans to develop eight wind farms that will generate 2,300 MW at a cost of some 52 billion pesos ($3.55 billion).
Calif. raises the bar on the nation’s most aggressive clean energy goals
January 2015: In his inaugural address at the beginning of 2015, California Gov. Jerry Brown issued an ambitious plan that will greatly increase renewable energy development in the state, already a leader in the field. Even though California has the nation’s most aggressive renewable energy standard, requiring a third of its power to come from clean energy by 2020, Brown said it is not enough. He set a new goal of one half the state’s energy coming from renewables by 2030. Although short on specific plans, Brown did outline a number of initiatives he said he would support, including cutting fossil fuel use in cars and trucks in half over the next 15 years, and doubling energy efficiency in existing buildings, as well as “more distributed power, expanded rooftop solar, micro-grids, an energy imbalance market, battery storage, the full integration of information technology and electrical distribution and millions of electric and low-carbon vehicles.”
Ecolab goes all solar; more than doubles Minnesota’s solar footprint
January 2015: St. Paul, Minn.-based Ecolab Inc. has signed an agreement with renewable energy developer SunEdison that will provide the company with enough solar power to offset all of its electricity use in the state. Ecolab, a Fortune 500 company that markets hygiene, energy and water technologies to businesses and had more than $13 billion in sales in 2013, will buy 16 megawatts of solar power from SunEdison. Minnesota’s entire statewide solar capacity is currently only 14 megawatts. An Ecolab vice president said the company pursued the solar agreement because “it makes business sense to do this.”
Cold winds blew big savings into customers’ pockets in ‘polar vortex’
January 2015: Last year, during the frigid polar vortex that froze much of the country early in the year, wind energy saved consumers in 13 Mid-Atlantic and Great Lakes states more than $1 billion on electricity bills by protecting them from extreme price spikes, according to an analysis by the American Wind Energy Assocation. Extreme temperatures from the Arctic blast on Jan. 6 and 7, 2013, created unusually high demand for electricity and natural gas, driving prices for both to dozens of times their normal levels. AWEA analyzed grid operator data and fuel price information for every power plant in the region to determine how much more electricity prices would have increased had wind generation not been online. Because there are zero fuel costs, wind is insulated from market price spikes, and AWEA determined that customers in the 13 states save $408 million on Jan. 6 and $601 million the following day because comparatively wind was available.
Renewables top Germany’s list of energy resources for 2014
January 2015: Renewable energy accounted for more than a quarter of Germany’s electricity generation for 2014, displacing lignite as the country’s main source of energy, according to analysts. Almost 26% of the country’s power generation came from wind, solar and biomass, up 2 percentage points from 2013. In all, electricity output from renewables has grown eightfold in Germany since 1990. “Renewable energies were the number one source of power production for the first time ever,” the think tank Agora Energiewende told the Financial Times. “They have now permanently displaced lignite as the top source of power in the [German] electricity mix.”
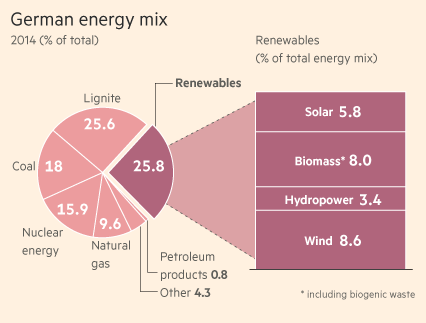
Source: Agora Energiewende via the Financial Times
Google sinks $157 million into building Utah’s biggest solar plant
January 2015: Google is investing $157 million to build the largest solar plant in Utah. Being developed jointly by Google and Norwegian power company Scatec Solar, the 104-megawatt project will generate enough electricity annually to power roughly 18,500 homes. In exchange for its majority investment, Google will receive tax incentives and a share of the project’s income. The plant will be Google’s 18th renewable energy project worldwide, some powering the company’s massive data centers and others, like the one in Utah, built simply as a means of generating healthy investment returns. “We’ve invested over $1.5 [billion] in bringing new sources of renewable energy to the grid and have no plans to stop,” a Google spokesman said in an email to E&E News (subscription only).
Despite rosy talk, coal executives are fretting on the inside
April 2016: Despite what they might say publicly about a rosy future for coal, coal mining executives don’t see it that way behind the scenes. Executives at Australian coal mining giant BHP Billiton told analysts recently that if the world followed through on its pledge to limit global warming to a 2°C temperature increase, then thermal coal would see a massive drop in demand and earnings. The analysts at Macquarie Research said they “remain negative on our outlook for BHP and their commodity exposures,” and that they expected the company to underperform on the stock market.
Board dismisses application for proposed Montana coal rail line
April 2016: A decision by the Surface Transportation Board to dismiss the Tongue River Railroad Co.’s application to for a rail line that would have connected a proposed Montana coal mine with ports in the Pacific Northwest formally puts another nail in the coffin of both projects. The railroad would have used the power of federal eminent domain to condemn family farm and ranch land in southeastern Montana in order to haul coal from Arch Coal’s planned Otter Creek mine to Asian export markets. Arch filed for bankruptcy in January.
Peabody, the world’s largest coal producer, declares bankruptcy
April 2016: Saddled by $9 billion in debt, Peabody Energy, the world’s largest publicly owned coal producer, has filed for bankruptcy in a move that surprised noone. Peabody’s Chapter 11 filing means three of the nation’s top five coal producers have fallen victim to collapsing coal prices, competition from natural gas and renewables, and tighter clean air safeguards. Peabody’s stock value has plunged to around $2 per share, 99% below its high in 2008.
U.S. coal production plunges 30% below 2015 level
April 2016: Reflecting the historic shift taking place in both the coal utility sectors, coal production in the U.S. in 2016 is running more than 30% below the comparable period last year, according to data provided by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis. The U.S. coal industry produced 11 million tons of coal in the seven days ended April 2, 38% less than in 2015, and only half the amount mined in the same week in 2008, the year of peak U.S. coal output. Data also show the situation won’t likely turn around any time soon, with coal stockpiles at their highest level in 25 years.
Cost overruns, delays continue to plague Miss. coal gasification plant
April 2016: Mississippi Power’s coal gasification power plant in Kemper is facing an additional $18 million in costs overruns and could be delayed even further after the company discovered problems in equipment that converts coal into natural gas. February marked the seventh consecutive month of cost overruns. The plant, with a $6.6 billion price tag, is nearly $4 billion over budget and two years behind schedule, and company offcials say any delay beyond Aug. 31 will cost an additional $25 million to $35 million per month, which cannot be passed on to customers.
PacifiCorp will retire Wyo. coal plant instead of converting it to gas
April 2016: Saying it no longer makes economic sense to convert one of its coal-burning units in southwest Wyoming to natural gas, PacifiCorp has abandoned its plans and instead decided to retire the facility. The projected cost of converting Unit 3 at the Naughton plant in Kemmerer, Wyo. to natural gas was around $160 million, but the utility determined that it would be more financially prudent to close it at the end of 2017. The plant’s other two units aren’t subject to the same environmental reviews, but PacifiCorp is also considering their future.
Low natural gas prices could force more coal, nuke plant retirements
April 2016: Persistently low natural gas prices are straining the economics of running coal-fired power plants and could lead to another wave of plant retirements, according to an analysis by Moody’s that. “Low natural gas prices have devastated most of the US merchant power sector,” Moody’s was quoted saying by SNL . “In the current commodity price environment, most unregulated coal and nuclear plants are generating little or negative cash flows. We believe that if the current gas price environment … does not improve in the next 12-18 months, there could be more large-scale coal and nuclear plant closures.”
China takes drastic steps to cut back on oversupply of coal-fired power
April 2016: Less than a month after 15 provincial governments were ordered to stop building up to 250 already approved coal-burning power plants, the Chinese government is taking further steps to cut back on the massive over-supply of power. According to Chinese press reports, China’s National Energy Agency is poised to introduce a new policy mandating that all but three of China’s 31 mainland provinces suspend approvals for new coal plants, which could halt 90% of plants currently in the approval pipeline.
Coal-fired power’s decline in Ohio a snapshot of nationwide woes
March 2016: The decline of coal as a source of power in Ohio over the past six years has been dramatic and provides a snapshot of what is happening across the country, according to an analysis by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis. In 2010, Ohio had more coal-fired units than any state in the country, with 20 plants providing 82% of Ohio’s electricity. But as a result of shifting market forces, utility decisions to put off pollution controls and public opposition to highly polluting plants, utilities have closed 10 of those plants and six others appear to be surviving only through bailouts. All told, coal’s share of Ohio electric generation declined to 59% in 2015.
DOI policy proposal would increase federal coal royalty rate by 50%
March 2016: The Department of the Interior is mulling several policy reforms to the the federal coal lease program, including a 50% hike in royalty payments for some U.S. coal producers. DOI officials are drafting a Programmatic Environmental Impact Statement to address concerns raised over the past few years that American taxpayers are being cheated out of billions of dollars of revenue from coal leases on federal whose royalties are far below market value. The most notable policy change would increase the royalty rate on coal surface mining to 18.75% from the current 12.5% to match the current rate for offshore oil and gas production.
Plummeting rig count, tax revenue bring oil & gas bust into harsh focus
March 2016: Just two years after hitting an all-time high, the oil and gas boom appears to be headed for a painful bust. In September 2014, 1,931 oil and gas rigs were operating in the U.S.; today there are just 476, a 75% decrease and 50% lower than in 1987 following the biggest bust ever. Other data paint an equally bleak picture. In North Dakota, the epicenter of the drilling boom, nearly 20,000 jobs have been lost in the last year, and the state took in $400 million less — in just one quarter — than it did in the final quarter of 2014. Wyoming saw one of the nation’s biggest unemployment increases in 2015. “It’s the hardest bust I’ve been through and I have been in this business for 57 years,” one New Mexico oil and gas executive was quoted saying in the Farmington Daily Times and High Country News.
Scotland closes its last coal plant on the march toward clean energy
March 2016: Scotland has burned its last lump of coal for electricity with the closure last coal-fired power plant operating in the country. The closure of the 46-year-old Longannet station, which was Scotland’s largest, comes as officials continue the push to meet 100% of Scotland’s electricity demand with renewable energy by 2020. The country has more than doubled its renewable energy output, maingly from onshore and offshore wind since 2007, generating the equivalent of half the electricity consumed.
Testimony: Colstrip plant’s owners could lose hundreds of millions
March 2016: Units at one of the biggest coal-burning power plants in the West are on even shakier financial footing than previously believed, according to testimony presented to the Washington state Utilities and Transportation Commission by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis. David Schlissel, the group’s IRP analysis director, told UTC commissioners that worsening market changes for coal over the past year will almost surely mean that the Colstrip plant in Montana operates at large losses, possibly in the hundreds of millions of dollars. Natural gas is even cheaper than estimated a year ago, and projections are for prices to remain low for years, which makes generating power at Colstrip substantially more expensive for the plant’s owners. An analysis from a year ago showed Colstrip’s two oldest units operating in the red, but updated analysis by IEEFA indicates that one of its newer units also “now has zero to negative valuation over the next 20 years.”
Bankrupt Arch kills plans for controversial Montana coal mine
March 2016: Two months after it filed for bankruptcy, Arch Coal has suspended its application to build a major mine in southeastern Montana. Amid a bleak global market that has already sunk a number of coal companies, Arch said it could “no longer devote the time, capital and resources required to develop a coal mine on the Otter Creek reserve.” The proposal, along with equally controversial plans for the $400 million Tongue River Railroad that would have carried coal from the mine to Pacific Northwest ports for export, drew strong opposition from landowners, the Northern Cheyenne tribe and conservation groups.
Wash. bill lays financial foundation for retirement of Mont. coal plant
March 2016: Legislators in Washington are laying the groundwork for the state’s largest utility to retire its share of aging units in a Montana coal-burning power plant. While the bill, which has passed both the House and Senate in Washington, does not require a shutdown or specify any timeline for the retirement of units 1 and 2 at the Colstrip plant in eastern Montana, it does provide a mechanism for Puget Sound Energy to raise money to pay for closing the units at an undetermined date in the future. The measure allows PSE to apply tax credits from clean energy project to offset the costs of decommissioning and clean-up of Colstrip, which analysts such as UBS say is losing money because it can’t compete with less expensive forms of energy generation.
OR bill to cut coal by 2030 has support of major utilities
March 2016: The Oregon Legislature has approved a bill that will require the state’s two largest utilities to wean themselves completely off of electricity generated from coal-burning power plants by 2030. The Clean Electricity and Coal Transition bill had the support of both utilities, Pacific Power and Portland General Electric, which supply about 70% of Oregon’s electricity. To replace the energy from coal, the measure also increases the amount of renewable resources the utilities will need to provide to 50% by 2040. “Even in an era of historically low natural gas prices, our analysis shows that renewable generation is the less expensive option and that additional renewable resources can be added while maintaining grid reliability,” said a Pacific Power executive.
Vietnam reverses course, halts plans for new coal plants
February 2016: Vietnam’s government has announced its intention to “halt any new coal power development,” a stunning retreat for a country that at one time had one of the largest pipelines of new coal plants in the world planned outside of India and China. In addition to the move away from coal, Vietnam’s prime minister also made a commitment to accelerate investment in renewable energy, including building market mechanisms, encouraging policies and initiatives, and attract investment for solar and wind energy.
Bank: awash in fuel, global decline in coal demand may be “irreversible”
February 2016: A glut of coal being mined from India will add to the depressed global coal market, which is already dramatically over-supplied, analysts at Goldman Sachs said in a new report. the combination of the oversupply and weakening electricity demand will likely cause a 10% contraction in coal export trade by 2020, the bank’s analysts said, which prompted Goldman to lower its price forecasts for thermal coal for the next three years. The bank also noted that the world is awash in liquified natural gas, a fuel competitor to coal. “Unlike most other commodities, thermal coal is unlikely to experience another period of tightness ever again because investment in new coal-fired generation is becoming less common and the implied decline in long-term demand appears to be irreversible.” the analysts wrote.
New York PSC rejects plan to retool coal plant with ratepayer funding
February 2016: The New York Public Service Commission has rejected a request to repower a coal plant to burn natural gas using $145 million in ratepayer funding. The decision makes the Cayuga power plant near Ithaca, one of the few remaining coal plants in New York, all but obsolete. In 2012, it operators notified the PSC they would need to mothball the facility without the retooling. Since then, Cayuga has operated only through ratepayer subsidies of approximately $4 million per month.
Pullout of railroad likely sinks massive Australian coal project
February 2016: A massive coal mine complex proposed for the remote Galilee Basin in northeastern Australia is all but dead after the railway company that would serve project has pulled out. Aurizon announced in its mid-year earnings report that had written off $30 million (Australian) it had invested in the railway to the proposed mines in Queensland, which contain billions of tons of coal. The company wrote that the “carrying value of the project is now nil,” leaving the project without a rail line to transport coal to port.
Jewell to ailing coal companies: you still have to pay for cleanup costs
February 2016: Despite industry woes nd even looming bankruptcies, coal companies still must be held accountable for the costs of cleaning up their mines, according to U.S. Interior Secretary Sally Jewell. Alpha Natural Resources and Arch Coal, which have both declared insolvency, are seeking to ditch most of their cleanup liabilities in court. Arch has liabilities topping $450 million and Alpha’s are $411 million. In response, Jewell said officials will not tolerate such maneuvers, telling reporters that even amid financial distress, “it is still the responsibilities of these companies to do the reclamation that they signed up for” so that taxpayers aren’t left to cover cleanup costs.
Financial struggles prompt coal producers to slash lobbying
February 2016: Strapped for cash and seeing little value in trying to persuade the Obama adminstration to change its aggressive climate and energy policies, the coal industry has sharply scaled back lobbying. Spending by major coal producers on lobbying has fallen by about half to under $8 million since 2012, according to a Bloomberg analysis of disclosure filings. The biggest cuts came from top coal producers. Alpha Natural Resources, which filed for bankruptcy in August, spent just a third on lobbying of what it did in 2012. Peabody Energy, the country’s top coal producer, halved its lobbying over the same time.
Cloud Peak lost $205M in 2015, still did better than other coal producers
February 2016: Cloud Peak Energy, one of the largest coal mining companies in the West, reported a loss of $205 million for 2015. The company, which mines exclusively in the Powder River Basin, had pinned its hopes on coal exports to Asia, but the fizzling global coal market has dried up that prospect. Cloud Peak’s coal shipments fell off 13% last year and are expected to drop further this year, with none of it expected to be exported. “We expect 2016 to be another difficult year for U.S. thermal coal producers,” said its president and CEO.
Calif. bills would prohibit coal shipping from planned Oakland port
February 2016: In reaction to a highly contested proposal for a new port in Oakland to ship coal overseas, a state senator has introduced a package of bills squarely aimed at restricting coal exports in California. When the port project was first proposed in 2013, there was no mention of coal. The emphasis on coal as the $250 million port’s main commodity has outraged the community. Among other things, the bills would declare shipping coal through West Oakland a health and safety danger and prohibit public funds being used to build or operate coal-export facilities located next to poor communities.
WY econ prof: leasing moratorium is “more nails in the coffin” for coal
February 2016: In an interview for a story on the accumulating woes facing the coal industry and their impact on Wyoming, a University of Wyoming economics professor and industry expert told the Associated Press that “the damage has already been done” to the coal industry by a combination of market conditions and the EPA’s efforts to regulate carbon dioxide through the Clean Power Plan. Prof. Robert Godby, who directs the Center For Energy Economics and Public Policy, also said the administration’s recent moratorium on new federal coal leases represented “more nails in the coffin. I don’t want to say they’re already dead, but you get the idea.”
Coal slumps to record low as a source of America’s electricity
January 2016: Use of coal to generate electricity in the fell to its lowest level ever in November, according to data just release by the U.S. Energy Information Administration. Coal’s share of total electricity generation sunk to 29% as use of natural gas and clean energy continued to increase. Natural gas comprised 34% of the U.S. power mix. At the same time use dropped, utility stockpiles of coal have been accumulating to the point they now have 189 million in reserve, the most since June 2012, the EIA data show. The surplus all but guarantees continued slumping for already rock-bottom coal prices.
Falling imports signal a possible end to India’s need for foreign coal
January 2016: India’s coal imports fell precipitously in November and December, an ominous trend for a country whose growing energy use is one of the last remaining flickers of hope for the beleaguered coal industry, particularly in Australia. Imports fell a record 49% in November from the same month in 2014 and another 34% in December, bringing the decline for the year to 15%. Forecasts anticipate further declines in 2016.
Proposed Wyo. coal plant all but dead after 20 years on drawing board
January 2016: A proposed coal plant in Wyoming that has been in the planning stages for two decades is all but dead following years of delays. The Campbell County, Wyo. Attorney’s Office is putting the property for the Two Elk plant up for auction to recover more than $200,000 in unpaid property taxes. A federal investigation is looking into potential misuse of $10 million in stimulus fund. The company was denied a request for a permit extension. And PacifiCorp, a key utility partner, has terminated a transmission agreement for power from the plant, which was first proposed in 1996. Although the company says it intends to continue with the project, it will have to start its permitting from scratch.
AEP to move away from coal, with or without the Clean Power Plan
January 2016: Citing cost as a driving factor, an executive at American Electric Power said during a presentation that the company will reduce the amount of coal it burns and instead turn to more wind and solar energy – regardless of whether the Clean Power Plan is implemented. AEP generates power from conventional at a cost of $95 per megawatt hour, while electricity from both wind and advanced natural gas can be produced for just $73 per megawatt hour. West Virginal State Sen. Ron Stollings, whose district relies heavily on revenue from coal mining, said it’s urgent to begin planning for a new future. “We have to change. … We should have been planning years ago for this eventuality to try to diversify our economy.”
Gov. Cuomo sets goal to phase out coal-fired power from New York
January 2016: New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo has set a goal of phasing out coal-burning power plants in the state by 2020. Cuomo announced the goal in his state of the state address, saying he wants to bring more clean energy to New York and reduce its carbon pollution. New York gets only about 1.3% of its electricity from coal. “We will help the few remaining coal plants transition but we must clean our air and protect our health and that must be our first priority,” he said.
China clamps down on coal mining
January 2016: China’s National Energy Administration has banned new coal mines for the next three years and also ordered more than 1,000 existing mines to be closed over the coming year. The moves, a response to falling coal demand and growing concerns about pollution, will reduce the country’s coal production by 70 million tons, in accordance with an agreement reached with the U.S. in late 2014 and pledges made at the recent Paris climate summit
Bill would phase out coal as a source of energy in Oregon
January 2016: Utilities in Oregon have agreed to support a bill in the Legislature that would phase out coal-fired power in the state by 2030. The proposed measure would impact Pacific Power and Portland General Electric, which together provide about 70% of Oregon’s electricity. It also calls for doubling the amount of renewable energy the utilities generate by 2040. The agreement leading the utilities to support the measure came about following a proposed ballot measure that would have set the same target for phasing out coal and replacing it with renewables, an idea that surveys show is popular with the voters. The agreement allows the utilities more flexibility for phasing out coal than a ballot measure would.
Obama halts new federal coal leases
January 2016: The Obama administration has halted all new coal leases on federal lands as it considers overhauling a program that has been criticized for costing American taxpayers billions of dollars in lost royalty fees. Coal producers will be able to keep mining existing reserves but the move freezes new coal production from federal lands. In announcing the move, Interior Secretary Sally Jewell said that “serious concerns” about the coal leasing program, including critical findings from investigations by the DOI inspector general and the Government Accountability Office, made the moratorium a “prudent step.” DOI officials last conducted a comprehensive review of the program three decades ago.

East Coast coal terminals end 2015 with decade-low exports
January 2016: Coal exports from terminals in Virginia’s Hampton Roads region were down 35% from 2014, falling to their lowest annual total since 2007. A key reason behind the decline is low global coal prices, which make it difficult to turn a profit from exports.
Paris agreement fuels negative market reaction to fossil fuels
December 2015: The negative market implications of stranded assets tied up in coal mines, coal-fired power plants and coal-related rail and port infrastructure have increased as markets have begun to factor in the business prospects of a successful Paris climate accord, according to the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis. In the U.S., Peabody Energy shares fell 36% in the month leading up to and during the Paris negotiations and are down 92% for the year. Shares in London-based Anglo-American were down 36% for the month and 73% for the year, Chinese coal stocks dropped, and Australian coal stocks have been battered. “As the world wakes up today to new ambitions around lowering the industrial world’s effects on climate,” said IEEFA’s Tom Sanzillo, the Paris deal “serves ultimately to underscore the immense impact such policy can have on investment decisions.”
Closure of units at NM plant will cut 290 MW of coal capacity in Southwest
December 2015: State regulators in New Mexico have approved a plan years in the making to retire part of one of the West’s biggest coal-burning power plant. The New Mexico Public Regulation Commission voted 4-1 to close down two units of the 1,850-megawatt San Juan Generating Station as part of efforts to reduce pollution and improve air quality in the Southwest. The plan, which will result in a net reduction of nearly 290 megawatts of coal-generated electricity from the portfolio of utility PNM, also will require new pollution controls on San Juan’s other two units.
Market value of West’s 2nd biggest coal plant plummets 87% in two years
December 2015: One of the owners of the second largest coal-burning power plant in the West has slashed the market value of the plant by 87% in just the past two years, according to figures provided by Montana revenue officials and reported by the Associated Press. In 2013, Pennsylvania-based Talen Energy, one of six owners in the Colstrip plant in southeastern Montana, valued its 25% stake in the plant at $334 million. Two years later, Talen said its ownership is worth only $46 million. The massive write-down comes on top of a $400 million hit the company – then PPL – took in 2013. In particular, said Thomas Power, former chairman of the University of Montana’s Economics Department, Talen’s half ownership in Colstrip’s two older, less efficient and dirtier units, “is certainly not going to bounce back up.”
In “radical” restructuring, Anglo-American to cut 85,000 mining jobs
December 2015: London-based mining company
Anglo American will cut 85,000 jobs over the next several years as part of a “radical” restructuring that comes in response to the prolonged slump in low commodities prices and weak Chinese demand, including for coal.
Report details coal’s “zombie mines” and “slow-motion train wreck”
December 2015: In a harsh report about the prospects of the coal industry, analyst firm McKinsey and Co. warns that coal producers are facing “crippling liabilities” from a number of problems. The report, “Downsizing the U.S. coal industry: Can a slow-motion train wreck be avoided?” said the coal industry’s problems are multifaceted: overcapacity, shrinking demand, “chronic indebtedness,” environmental liabilities and insufficient profitability. McKinsey said while the U.S. has strong coal supplies, “the world does not need it” and projects that demand is likely to fall at least 20% below current production, which is already almost 20% below 2008 levels. Even with cutbacks, the report notes, many coal mines are not breaking even, but cannot close because shutting them down is more costly, leaving them operating as “zombie mines,” that cannot service the industry’s approximately $70 billion of debt and liabilities. Said one coal executive interviewed by SNL Energy: “[T]he coal industry, as a whole, taking all producers together, is now bankrupt.”
DOI concerned about taxpayer liabilities for coal mine clean up
December 2015: With numerous coal mining companies headed toward bankruptcy, the Obama administration is expressing concern that taxpayers could be saddled with billions of dollars in liabilities for cleaning up coal mines. Speaking to reporters after a congressional hearing, an Interior Department official said the agency is working to shore up holes in a program known as self-bonding, which allows coal companies to forego insurance for future mine cleanup costs, as long as they have strong financials. Recently, coal producer Alpha Natural Resources filed for bankruptcy, leaving behind more than $670 million in clean-up liabilities, and it’s not clear whether taxpayers will have to pick up the bill. An estimated $3.6 billion in self-bond liabilities could fall to taxpayers based on the current condition of the coal sector.
2015 will be the worst year ever for coal mining companies worldwide
December 2015: There seems to be no end in sight for coal’s freefall as 2015 shapes up to be the worst ever for the industry. Benchmark prices for coal companies are at record lows. In the U.S., power plant closings, cheap natural gas and low seaborne coal prices have pushed a number of companies into banktruptcy. China’s slowing economy has slashed coal producers’ biggest hope for business, and their fallback, India, has indicated that the country will not need any coal imports. Listed coal companies from Australia, Indonesia and the U.S. have seen their value collectively plummet by 73% from last year.
Bankrupt coal producer adding seven mines to the auction block
December 2015: Coal producer Alpha Natural Resources, which filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in August, has added seven active coal mining complexes in West Virginia and Kentucky to this list of assets it is trying to liquidate. The company had initially planned to sell 16 coal mining complexes in West Virginia, Kentucky, Virginia and Illinois.
Permit for coal train suspended over mine delays and weak market
December 2015: Just weeks after Arch Coal declared that it may file for bankruptcy, proponents a planned $400 million coal railroad to haul coal from Arch’s proposed mine on the Montana-Wyoming border to West Coast ports have asked for the permitting process to be suspended. The Tongue River Railroad Co., of which Arch is an owner, requested that the federal Surface Transportation Board suspend the permitting process for the 42-mile line, citing delays in obtaining the permit for the Otter Creek mine and a weakening coal market as reasons. Montana’s Department of Environmental Quality said in March that it would not move forward on the mine permit until Arch Coal addressed hundreds of deficiencies in its application.
Over-budget coal plant brings credit rating down for Mississippi Power
November 2015: As a result of two “less credit supportive” commissioners being elected to the Mississippi Public Service Commission, investment firm Moody’s has downgraded the credit rating for Mississippi Power and given the company a negative outlook. The utility is building a new coal-burning power plant that will capture carbon emissions, but the Kemper project is three years behind schedule and more than $3 billion over budget. “The election of two new commissioners,” Moody’s said, “increases regulatory uncertainty and heightens the risk that the utility will not obtain full and timely rate recovery” on nearly $3 billion of costs that have to be approved by the PSC.
OECD countries agree to restrict financing for int’l coal projects
November 2015: The U.S., Japan and other major nations have agreed to restrict international financing to build coal-burning power plants overseas, although they did not eliminate it completely. The Obama administration announced in 2013 that it would end U.S. financing for overseas coal plants, and after pressuring others to follow suit, finally persuaded Japan to drop its opposition. The agreement among the 34 member countries of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, which takes effect in 2017, would still allow financing for the most advanced “ultra-supercritical” plants, and for some other plants in poor countries.
Bankrupt coal producer wants to drop miner benefits
November 2015: As part of its bankruptcy proceedings, one of the biggest coal companies in the U.S. wants to drop employee benefits for more than 4,500 miners and their families. Alpha Natural Resources, which filed for bankruptcy in August, has asked permission to drop “hospital, medical, prescription, surgical and life insurance” benefits at the end of December, according to a court filing reported on by Reuters.
NY AG forces Peabody to disclose investment risks of climate policies
November 2015: The largest coal producer in the U.S. has struck a deal with the New York state attorney general’s office that will force the company to more realistically disclose the risks to its business of climate change policies. The settlement requires Peabody Energy to revamp its “one-sided” projections on the impact of climate laws, regulations and policies to the company’s coal business prospects. It also prevents Peabody from suggesting it cannot reasonably project the impact of laws, regulations and policy related to climate change. “As a publicly traded company whose core business generates massive amounts of carbon emissions, Peabody Energy has a responsibility to be honest with its investors and the public about the risks posed by climate change, now and in the future,” a press release from the AG’s office said.
Amid weak market, Peabody drops application for new coal mining
November 2015: With low prices and weak demand quelling any appetite for expansion, Peabody Energy has withdrawn an application to lease additional coal from federal land in the Powder River Basin. Peabody expressed interest to mine nearly 1 billion tons of coal from tracts in the Antelope Ridge area back in 2011. There hasn’t been a new federal coal sale since 2012.
Bankrupt coal producer seeks to drop miner benefits
November 2015: Alpha Natural Resources, one of the largest U.S. coal companies, has proposed dropping benefits for more than 4,500 miners, spouses and their dependents as part of the company’s bankruptcy proceedings. Doing so would cut roughly $125 million in obligations, but it also would erase life insurance and health benefits for about 4,580 non-union retirees, disabled former workers and their families, according to reporting by Reuters.
Reeling coal industry cuts back on lobbying, takes hit to political clout
November 2015: One of the consequences of the U.S. coal sector’s reeling misfortunes is a notable loss in influence over policy and political clout – at a time when the industry needs it most. An analysis of coal industry lobbying expenditures over the last year by SNL Energy shows that spending has dropped substantially, down almost $400,000 since the second quarter of 2015 and down about $700,000 from the same period in 2014.
Union rep believes retirement is on the horizon for Montana coal plant
November 2015: Following a visit by Washington state legislators to the Colstrip power plant in Montana, a union rep said he thinks a deal is in the works to retire the two oldest boilers at the second largest coal-burning plant in the West. Owned jointly by Washington-based Puget Sound Energy and Pennsylvania-based Talen Energy, units 1 and 2 were built in the mid-1970s, and indicators show they are struggling financially (see here and here). A representative of the International Brotherhood of Boilermakers told the local Independent Press newspaper (not online) that “it’s all over but the crying for Units 1 and 2.”
2nd largest coal producer in the U.S. is on the verge of bankruptcy
November 2015: The second largest coal producer in the U.S. is poised to file for bankruptcy with the company’s cash flow unable to sustain $5.1 billion in debt. St. Louis-based Arch Coal is negotiating with creditors over a “significant restructuring” through Chapter 11, according to a filing with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission reported by Bloomberg. Arch reported a $2.1 billion “asset impairment” in the third quarter and has not posted a quarterly profit since 2012.
G20 economies still subsidize fossil fuels with a half-trillion in support
November 2015: A new report documents that the world’s G20 major economies still provide fossil fuel development with nearly half a trillion dollars in subsidies annually. Altogether, the G20 countries spend $452 billion annually to support fossil fuels subsidies, according to the report by the Overseas Development Institute and Oil Change International. The U.S., for its part, spends upwards of $20 billion annually subsidizing fossil fuel production, the report found.
Coal producers abandon plans for new federal mine leases
November 2015: The coal industry’s deteriorating financial condition and bleak future have prompted a number of producers to abandon applications for new federal coal leases. Notable companies withdrawing permit requests include Peabody Energy, which yanked a proposal to mine nearly a billion tons of coal in Wyoming. In all, companies this year have abandoned nearly 2 billion tons in reserves they had planned to mine. “To make these long-term financial commitments is difficult in this environment,” said one coal analyst.
Utah power plant agrees to curb pollution, coal use
October 2015: As part of a proposed legal settlement, a Utah utility has agreed to limit the amount of coal it burns at a 500-megawatt power plant, a move that potentially will end its operations by 2030. The settlement resolves an appeal filed by conservation groups challenging the air permit for the Bonanza plant, Utah’s fourth largest. It caps total use of coal at 20 million tons after 2020, unless the plant fully upgrades its emission controls, which would cost the owner, Deseret Electric Power Cooperative, tens of millions of dollars to install.
Analysis: closing unreliable Fla. coal unit will save consumers money
October 2015: An aging coal-burning unit at a Florida power plant should be retired based on its rising operational costs and sinking performance, according to an analysis by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis. Unit 3 of the C.D. Mcintosh Jr. plant in Lakeland is 33 years old and being out-competed by natural gas. The amount of electricity it generates has declined precipitously since 2008 due to unreliability. According to IEEFA’s analysis, if the 364-megawatt unit is retired, replacement power, if needed at all, could be purchased more cheaply from existing natural gas plants, with savings invested in energy efficiency and solar, all with no effect on grid reliability.
Poll: majority of voters would support anti-coal candidates
October 2015: A new poll by researchers at the University of Texas at Austin found that 52% of respondents said they would be more likely to vote for a candidate who supports reducing the use of coal as an energy source, a 9-point increase from a similar poll in March. Voters supporting reduced use of coal include 62% of Democrats and 65% of respondents age 35 and younger. The biannual poll also found that U.S. attitudes on climate change have shifted significantly with 76% of Americans now believing that climate change is occurring, an increase from 68% a year ago.
Cloud Peak to halt all coal exports through 2018; will pay stiff penalties
October 2015: In a stunning development from a company that has made coal exports the centerpiece of its strategy, Cloud Peak Energy has announced that it expects to mothball all coal exports from 2016 through 2018. Two years ago, when international coal prices were high, Cloud Peak locked in a 10-year contract to ship 4 million tons of coal annually through the Westshore export terminal in British Columbia. The contract called for significant penalties if it didn’t provide enough coal shipping business. For two years, it has been shipping coal to Asia at a substantial loss, but with coal prices highly depressed, Cloud Peak has decided it is less costly NOT to export the coal and instead pay the export penalties. In the second quarter this year, Cloud Peak coughed up $11 million in penalty payments.
Montana regulators reject mine expansion over water concerns
October 2015: In a 4-1 vote, Montana’s Environmental Review Board has rejected an application to expand a coal mine over concerns about the long-term impacts on groundwater supplies. Signal Peak Energy had proposed expanding its coal mine near Roundup in the Bull Mountains by 7,100 acres in order to access 110 million tons of mineable coal. But after an appeal by a Montana conservation group, the state board agreed that the state Department of Environmental Quality did not do a sufficient job analyzing the impacts to groundwater and streams that supply homes and ranches nearby longer than 50 years from now.
Once mighty clean coal lobbying group beginning to crumble
September 2015: Reflecting Big Coal’s unending financial woes, the industry’s most prominent “clean coal” lobbying firm is slashing its staff and reorganizing. The American Coalition for Clean Coal Electricity, founded 22 years ago, is laying off its chief of staff and cutting middle-management positions. It is also trying to get out of its expensive downtown DC office lease. In recent years, utility stalwarts such as MidAmerican, DTE, Duke and First Energy have dropped out of ACCCE, leaving railroads and coal producers as its main members. “Like many of our members, we are facing tough times that necessitate tough decisions on how best to effectively operate,” the group’s CEO, a former chairman of the Republican National Committee, said in a statement Monday to POLITICO.
Chinese coal company axes 100,000 workers to “stop bleeding”
September 2015: In the biggest layoff ever for China’s coal sector, a mining company has announced that it will lay off 100,000 workers in the last quarter of 2015, or 40% of its labor force. Heilongjiang Longmay Mining Holding Group said it was taking the action to “stop bleeding” in the company as the Chinese coal industry follows others globally in a steep descent.
Opposition grows against proposed Montana coal export railroad
September 2015: Two major voices have joined the chorus of opposition against a proposed railroad to connect Montana’s coal fields with export facilities in the Pacific Northwest. The Missoula, Mont. city council has asked the federal Surface Transportation Board to consider local health and environmental impacts of the proposed Tongue River Railroad, joining other communities who argue that additional coal trains would have severe local impacts. The Northern Cheyenne Tribal Council also has voted unanimously to oppose the railroad, citing concerns about damage to tribal culture and the environment.
Notre Dame to stop burning coal
September 2015: In response to Pope Francis’ plea for bold action to curb climate change, the University of Notre Dame has announced plans to stop burning coal within five years and to cut its carbon footprint by more than half in the next 15 years. Notre Dame plans to spend $113 million on renewable energy to reduce the university’s carbon emissions by 47,500 tons annually.
Coal divestment bill passes California state legislature
September 2015: A bill requiring California’s state pension funds Calpers and CalSTRS to sell their investments in coal companies has passed the Assembly. The bill would require the public employee pension funds, which manage a combined $476 billion in assets, to liquidate holdings in companies that generate at least half of their revenue from coal mining by July 2017. A spokesman said the bill would affect investments in about 20 to 30 thermal coal mining companies valued at approximately $140 million to $240 million. “Coal is losing value quickly and investing in coal is a losing proposition for our retirees,” said Senate President pro Tempore Kevin de Leùn, the bill’s author. “It’s a nuisance to public health and it’s inconsistent with our values as a state on the forefront of efforts to address global climate change.”
Lung Association Poll: Americans favor stricter smog standards
September 2015: An overwhelming majority of voters across the United States support updating standards to place stricter limits on air pollution, according to findings from a poll by the American Lung Association. In the poll of 871 voters nationwide, 73% said they support the EPA placing stricter limits on the amount of smog that industrial facilities including power plants, can release. The ALA noted that support for tighter smog limits is even stronger now than it was in a November 2014 poll, even after a multi-million dollar industry ad campaign opposing stricter regulations.
Alberta considers coal plant closures as an option to cut CO2
September 2015: Officials in Alberta, Canada will consider early closure of the province’s coal-fired power plants as an option for addressing climate change. At a conference in Edmonton, Alberta Environment Minister Shannon Phillips said the province’s government “will do the unexpected” to achieve CO2 reduction goals and that Alberta’s “credibility is crucial to our economic future” because “the rest of the world is looking to transition to a low-carbon economic future, with or without us.” Alberta is responsible for more than a third of Canada’s total greenhouse gas emissions.
Florida PSC OKs utility plan to buy coal plant and close it to save money
September 2015: The Florida Public Service Commission has approved an agreement that will allow Florida Power & Light to buy a coal-fired power plant it currently purchases energy from and close it to save money. FPL is under contract to buy power from the Cedar Bay Generating Plant in Jacksonville through 2024, at a current cost of more than $120 million a year, but the company has determined it can generate its own electricity at a much lower cost without coal. So its plan is to buy the plant and end its contract, dramatically ramping down operations and then closing the plant in the next few years. The phase-out, said FPL’s president and CEO, is expected to save FPL customers more than $70 million a year.
Minnesota’s 2nd biggest utility plots its future with far less coal
September 2015: Minnesota’s second largest utility told state regulators that it will continue to move away from coal-fired electricity over the next 15 years. Duluth-based Minnesota Power’s Integrated Resource Plan calls for ending coal-burning at its Taconite Harbor plant and taking other as-yet unspeficied coal capacity offline, as well as adding more wind, solar, hydro power and natural gas.
Planned coal port in India scrapped
August 2015: India’s largest engineering and construction company has scrapped a plan to develop a new port that would have processed imported coal for a proposed 2,000-megawatt power plant. The company, Larsen & Tourbo, publicly said the reason for pulling out of the project was the potential environmental impact on coastal reefs and mangroves at the proposed site.
Request to switch coal plant to gas comes with a $265 million price tag
August 2015: A plan to repower a power plant in New York with natural gas instead of coal is not financially sound and would harm ratepayers over the long term, according to an analysis by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis. The 60-year-old Cayuga plant in upstate New York has asked for approval from the New York Public Service Commission to repower the plant and increases rates to cover the cost of switching fuels. But IEEFA calculates that retooling the plant would require more than $265 million in subsidies from ratepayers over 10 years and possibly longer.
Chinese coal imports and demand for coal continue dropping
August 2015: Through July 2015, coal imports into China had fallen off 34% from the same time the year before, and prospects for a rebound are dim with projections for China’s manufacturing demand remaining well below average. Domestic coal production in China, down 10% in the first half of the year.
NY coal plant closing because it is no longer financially viable
August 2015: As projected by an analysis more than a year ago, the owner of a 380-MW coal-burning plant in New York has announced plans to retire the facility because it is no longer financially viable. NRG Energy said it will retire the C.R. Huntley plant outside Buffalo on March 1, 2016 because, a company spokesman told SNL Energy, sustained low natural gas prices and low energy margins “basically have made the plant unviable economically.” A study last year by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis predicted that that aging and inefficient plant would be shuttered because it would continue to bleed money.
French energy giant keeps promise to divest all its coal interests
August 2015: French energy giant Total has announced that it will no longer be in the coal production business after selling off a South African coal mining subsidiary. In a press release, Total’s CEO said his company “cannot claim to be providing solutions to climate change while continuing to produce or market coal, the fossil fuel that emits more greenhouse gas than any other.” The company will also divest from all of its coal marketing operations so that by the end of 2016, it will “no longer be involved in the coal business.”
‘Make the bad man stop’ — coal braces for dark earnings reports
July 2015: The second quarter of 2015 saw little change in the coal sector’s misfortunes, with more dire news expected from quarterly earnings reports in the coming weeks. One investment analyst penned a report titled “2Q15 Coal Preview: Make the Bad Man Stop.” SNL Energy reported “disappointing” announcements from a number of companies in advance of earnings calls and projected that many producers will hit new share-price lows this summer. The total combined market capitalization of publicly traded U.S. coal companies, according to a June analysis by SNL, had sunk to under $13 billion, down almost 50% from June 2014 and down more than 80% since April 2011.
graphic – http://bit.ly/1Krstng
Analysis: Majority of U.S. export coal is uneconomic at current prices
July 2015: Approximately 80% of U.S. thermal coal exports and 98% of Appalachian metallurgical coal exports are uneconomic at current prices, a new market research report has concluded. Factors affecting U.S. coal producers, Morgan Stanley said, include cheap natural gas prices, tight regulations and declining commodity prices.
Miss. utility must refund $350 million for over-budget coal plant
July 2015: The Mississippi Public Service Commission has ordered the state’s biggest utility to refund $350 million to customers for illegal rate increases to pay for construction of a new coal-burning power plant. Mississippi Power’s Kemper plant has faced numerous delays and is nearly $4 billion over budget. The utility raised rates by 18% in 2013 to cover spiraling costs, but the Mississippi PSC said the company now must return that money, which will amount to $500-$600 for an average residential customer.
Minn. utility agrees to stop burning coal, close Lake Superior plants
July 2015: A Minnesota utility has decided to stop burning coal at two power plants on Lake Superior’s North Shore as part of a legal settlement. Minnesota Power will first idle its Taconite Harbor power plants in 2016, giving it flexibility to restart them if needed to maintain electric reliability, then close them completely by 2020. Lost power from the plants will be replaced with a combination of renewable energy sources, natural gas and other coal resources, in equal amounts.
NYSE delists Alpha Coal as stock price sinks to junk status
July 2015: The New York Stock Exchange has decided to remove coal producer Alpha Natural Resources from its listings because of the company’s “abnormally low” price indi cations. Prior to the delisting, Alpha’s stock last traded at 24 cents. Some analysts project that the company could soon join other coal producers that have already filed for bankruptcy this year.
Bond market the latest to snub coal
July 2015: In another sign of how bad market conditions have become for the coal sector, one of its few remaining financial safety nets has also started to unravel. Historically, coal producers have been able to turn to relatively safe bonds, which fluctuate less than stocks, to raise money for new mines and environmental cleanups. But investors are becoming increasingly reluctant to lend them even that. Coal bond prices tumbled 17% in the second quarter of 2015, according to an analysis by Bloomberg, the fourth consecutive quarter of price declines and the worst performance of any industry group monitored.
$3 billion in debt, Alabama coal producer files for banckruptcy
July 2015: Birmingham, Ala.-based coal producer Walter Energy has filed for bankruptcy after accumulating more than $3 billion in debt and annual interest payments of $264 million. The company, which mainly produces metallurgical coal, is “rapidly losing cash” and at risk of exhausting its liquidity by the end of 2015 because of its heavy debt and declining markets for its coal, the company’s CFO said in its Chapter 11 bankruptcy documents. Walter hasn’t posted an annual profit since 2011. In May, the company issued notices to 370 employees at four mines it operates that they would be laid off.
Fitch Ratings sees trouble for coal companies with self-bond problems
June 2015: Fitch Ratings said it anticipates additional bankruptcies and restructuring as a result of tighter restrictions on coal producers’ ability to self-bond for cleaning up mines. Self-bonding allows financially sound coal companies to cover reclamation costs on mined land without having to buy expensive insurance. In an analysis, Fitch noted that coal companies are losing their ability to qualify because their finances are so poor. Losing the ability to self-bond “would reduce liquidity and could hasten restructuring,” Fitch said.
Peabody removed from S&P 400 index
June 2015: Stung by a coal divestment bill in the California Legislature, Peabody Energy, the world’s biggest coal mining company, has been removed form the S&P MidCap 400 stock index. Peabody wa added to the bellwether S&P 500 in November 2006, when the company was worth about $10 billion. Its value had fallen 60% when it was dropped to the less prestigious S&P 400 MidCap in September. And when it was removed from that index June 24, its market cap was about $688 million.
Former employee sues Arch Coal for lost retirement plan value
June 2015: In addition to mounting financial woes, Arch Coal is now facing a class action lawsuit from a former employee who claims the finance committee of Arch’s board harmed workers retirement by continuing to grow retirement holdings in the company even as they knew stock prices were on a downward spiral and “no longer a prudent investment.” In spring 2011, Arch was worth $5.8 billion. The company’s value is now a fraction of that at $108 million. Yet during the slump, even as “experts and analysts saw little to no hope for the coal markets to rebound,” the company and its advisors doubled the number of shares in the employee thrift plan. The lawsuit, according toa story in SNL Energy, asks the court to require Arch to “make good” on losses to the worker retirement plan.
Clean-up insurance questions send big ripples through coal stocks
June 2015: Questions about the coal industry’s financial ability to cover clean-up costs and possibly having to buy expensive insurance on the open market have sunk already depressed stock values even lower for U.S. producers. Stocks for both Peabody Energy and Arch Coal sank to all-time lows in trading as officials in Wyoming review data to determine if the companies are financially healthy enough to qualify for self-bonding. Another company facing bonding doubts, Alpha Natural Resources, fell to within a penny of its all-time low. “Investors don’t know how to handicap this self-bonding issue,” one stock analyst tol Bloomberg. “Until the companies come out and give Wall Street certainty that they know how to deal with it, I think we’re going to be stuck in this vortex.”
BC coal export terminal reports dismal 2014; 2015 looks even worse
June 2015: The Ridley coal export terminal in British Columbia suffered through a dismal 2014, according to its annual report, and unfortunately for the operator, this year is shaping up to be even worse. The amount of coal unloaded by trains at the terminal dropped of 41% from 2013 to 2014 and net profit sank by almost 60%. Business has been even slower this year, with total exports sinking another 46% in the first four months of this year compared to 2014’s already bleak totals. The port’s COO understatedly said in the report that depressed coal prices, coal mine closures and the disappearance of key customers presented “a threatening development.”
Peabody lays off 250 corporate staff
June 2015: As part of a major cost-cutting initiative, Peabody Energy, the largest coal company in the world, is cutting 250 corporate jobs and closing the company’s office in Gillette, Wyo. The layoffs amount to roughly 25 percent of the St. Louis-based company’s corporate and regional support positions.
Federal officials are scrutinizing coal companies’ clean-up insurance
June 2015: As a result of slumping coal prices that have gutted coal industry balance sheets, federal regulators are taking a closer look at rules that allow coal producers to self-insure to cover the costs of cleaning up old mines. A spokesman for the Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement told Reuters that the agency is examining “all aspects of bonding and self-bonding.” Federal rules require a certain ratio of liabilities to assets in order for a coal producer to be able to self-bond, but the ailing financial health of coal producers cast doubt on whether companies such as Peabody, which reported a $787 million loss in 2014, qualify to cover clean-up costs themselves. Without self-bonding, coal companies would have to pay far higher market rates to insure the billions of dollars required to reclaim old mines and the surrounding landscapes.
PacifiCorp’s future has less coal
June 2015: One of the West’s largest utilities has mapped out a future that details “a gradual, orderly transition away from coal.” Under PacifiCorp’s updated integrated resource plan, by 2025, the company, which serves 1.8 million customers across six states, will cut coal use from 60% of its generation portfolio to only 50%, while electricity from natural gas and renewables will increase. “Coal is an increasingly challenged fuel source,” Robert Godby, an energy economics professor at the University of Wyoming, was quoted saying in the Casper Star Tribune. “That regulation makes coal power more expensive at a time when natural gas and renewable generation has become cheaper. You add to that potential future regulations and you can you see why a company would not be investing in coal.”
Judge to OSM: assess climate impacts of burning coal from Colo. mine
May 2015: A federal judge in Denver has given a northwest Colorado coal mine 120 days to redo an environmental analysis for a proposed mining expansion and take into account the climate impacts of burning coal mined from the project. U.S. District Court Judge R. Brooke Jackson said the BLM’s Office of Surface Mining, which oversees permitting for coal mines on federal land, should have considered greenhouse gas emissions from burning the estimated 12 million tons of coal before “rubber-stamping” revised permits for the expansion of the Colowyo Mine, which feeds the nearby Craig power plant. If the OSM “can predict how much coal will be produced, it can likewise attempt to predict the environmental effects of its combustion,” the judge wrote in his ruling.
Mississippi electric co-op backs out of deal for high cost coal power
May 2015: Citing soaring costs and lack of value for its customers, a Mississippi electric cooperative has backed out of its planned contract to buy output from the beleaguered Ratcliffe coal-fired power plant being built by Mississippi Power in Kemper County. The South Mississippi Electric Power Association, which had planned to buy 17.5% of the plant’s power, said its board voted to back out of the deal with owner Mississippi Power because of delays, cost escalations and “changing needs.” Mississippi Power has submitted three rate-increase proposals to the state Public Service Commission that would raise average rates $34-$37 per month to help pay for the coal plant, which is several billion dollars over budget. The utility already has been ordered to return earnings from a previous rate increase to customers following a court ruling against it.
Senate bill would overhaul ‘broken’ federal coal leasing program
May 2015: U.S. Sen. Edward Markey has introduced legislation that would modernize the Department of Interior’s federal coal-leasing program by forcing coal producers to pay fair market value for the coal they mine from public lands. The Coal Oversight and Leasing Reform Act (S. 1340) would end noncompetitive leasing and close other loopholes that cost taxpayers hundreds of millions of dollars in lost revenue each year. It also would put a temporary moratorium on new coal lease sales until the reforms have been enacted. “The federal coal program is rife with sweetheart deals, outdated regulations and mine-sized loopholes,” Markey said in a statement. A copy of the COAL Reform Act is available online HERE.
Alpha may have to come up with $411 million to cover reclamation bond
May 2015: Officials in Wyoming have informed one of the nation’s largest coal mining companies that it no longer meets self-bonding requirements to cover the costs of reclamation on mined lands. Alpha Natural Resources will likely have to come up with $411 million by late August to ensure it financial obligations for reclamation in Wyoming or face violations from the state.
Bank of America will limits its financial exposure to coal’s risks
May 2015: In a bow to the mounting financial risks of coal and pressure from divestment proponents, Bank of America announced at its annual meeting that it will reduce its financial exposure by cutting back on lending to coal extraction companies and coal divisions of broader mining companies. Rainforest Action Network Climate, one of the groups that pressured Bank of America on this issue, said the bank had come a long way in since 2011, when it was one of the biggest bankrollers of the coal industry.
Hedge funds shed their coal holdings
May 2015: An analysis of financial filings by SNL Energy shows that a number of major U.S. hedge funds have dumped their coal equity holdings as stock values have plummeted. Fund managers such as Highbridge Capital, Soros and Tudor Investment have liquidated millions of shares in U.S. coal companies in the last quarter. According to SNL, common stock holding in coal producers held by seven major hedge funds fell by almost 31% from the last quarter of 2014 to the first quarter of this year. The funds’ stock ownership in coal companies is at the lowest level since at least the beginning of 2012.
Patriot Coal files for bankruptcy for second time in three years
May 2015: With more than $1 billion in liabilities, Patriot Coal has filed for bankruptcy, the latest company to do so as slumping markets continue to hammer the coal sector. Patriot officials said they are in negotiations to sell off almost all of the company’s assets. According to a report in Bloomberg, since 2012, at least a half dozen other coal producers also have filed for bankruptcy protection, including Longview Power, Dynegy, Edison Mission Energy and James River Coal, some of them, like Patriot, are doing so for the second time.
DOJ prosecution of Duke coal ash violations should ‘terrify’ utilities
May 2015: The U.S. Justice Department’s prosecution of Duke Energy and three of its subsidiaries for illegally managing their toxic coal ash ponds sends a clear warning to other utilities about the massive waste stream’s financial risks. Duke pleaded guilty to nine criminal violations of the Clean Water Act. Duke and its subsidiaries were fined $102 million and required to set aside $3.4 billion for cleanup costs related to the 2014 Dan River coal ash spill and potential problems at 18 other plants. Experts interviewed by Inside Climate News said the crackdown will force other utilities to take coal ash seriously. The Justice Department’s coal-ash crackdown, said Vermont Law School professor Patrick Parenteau, “brought down the biggest utility in the country; It should terrify other utilities. If Duke’s not safe, nobody’s safe.”
Norway to divest up to $10 billion from coal and utility companies
April 2015: In the most striking move yet for the fossil fuel divestment effort, Norway’s parliament has agreed to pull up to $10 billion of investments out of both coal mining companies and coal-fired utilities. Norway’s pension fund had previously divested from coal producers, but the new policy also withdraws investments from utilities that get more than 30% of their power from burning coal. “It sends a clear message to investors that we don’t want the fund to invest in coal and that Norway is in the forefront of developing climate risk criteria,” Labour party finance committee member Torstein Solberg was quoted saying in the Financial Times.
UN climate chief tells Australian officials: “no space for new coal”
May 2015: At meetings in Australia, the director of the United Nations’ climate program said that new coal cannot be a part of the global energy picture and stressed the importance and benefits of setting ambitious renewable energy targets. According to an official communique from the meeting, Christiana Figueres, the executive secretary of the United Nations framework convention on climate change, said “the science is clear that there is no space for new coal or unmitigated coal.”
8 in 10 Chinese coal producers lost money in first two months of year
April 2015: Like their counterparts in the United States, Chinese coal companies are struggling amid shifting energy markets that have dramatically decreased demand for coal. The China National Coal Association reported that 71 out of 90 major coal producers in the country lost money in the first two months of 2015 and that producers were cutting or even defaulting on wages to cut costs during the slump. “It’s impossible for the coal industry to go back to the previous good days,” the South China Morning Post quoted one coal industry executive saying.
Church of England pulls its investments out of coal, tar sands
April 2015: The Church of England has announced it will cease investing in coal- and tar sands-related companies. Under a new policy on climate adopted recently by the Church’s Ethical Investment Advisory Group, its commissioners and pensions board decided to divest £12 million (about $18.3 million) from any company that derives more than 10% of its revenues from coal or the production of oil from tar sands. “From an ethical perspective, the focus of the investing bodies must be on assisting the transition to a low carbon economy. The Church has a moral responsibility to speak and act on both environmental stewardship and justice for the world’s poor who are most vulnerable to climate change,” said The Rev. Canon Professor Richard Burridge, deputy chairman of the EIAG.
Utah’s dirty coal faces off against the state’s lucrative tourism
April 2015: Coal-fired power is running up against competing economic interests in Utah as the EPA considers how to cut hazy pollution that regularly clouds five popular and lucrative national parks in the state. In comments to the EPA, the National Park Service said “the state clearly values the importance of the five national parks in Utah and actively promotes national tourism, yet at the same time it appears unprepared to fulfill its legal requirements under the Clean Air Act and associated regulations to protect and enhance the very scenic views that attract millions of visitors to the parks every year.” The five parks in Utah – Zion, Bryce Canyon, Arches, Canyonlands and Capitol Reef – drew 7 million visitors in 2014, generating $730 million in economic impact, according to a recent study.
CEO: a number of coal companies will fail in the coming months
April 2015: Investors expect the U.S. coal industry to end the first quarter in another disappointing round of earnings reports as the sector “continues to take a beating from challenges that range from new emissions regulations and transportation snags to increasing difficulty in competing against other fuel sources,” according to insight from SNL Energy. Of 12 large public coal companies it covers, SNL said six are expected to report a loss per share to investors and none will report earnings of more than a dollar per share. “Under the present situation, you will see a number of America’s coal companies financially fail in the months ahead. This is the most dangerous time that I have observed in the coal industry in my 58-year career in it,” SNL quoted Murray Energy President and CEO Robert Murray saying at a coal conference.
Risks drive investment managers to boost their fossil-free portfolios
April 2015: A survey of financial professionals in the U.S. indicates that there is a strong and growing interest by portfolio managers to invest in low-carbon and fossil-free assets. In fact, the number of investment advisors offering fossil fuel-free portfolios to clients nearly doubled from 2013 to 2015, up from 22% to 42%, according to the survey of more than 500 socially responsible investment advisors, asset managers and institutional investors by First Affirmative Financial Network. More than three-quarters of the respondents said decisions to divest portfolios of coal and other fossil fuels is a result of growing financial risks associated with carbon-intensive industries, and 61% said they are concerned about “stranded asset” risks created by climate change.
Regulators say proposed rate hike for coal is not fair or reasonable
April 2015: With two of its four units already slated for closure, the San Juan Generating Station in New Mexico faces another hurdle as the state’s Public Regulation Commission has recommended rejecting a request by the plant’s owner to raise rates. PNM has proposed buying an increased percentage of the output from the remaining two units and has requested a rate hike that would result in nearly a $10 month increase to the average residential bill to cover the costs. But the PRC said the plan “is not fair, just and reasonable and in the public interest.” A hearing examiner said the risks of the plan “significantly exceed the dollars saved. … PNM’s increasing ownership and responsibility for San Juan may pressure PNM to continue to act as the owner of last resort, absorbing exiting owners’ shares to protect its investment even if the plant has become uneconomic in a version of the ‘too big to fail’ syndrome.”
Utah coal plant closed to avoid added expense of mercury controls
April 2015: In a surprise move, the owners of Utah’s oldest coal-burning power plant have closed its doors rather than incurring the expenses of complying with stricter new federal mercury-pollution rules. Rocky Mountain Power said the age and location of the 172-MW Carbon Power Plant in a tight canyon made retrofitting the 60-year-old facility too costly. The plant will maintain a workforce of about 45 over the next two years while the plant is dismantled, and the rest of the plant’s 74 employees will be transferred to other power plants in nearby Emery County. Carbon’s capacity will be replaced by a 545-MW natural gas-fired.
Weak finances may force Alpha to buy costly clean-up insurance
April 2015: Officials in West Virginia and Wyoming are considering how to address the struggling finances of Alpha Natural Resources, a major coal producer in both states. The company, which reported a loss of $875 million last year, may not have the money to clean up its mines. Typically, companies with strong financials are allowed to “self-bond” to cover reclamation costs, but Alpha’s financial position is so weak that it may have to buy additional insurance to cover its clean-up liabilities. In Wyoming, Alpha is on the hook for $411 million in cleanup costs at two mines, and in West Virginia, it has $262 million in obligations. Premiums for insurance could cost Alpha upward of $10 million a year, an added cost that the company said could lead to a “significant decline in our financial position” and hurt its creditworthiness.
Poll: Americans offended by federal coal subsidies and want reforms
April 2015: A majority of Americans support reforms to federal coal leasing, according to new polling. In a survey of more than 800 voters nationwide, 69% supported requiring mining companies to pay royalties on the price at which they sell coal, rather than the price at which it is sold to subsidiaries or middlemen. Nearly two-thirds also reacted negatively to hearing that the federal government provides subsidies to coal companies to mine on public lands, and they favored ending them by nearly a two-to-one margin, 53% to 29%. “A strong majority of Americans say the government should be better defending their interests as taxpayers by collecting every dollar of coal royalties that are owed,” said Geoffrey Garin, president of Hart Research Associates, which conducted the poll.
Goldman Sachs reportedly shedding unprofitable coal mines in Columbia
April 2015: Goldman Sachs is in talks to sell two beleaguered coal mines it owns in Columbia at a loss, according to reports. The financial company bought the mines in 2010 and 2012, but environmental and labor issues at both mines, along with a highly depressed global coal market, leave their profitability in doubt. “It now appears that Goldman has had enough,” a story in the Wall Street Journal (subscription required) said. “The firm is in talks to sell the coal mines at a loss, according to people familiar with the negotiations.” According to SNL Energy, Goldman Sachs’ ownership of the mines amid the volatility of global coal markets prompted scrutiny from a U.S. Senate subcommittee, with members expressing concern that severe enough losses might require intervention from the Federal Reserve or a taxpayer bailout.
Mountain towns want coal companies to pay fair share for climate impacts
April 2015: Officials from 10 Western mountain towns are demanding reforms to the royalty system for coal mined from federal land. The towns – eight in Colorado and one each in Utah and New Mexico – wrote to Interior Secretary Sally Jewell saying they are being cheated out of hundreds of millions in royalty payments a year by a system that allows mining companies to sell coal from federal lands cheaply to themselves to avoid paying higher royalties. Half of the money raised by coal royalties goes back to local communities, and the towns say the money is needed to help them cope with the economic impacts of global warming. “The costs of adapting to a changing climate are rising,” the towns wrote, “but at the same time coal companies are taking advantage of gaping loopholes that allow them to pay less, thus depriving many Western states and taxpayers across the country their fair share of the revenues from coal leased on federal land.”
Moody’s analyst: Subsidizing coal in Ohio “a big credit negative”
March 2015: At a coal financing conference earlier this month, an analyst for Moody’s Investor Service told attendees that efforts by regulators in Ohio to subsidize aging and increasingly costly coal-burning power plants by passing costs to customers could actually harm utility credit, according to coverage provided by one of the sponsors. If the Ohio Public Utilities Commission moves forward with the plan, said Jim Hempstead, the associate managing director in the Global Project and Infrastructure Finance Group at Moody’s, “then we actually think that’s a big credit negative for everybody in Ohio, because they’re taking a step back … That is not transparent, that is not stable, that is backtracking.” Hempstead was speaking on a panel at the conference sponsored by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis.
Scottish coal-burning plant to close after losing contract to natural gas
March 2015: A coal-burning power plant in Scotland that is one of the most polluting in Europe will be retired in March 2016 after losing out in competition to secure a valuable and much-needed electricity supply contract. Built in 1973 and now inefficient, the Longannet plant is responsible for nearly a fifth of Scotland’s total carbon emissions, according to a story in The Guardian. The plant was outbid for the short-term contract by a newer natural gas-fired plant.
After years-long fight, tiny island of Mauritius says no to new coal plant
March 2015: The government of the tiny island of Mauritius, off the east coast of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean, has abandoned plans to build a controversial 115 MW coal-burning power plant. Officially, the government said it would “consider other feasible options, with necessary transparency and clarity, to meet electricity demands for the period 2015-2019 and ensure energy security for Mauritius,” but realistically, the decision ends plans for the plant, which faced stiff local opposition for the past nine years while the project was being planned.
Like a bad birthday, 2015 to leave coal “another year older, deeper in debt”
March 2015: In commentary on new coal supply data released by the U.S. Energy Information Administration, the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis says the coal industry is looking at being “another year older and deeper in debt.” EIA projects coal production to decline by 20 million tons this year and prices to remain flat as demand for coal shrinks in the face of competition by renewables and natural gas. This, says the IEEFA’s Tom Sanzillo, will leave most U.S. coal companies “posting losses or incurring extraordinary costs related to speculative ventures.”
The last of Beijing’s four coal-burning plants set for closure in 2016
March 2015: In yet another bid to clean up Beijing’s heavily polluted air, China has announced that it will close the last of four major coal-fired power plants in the city next year. One plant was closed last year, two earlier this month and the last, an 845-MW plant, will close in 2016. The plants will be replaced by four natural gas-fired stations. The closures are expected to decrease annual coal combustion by 9.2 million metric tons in Beijing, where pollution averaged more than twice China’s national standard last year. “Most pollutants come from burning coal, so the closure will have a clear impact to reduce emissions,” Bloomberg quoted an analyst saying. China is the world’s top consumer of coal, and nationwide, the country is aiming to cut consumption by more than 80 million tons by 2017 and more than 160 million tons by 2020, according to Reuters through efficiency measures, under the 2015-2020 plan from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology.
Financial think tank says U.S. coal sector is in ‘terminal decline’
March 2015: With 26 coal producers going bankrupt in the past three years, 264 mines closed between 2011 and 2013 and the coal sector losing 76% of its value in the past five years, coal in the U.S. is in a “terminal decline” that will leave investors with billions of dollars in stranded assets, according to a report from a financial think tank. The Carbon Tracker Initiative argues that the coal industry is overvalued and has reached a “carbon bubble,” with stricter regulations and competition from cheaper gas and renewables making coal less and less valuable. “The roof has fallen in on U.S. coal, and alarm bells should be ringing for investors in related sectors around the world. These first tremors are amongst the clearest signs yet of a seismic shift in energy markets, as high carbon fuels are set to be increasingly outperformed by lower carbon alternatives,” said Andrew Grant, a co-author of the report. CTI also noted that coal’s rapid decline happened amidst the Dow Jones industrial average actually increasing 69% over the same period, indicating that U.S. economic growth has “decoupled” from coal, a pattern that is spreading across the globe. “The collapse in the share prices of the U.S. coal sector 2011-14 is an illustration of how markets can punish investors in a climate-constrained world where lower carbon technology is developing rapidly,” said Mark Fulton, research advisor to Carbon Tracker and formerly head of research at Deutsche Bank on climate.
China aims for ‘zero-growth in consumption of coal’ in some regions
March 2015: In its continuing effort to battle air pollution, China is strengthening its commitment to cutting the country’s reliance on coal. In it annual report, China’s National Development and Reform Commission said it would implement policies aimed at reducing coal consumption and also that it would aim to replace lost coal capacity with alternative energy sources. In outlining China’s plans fight pollution, Chinese Premier Li Keqiang told parliament country “will strive for zero-growth in the consumption of coal in key areas of the country. … Environmental pollution is a blight on people’s quality of life and a trouble that weighs on their hearts.”
Bank tightens restrictions for lending to MTR coal producers
March 2015:A Pennsylvania-based Bank has ratcheted up restrictions to its corporate lending policies to companies that engage in mountaintop removal coal mining. In 2010, PNC Bank decided to stop financing companies that for whom mountaintop removal accounts for more than 50% of their coal production. Under the new policy, the bank will no longer lend to coal producers who get 25% or more their production from MTR. At the end of 2014, banks including JP Morgan, Wells Fargo, Goldman Sachs, RBS and UBS also pledged to move away from financing MTR coal projects.
Indiana officials revoke permit for planned coal gasification plant
March 2015: State officials in Indiana have revoked the air permit for a proposed coal gasification plant near Rockport, all but ending prospects for the $2.8 billion plant. The Indiana Department of Environmental Management rescinded the permit, which was issued in 2012, after getting a request from the project’s financer. The project had already been granted a one-year extension for construction to begin, which would have required work to start by June. Opponents said the plant, which had guaranteed contracts with the state to buy synthetic natural gas from the plant, would have cost Indiana utility customers more than a $1 billion over the plant’s first eight years of operation.
Oslo becomes first international capital to divest from coal
March 2015: On the heels of a demonstration in February by more than 1,000 climate activists, Oslo, Norway has committed to selling off all of its investments in coal companies, and in doing so, becomes the first international capital to take a bold stand on fossil fuel divestment. Although its holdings total only $7 million, Olso’s finance commissioner said that coming from a capital city, the move sends a clear signal. “We are pulling ourselves out of coal companies, because power generation based on coal is one of the most environmentally harmful in the energy sector. We want to use our investments to promote more environmentally-friendly energy and a more environmentally-friendly society.” More than three dozen other cities around the world, including San Francisco and Oxford, England, have also committed to divesting from their fossil fuel stock holdings, as have almost 200 institutions, whose collective investments total around $50 billion.
Feds ordered to assess power plant pollution for coal mine expansion
March 2015: As if coal mining didn’t have enough problems to deal with, a federal judge has ruled against a mine expansion on Navajo land in New Mexico because officials failed to assess the impact of pollution from a power plant in their review. U.S. District Court Judge John Kane said that the federal Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement now has to review not only the direct environmental impacts of the expansion at the Navajo Mine, but also impacts from burning coal from the mine in the adjacent Four Corners Power Plant, one of the biggest and dirtiest in the country. “Given the potentially significant impacts of mercury pollution, OSM’s failure to discuss or analyze the deleterious impacts of combustion-related mercury deposition in the area of the Four Corners Power Plant is troubling,” the judge wrote in his opinion. He ordered stakeholders to come up with an agreement over how to factor in pollution from the plant in the environmental assessment for the mine expansion.
State Bank of India to reject $1 billion loan for Aussie coal mine
March 2015: The State Bank of India is expected to renege on a previous agreement and turn down a request for a $1 billion from a company that wants to build a massive coal mine in Australia. Adani Enterprises had secured a preliminary deal for a loan in November for the $16.5 billion mine in Queensland, but according to a report from Reuters, a source said the loan will be rejected because of coal’s low prices and a dismal market. “The credit guys are not comfortable with the project,” the source said. “Nothing is moving on that project.”
Bank of America Merrill Lynch report: ‘Coal Bites the Dust’
March 2015: Coal supplies worldwide remain over-stocked, and with little chance of the glut being alleviated, SNL Energy reports that Bank of America Merrill Lynch has lowered its expectations for the price of coal exports for the next two years. In a report titled “Coal bites the dust,” the finance giant predicted a bearish coal market through 2016 and slashed its forecast for thermal coal prices. In Australia, it predicted a drop of 12% to already rock-bottom prices, lowering its forecast from $65 per ton to $57 per ton this year. The drop was even bigger for Newcastle thermal coal prices, which the company slashed 28%, from $72 per ton to $52 per ton. “[Coal] stocks are high virtually everywhere and the demand picture is looking bleak from the United States to China,” the report said.
Analyst: 17% of U.S. coal production is uneconomic in today’s market
March 2015: Energy and mining analysts at Wood Mackenzie say that around 17% of the coal production forecast for this year in the United states is “unprofitable” in today’s market, the equivalent of 162 million tons. With so much coal being mined without turning a profit, or even at a loss, the analysts said, there are increasing risks of more mines being idled or closed. Years of declining productivity, thinning seams, new regulations and a high-paid workforce make Central Appalachia the region with the highest costs, leaving almost three-quarters of its total coal output unprofitable.
Florida utility says it will save money by buying coal plant and closing it
March 2015: Florida’s biggest utility has announced its intention to buy a relatively new coal-burning power plant and then shutter it. Florida Power & Light, which serves 4.7 million customers, is currently in a long-term contract to buy power from the 250-MW Cedar Bay Generating Plant in Jacksonville, but the company says that buying the coal plant for $520 million and closing it down to switch to other energy sources will cut costs by $70 million. If the plan is approved by state regulators, the plant will operate at only 5% capacity through this year and next, then close for good in 2017. “Customer savings will diminish if the closing is delayed,” the company said.
Coal producers abandon two major mine proposals in the West
March 2015: Two coal producers have abandoned major projects in the West this year, both citing the weak global market for coal as the main culprit in their decisions. Kentucky-based Rhino Resources has announced it is scrapping plans to develop the Red Cliff mine near the Colorado-Utah border. The company said it will record a $22.2 million loss on the project, which was first proposed for leasing in 2006. In Wyoming, Arch Coal has withdrawn a lease proposal to the BLM to mine 6,000 acres in the Powder River Basin that contain approximately 1 billion tons of coal. The company said weak economic conditions were behind its withdrawal of the West Jacobs Ranch lease application.
2014 was another bleak year for employment in America’s coal mines
March 2015: Employment in America’s coal mines continued its long slide in 2014, with the sector shedding another 6% of its workforce last year and 21% since 2011, according to an analysis by SNL Energy. There were about 75,030 employees working in coal mines in 2014, down 4,800 from the year before. Central Appalachia has been hardest hit by dismal coal market conditions, with employment down 13.1% from last year.
Dragged down by coal, FirstEnergy desperately looks to bailout in OH
March 2015: With a failing business model “dominated by obsolete coal-fired generation that is struggling to compete,” FirstEnergy is asking Ohio regulators to allow it to charge customers higher-than-market prices for electricity. The proposal by FirstEnergy is a last-ditch effort to survive, and according to a critique by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis, likely to fail given recent decisions in Ohio, which could force the company, the nation’s largest investor-owned utility, to sell its entire merchant-generation business. FirstEnergy’s net income has spiraled fallen off by $570 million since 2011, its earnings per share are at the lowest point in a decade and long-term debt ballooned by 20% to $19.2 billion in just the past year, IEEFA noted.
“Soft market” keeps Koch-owned Colorado coal mine shuttered
March 2015:The owners of a Colorado coal mine that was idled just over a year ago have said there are no plans to reopen the mine because “the marketplace for coal is so soft.” Once one of the most productive underground coal mines in the nation, the Elk Creek mine near Paonia, which is owned by Bill Koch-controlled Oxbow Mining, was shuttered following a mine collapse and underground fire that started in 2012. Oxbow laid off 150 employees in December 2013. The company’s executive VP also said the dour coal market was keeping plans for its proposed Oak Mesa coal mine in Colorado on hold.
Federal court rejects proposal to expand New Mexico coal mine
March 2015:A federal district judge has rejected a 2012 Office of Surface Mining plan to expand coal production at a mine in northwestern New Mexico. The plan would have allowed strip mining of 12.7 million tons of coal at the 13,000-acre Navajo Mine near the San Juan River, but U.S. District Judge John L. Kane said the OSM ignored harms that would result from the mine expansion including toxic mercury pollution that would be emitted from when the coal is burned at the nearby Four Corners Power Plant, one of the most polluting plants in the United States.
Coal producers cutting losses as “horses bolt the burning barn”
March 2015: The restructuring last week of global mining giant Rio Tinto and the loss of its chief coal executive are the latest signals that industry sees no prospect for improvement in a bleak global coal market, according to an industry analyst. Tim Buckley, director of energy finance studies in Australasia for the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis, points to a steady string of ominous developments for coal: BHP spinning off mines to cuts its exposure to coal in half; Rio Tinto writing off coal holdings in Mozambique and its sale of a coal mine in Queensland, Australia; Peabody Energy slashing capital expenditures by 80% from three years ago. “Five of the world’s largest mining conglomerates are rapidly reducing their coal exposure as the horses bolt the burning barn,” Buckley said.
World public health associations: divest assets from coal
February 2015: Among the initiatives agreed to by delegates from 70 countries at the 14th World Congress on Public Health on Feb. 15 in Calcutta were several initiatives calling for an end to the use of coal and fossil fuels. In its call to action, the World Federation of Public Health Associations said climate change poses a “profound threat to human health” singling out coal as a key contributor to global warming. The association called for: a rapid phase out of coal for electricity production and greater investment in renewable energy technologies; and for public health associations to divest their assets from fossil fuel companies.
Miss. Supreme Court says rate hike to pay for coal plant was illegal
February 2015: In a 5-4 ruling, the Mississippi Supreme Court has determined that the state’s largest utility must return more than $200 million to customers whose rates were increased to pay for the spiraling costs of a new coal-burning power plant. Mississippi Power’s 582-megawatt Kemper plant was designed as to capture carbon emissions, but its construction has been plagued by delays and cost overruns that have more than doubled the initial price tag of $2.8 billion to nearly $6.2 billion. Ratepayers already have been hit with an 18% rate hike to pay for the original cost. But in a strongly worded opinion, the court ruled that the state’s Public Service Commission agreed behind closed doors to raise rates further, saying the secret deal violated the public trust and in no way could be considered “fair, just, and reasonable.” “The public has a right to see and hear its business being conducted,” the justices said.
Rejected: AEP plan to guarantee income from coal-burning plants
February 2015: The Ohio Public Utilities Commission has denied a controversial request by American Electric Power give it the ability recover costs from customers in order to guarantee income from old coal-burning power plants that are too expensive to operate in a competitive market. In a unanimous decision, the PUC said the proposal did not provide any benefit to consumers. “We are not persuaded that the (coal-plant proposal) would, in fact, promote rate stability, as the company claims, or that it is in the public interest,” the panel said.
Falling natural gas prices are the latest nail in the U.S. coal coffin
February 2015:Already low natural gas prices that have fallen dramatically since mid-2014 are but one of the factors hammering at the coal industry, according to an in-depth report in the Financial Times. Natural gas prices have dropped from a peak of $4.67 per million BTU last June to $2.67 this month. The perfect storm against coal, which includes a coal glut, declining exports and tightening regulations on power plant emissions, is leaving coal producers in critical condition. “I think you’re going to see multiple bankruptcies in US coal over the next 12-18 months. The outlook isn’t good: the outlook is getting worse,” Nomura analyst Curt Woodworth is quoted saying in the piece.
Coal use drops in China despite its growing economy and energy appetite
February 2015: Coal use in China decreases by 2.9% last year from 2013, according to data published by the Chinese government, confirming analysts projections that the world’s largest nation is changing course on energy. The drop in coal use occurred despite the Chinese economy growing by 7.4% and the country’s overall energy use increasing 2.2%. In fact, coal was the only major energy source that was used less than in 2013.
Layoffs and mine closures in W.V. as global coal slump lingers
February 2015:Alpha Natural Resources, one of the United States’ top coal producers, is idling three coal mines in West Virginia and laying off 91 workers as the coal industry continues its deep slump. About 1.5 million tons of thermal coal were mined from the facilities in 2014. The mine closures, said a company representative, were a result of “persistent weakness in U.S. and overseas coal demand and depressed price levels, along with regulatory pressures contributing to the premature retirement of coal-fired power plants across the nation.”
Study: EPA’s Clean Power Plan does not pose a threat to reliability
February 2015: The EPA’s proposed Clean Power Plan, which would cut carbon emissions from power generation 30% from 2005 levels by 2030, will not jeopardize the reliability of the country’s power system, according to a study by the Analysis Group. Although the plan is flexible and will leave implementation up to the states, cutting the use of coal will likely be one of the key tactics for achieving the plan’s emission reduction goals. In fact, the study says, “In the end, because there are such fundamental shifts already underway in the electric industry, inaction is the real threat to good reliability planning.”
Oregon bill would eliminate all electricity from coal by 2025
February 2015: Legislation introduced in Oregon would eliminate electricity generated by burning coal and set a high bar on carbon pollution for any new energy sources. In addition to requiring utilities to stop providing electricity that comes from coal-fired power plants to Oregon customers by 2025, the “Coal to Clean” bill, sponsored by by Rep. Tobias Read (D-Beaverton) and Sen. Chris Edwards (D-Eugene), also would require that energy sources be 90% cleaner than power from coal in terms of carbon dioxide emissions, all but ensuring that new capacity would come from solar, wind or other renewables energy sources. Oregon’s only coal-fired power plant, in Boardman, is scheduled to be retired in 2020. A poll conducted by the Sierra Club found broad support for the measure, with 71% of voters in support of a proposal to transition the state off coal to clean, renewable energy by 2025. This includes majority support from all party affiliations.
FutureGen 2.0 scrapped as feds yank funding for CCS coal plant
February 2015: After spending about $200 million of $1.1 billion in federal funding, the U.S. Department of Energy has decided to pull the plug on funding for FutureGen 2.0, a planned 200-MW coal-burning plant in central Illinois that was a pilot project for testing carbon capture and storage, zero-emissions technology. Without federal support, which came from the 2009 stimulus package, the backers of the $1.7 billion plant had no choice but to shut the project down. The controversial project has been on the drawing board for nearly a decade, first permitted in 2007 as a much larger plant, then scrapped by the Bush administration as the price tag soared, revived and funded in the scaled-down version, and now killed again, as DOE spokesman William Gibbons said in a statement, “to best protect taxpayer interests.” Many of the project’s biggest partners backed out after a decision to impose a 20-year electricity surcharge on Illinois ratepayers of about a dollar a month to cover the costs of the project’s private financing, leaving only a few coal companies promoting the plant.
Price tag for restarting Mont. coal plant too costly; it will be closed
February 2015: Unable to justify the economics of continuing to operate a coal-fired power plant in Billings, Mont., its owner has officially decided to shut the facility down this summer. PPL Montana had announced plans to temporarily shut down the 154-megawatt the J.E. Corette plant down beginning this spring and possibly restarting if reeling coal markets bounce back, but the company has now scrapped that idea in favor of retiring the plant permanently. A company representative said a recent re-analysis showed that the projected $38 million investment needed to resume running the plant, which started operating in 1968, was too costly.
Stockholm’s switch from coal to biomass the latest in a Nordic trend
February 2015: Stockholm’s oldest power plant, which has been in operation since 1903, will phase out its last coal-burning furnace by next year and replace it with a biomass generator. Operated by Swedish utility Fortum Oyj, the Vaerta harbor plant will soon be the world’s largest combined heat and power generator that runs only on wood chips and timber scraps. “It’s unacceptable having a coal plant in the city of Stockholm,” said Katarina Luhr, the vice mayor of Scandinavia’s biggest city, which has set a goal of being fossil-fuel free by 2040. Across Scandinavia, utilities are replacing their coal-burning plants. Denmark’s Dong Energy is switching half of its coal generators to biomass by 2020. Sweden’s Vattenfall has already sold two of its three Danish coal-fired plants and is looking to divest the last one.
Coal production slipped to a 20-year low in Colorado last year
February 2015: Beset by a combination of mine closures and a lingering weak market, coal production in Colorado slipped to a 20-year low in 2014, according to state data. The Denver Post reports that the state’s eight mines produced just under 23 million tons of coal in 2014, a 5% drop from 2013 and a decline of 39% over the past decade. The decreased production led to a loss of 345 mining jobs in 2014, a 20% decrease.
Survey: vast majority of utility execs see coal use waning
January 2015: In a survey of 400 utility executives from across the country by trade publication Utility Dive, an overwhelming majority (77% ) said they see the use of coal as part of their fuel mix declining over the next 20 years. In contrast, 79% and 77% said they see the respective use of utility-scale solar and wind energy increasing over that time frame.
Lack of investors kills planned Pakastani coal plant
January 2015:The Pakastani government has abandoned a massive 6,600-MW coal project after getting no interest from potential investors. The proposed Gadani Power project, which comprised 10 660-MW coal-burning plants that would have burned coal imported from China, was launched in 2013 and put on a fast track to be completed by 2017.
Econ report: coal industry short-changing taxpayers by billions
January 2015: By exploiting lax regulation and a number of loopholes, coal producers have been able to pay an effective royalty rate for coal mined from public land that is substantially below what they are supposed to pay, short-changing taxpayers out of billions of dollars, according to an analysis by Headwaters Economics, an independent research group based in Bozeman, Mont. Instead of the 12.3% royalty they should pay under the law, coal mining companies paid an average of just 4.9% on the value of coal mined from public lands from 2008-2012, most of it from the Powder River Basin in Wyoming and Montana. Had the coal been valued at true market prices, bringing the effective rate close to the legal requirement, Headwaters found, royalty collections to the U.S. Treasury would have $5.5 billion more than the industry actually paid to taxpayers.
Residents succeed in thwarting proposed coal mine in central Illinois
January 2015: After an eight-year battle, residents of two central Illinois communities have succeeded in stopping the development of a proposed coal mine. Capital Resource Co., which had state approval to build the 1,000-plus-acre strip mine north of Canton, has officially asked the Illinois Department of Natural Resources to terminate its permit. Residents of Canton and nearby Orion had sued to stop the mine on the basis of potential threats to streams within the mine area’s boundaries that feed Lake Canton and supply drinking water to more than 20,000 people in Fulton County.
Goldman Sachs analysts: Coal has reached ‘retirement age’
January 2015: Citing China’s ebbing demand for coal and regulatory risks across the globe for coal plants, analysts from financial investment firm Goldman Sachs have taken a firm position that coal is on the decline. “Just as a worker celebrating their 65th birthday can settle into a more sedate lifestyle while they look back on past achievements, we argue that thermal coal has reached its retirement age,” the firm’s analysts were quoted saying in a Thomson Reuters newsletter which also noted coal prices have fallen each of the last four years and 2015 may make it five.
Wall Street ratings firms beat up on Peabody’s poor performance
January 2015:Peabody Energy lost $513 million in the final quarter of 2014, and Wall Street took notice by giving the company a bleak outlook for the future. Standard & Poor’s has downgraded the company’s rating to “negative” from “stable” based on “the assumption that coal prices will remain depressed for at least another year.” Separately, The Street has given Peabody a “D” grade and rated the company as a “sell” based on a number of negatives that include “unimpressive growth in net income, generally high debt management risk, poor profit margins, weak operating cash flow and generally disappointing historical performance in the stock itself.” Peabody’s net income and earnings per share, The Street noted, have both decreased precipitously – by 477% and 1,066% respectively – when compared to the same quarter a year ago. “[W]e have only bad news to report on this stock’s performance over the last year,” The Street concluded.
Coal producers brace for worst as plant closures take away customers
January 2015:Coal producers in central Appalachia are some of the biggest losers as the U.S. transitions away from coal and toward natural gas and clean energy, as detailed in coverage by the Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. Across the country, coal plant closures or conversions to natural gas are forcing mine operators to cope with an exodus of utility customers who no longer rely on the fuel they once provided. Some of the hardest hit are mines in Virginia, southern West Virginia and eastern Kentucky, as more than 17 million tons of coal from Appalachia went to plants in 2013 that are slated to close. The Post-Gazette cited Bloomberg New Energy Finance projections for 91 million tons of coal demand to be shed by plant retirements by 2017. “That’s an unprecedented change to America’s power system in what constitutes the blink of an eye in energy markets,” an Arch Coal executive said in December.
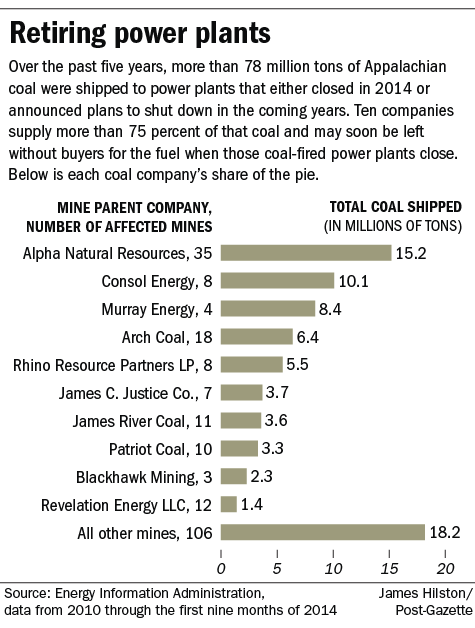
Source: Pittsburgh Post-Gazette
Lummi tribe says coal export facility would violate treaty rights
January 2015: Citing a violation of treaty rights that have been recognized for more than a century, the Lummi Nation has officially requested that the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers deny a permit for a proposed coal export terminal that would be built near tribal land in Washington. In a letter to the Corps, which must assess compliance with treaty rights as part of its review, Lummi elders said damage from the proposed Cherry Point facility to important crab and salmon fisheries, as well as an ancestral village site, would be irreparable. The terminal would process and ship up to 54 million metric tons of coal per year. “Our waters are a way of life and survival for our people,” Lummi Chairman Tim Ballew II said. “The bottom line is, you can’t mitigate or buy your way out of the damage that this proposed shipping facility would cause.”
Coal stocks being ‘clobbered,’ trading as junk bonds
January 2015: In a commentary on coal investment, MarketWatch and CNBC economics columnist Tim Mullaney did not mince words on the downsides of sinking money into coal stocks. What’s not to like, he asked. Plenty. “Coal stocks have been clobbered, and there remain few signs of life in the sector. The Dow Jones Coal Index has plunged 36.5% in the past year, and in the past five years (brace yourself) it is down almost 75% — 87% since before the last recession began in 2007. Of coal companies that have publicly traded debt, Moody’s Investors Service and Standard & Poor’s rate all their bonds as junk.”
CAP: coal producers ‘gaming the system’ to skirt royalties
January 2015: Evidence suggests that inside deals between U.S. coal producers and their own subsidiaries are part of an expanding scheme that allows the companies to dodge federal and state royalty payments and boost subsidies. According to an analysis by the Center for American Progress, more than 40% of all coal produced in Wyoming is first sold at greatly reduces prices to a subsidiary in a “captive transaction.” Key coal producers have built an elaborate network of hundreds of subsidiaries and shell companies. The companies pay royalties on the low sale price before its subsidiaries turn around and sell the coal to final buyers like utilities at much higher prices. CAP’s review of federal data found that five of the largest coal producers in the Powder River Basin collectively have a network of 566 subsidiaries, which were used to complete 17 times more captive transactions than in 2004. Mining giant Peabody alone, which operates the country’s largest coal mine in Wyoming, has 242 domestic and foreign subsidiaries. “This gaming of the system is costing federal and state governments millions of dollars in lost royalty payments,” said Matt Lee-Ashley, a senior fellow at CAP.
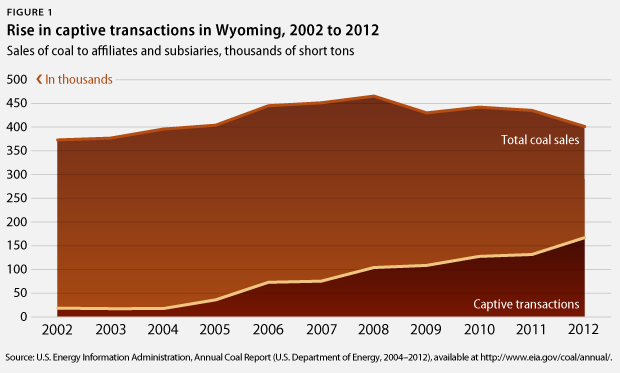
Source: EIA data compiled by CAP
Stanford profs call on university to divest from fossil fuel companies
January 2015: A group of 295 Stanford professors has written a letter to the school’s president and board of trustees urging them to divest the university’s $21 billion endowment from all fossil fuel companies. Stanford eliminated investments in coal companies last year, but continues to invest in oil and gas. “The urgency and magnitude of climate change … demand the more profound and thorough commitment embodied in divestment from all fossil-fuel companies,” wrote the group, which included two Nobel laureates and the first woman ever to wind the prestigious Fields Medal in mathematics, along with a diverse mix of economists, earth scientists, and engineering and liberal arts professors.
Coal drops to less than half of Midwest utility’s fuel mix
January 2015: The combination of added wind capacity and the closure of aging coal units is cutting the amount of coal-fired electricity from Indiana Michigan Power by 10%. With the retirement of 500 MW of coal at the coal-fired Tanners Creek plant, coal will fall to less than half (49.7%) of the utility’s generating capacity. Meanwhile, the recent completion of the Headwaters Wind Farm in Randolph County more than doubled I&M’s wind holdings to 8.6% of its generating capacity.
Proposed coal export terminals continue their losing streak
January 2015: Of 15 proposals to build major new coal export facilities across the U.S., all but four have been defeated or canceled within the past two years, Inside Climate News reports. The latest failures included the revocation of a permit for a coal terminal project in Louisiana, a legal challenge for a proposed export facility in Washington state and an Australian company suffering a huge financial loss as it sold off project proposals in the U.S. to a high-risk investment firm. “This is an ugly, ugly time for coal exports,” the publication quoted the research director of Sightline Institute saying.
Reuters: coal on “a slow spiral towards a bituminous bottom”
January 2015: The continued decline of coal prices is prompting some to wonder whether the industry’s problems are so severe that they will become permanent. Since hitting a high in July 2008, global coal prices have been on “a slow spiral towards a bituminous bottom,” as one commentator noted. As reported in Reuters, energy developments that normally would have driven demand – such as the Fukushima nuclear accident, which prompted Japan to boost its use of coal – haven’t translated into increased prices, leaving many wondering if coal has become an unwanted commodity.
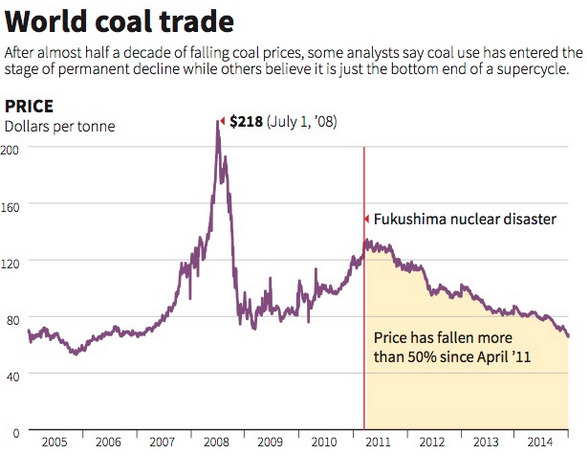
Source: Reuters